 Many probably have experienced at least once in their lives with the concepts of "thrombus", "thrombosis", but not everyone has a correct idea about this phenomenon.
Many probably have experienced at least once in their lives with the concepts of "thrombus", "thrombosis", but not everyone has a correct idea about this phenomenon.
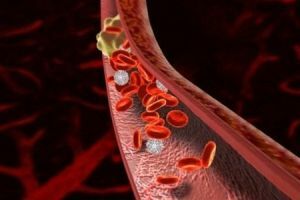
A thrombus is a pathological blood clot in the living body , which is located in the cavity of the heart or the lumen of the blood vessel.
Occurs due to a disruption in the function of blood coagulation. For the appearance of thrombus, it is necessary that the wall of the vessel is damaged from the inside or there is an atherosclerotic plaque.
The primary thrombus is a filament of fibrin that is deposited on the altered wall of the vessel. Then thrombotic masses are applied to it, the clot grows. Once the critical size is reached, the blood clot breaks and the blood flow stops.
Contents
- Causes of thrombus formation
- Causes of blood clots in the arteries
- Blood clot in the veins
- If the heart is affected
- Who is the most exposed to the formation
- Classification of the formations
- Symptoms that should alert
- Why does the gap occur?
- pulmonary thromboembolism - fatal vagus thrombus
- Diagnostics
- treatment of various forms of thrombosis
- Prevention clot formation
reasons clots
are three major reasons why the thrombus is formed, and in many cases off:
- Damage vessel wall( mechanical trauma, inflammation, injuryinternal walls of bacteria, toxins, viruses);
- Incorrect operation of blood coagulable function ( activation of coagulants and provocation of platelet aggregation - attachment to each other).In general, this process is associated with congenital abnormalities in the development of platelets, although sometimes changes occur at the chemical level( after exposure to bacterial, viral cells, taking certain drugs);
- Slowing of blood circulation ( associated with the transmission of arteries and veins, varicose veins, increased blood density).
Thrombi can form in any part of the circulatory system - in veins, arteries and even in the heart. The above reasons are applicable for each case.
However, there are still specific factors that affect only a certain part of the circulatory system.
Causes of blood clots in arteries
The main factor of blood clot formation in the arteries is obliterating atherosclerosis.
Cholesterol and lipids( fats) are deposited in the inner shell of the artery.
Around these accumulations, the lining vessel begins to be replaced( gradually) by a connective tissue, which then forms an atherosclerotic plaque.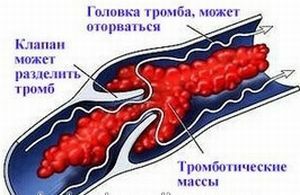 The plaque is perceived by the body as a certain defect, which must be "removed".
The plaque is perceived by the body as a certain defect, which must be "removed".
Fibrin clots and platelets are deposited on its surface, gradually forming a thrombus - at first unstable and soft, with time that condenses.
This process occurs in most people, but at different speeds.
Blood clot in the veins
Cholesterol on the veins can not be detected, since this substance enters the arterial blood. Venous thrombi are formed due to specific damage to the vessel wall: thrombophlebitis and phlebothrombosis.
Thrombophlebitis - the onset of a blood clot in an inflamed area of the vessel( inflammation can be caused by infection, chemical agents, venous valve defects, varicose veins. ..).
Phlebothrombosis - a thrombus is formed without symptoms of inflammation.
If the heart is affected
The main factor is the slowing of blood flow. This is possible, for example, after a myocardial infarction( part of the heart tissue is killed, replaced by a connective tissue).Often thrombi form after operations on the heart( for example, the installation of a valve).
The most vulnerable to the formation of
At risk group are:
- Men with age 40+ ( in women, before the onset of menopause, the blood composition is updated monthly, with menstruation, so in men after 40 years, the systems responsible for blood coagulation work worse).
- Women 50+ ( however, the age group of risk for women is more individual, will depend on the age of onset of menopause).
- People with excessive body weight .The risk of blood clots increases 10 times with obesity, since the accumulation of cholesterol on the walls of the vessels provokes the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques. Cholesterol rises after regular consumption of fatty and fried foods.
- People with a disturbed diet ( for example, after a month of extremely strict diet, a person eats all sorts of "goodies").
- People who drink a lot of alcohol. There is a belief that alcohol dilutes the blood. Yes, but not 2 liters of beer in the evening.20-30 grams of vodka or 100 grams.guilt per day will really benefit the blood. A large number of alcoholic drinks dehydrates the body, promotes clumping of blood clots.
- With reduced physical activity.
- Pregnant women ( in the state of pregnancy, the blood cools more, because the constantly growing uterus prevents normal blood flow), only those who gave birth to the mother( in the process of delivery can be damaged vessels).
- Postoperative abdominal surgery , on large joints.
- People, abusing coffee drinks ( caffeine narrows the blood vessels, therefore, worsens the blood flow).
- Smokers ( nicotine also narrows the vessels).

- Patients with oncological disease , inflammations.
- Women who take hormonal contraceptives ( drugs increase the level of hormones, the body perceives this as a signal of pregnancy, and the blood coagulation system is activated).
- Dutch scientists have discovered the connection of thrombosis and physiological parameters of : this disease is more often associated with people above 190 cm and below 160.
Also at risk are people with certain diseases:
- atherosclerosis;
- varicose, heart disease;
- diabetes mellitus;
- thrombophilia( "overstrained" blood);
- obliterating endarteritis( chronic inflammation of the artery wall);
- acute rheumatic fever( which affects the heart valve);Atrial fibrillation.
Classification of formations
Depending on the location of the vessel:
- pristenovy( one end is attached to the wall, the blood flow is preserved);
- continued( the kind of parietal, but quite long);
- lining( lining almost the entire wall of the vessel, for blood flow a small lumen);
- central( located, respectively, in the center, attached to the walls by strings, blood flow is limited);
- clogging( clogs the lumen in the vessel completely).
Depending on the forming mechanism:
- agglutination, white: formed from white blood cells, agglutinated platelets, fibrin filaments. It forms slowly, in arteries with fast blood flow;
- coagulation, red: formed with hyperfunction of blood clotting( mesh fibrin captures erythrocytes), localized in veins;
- mixed type( mucus structure, formed by alternation of adhesion( adhesion) and agglutination( sedimentation) of platelets);
is hyaline( consists of plasma proteins, platelets, hemolyzed erythrocytes).
Also thrombi can be divided into groups, depending on their location:
- venous( in deep and superficial veins);
- arterial( in deep and superficial arteries);
- wandering( a clot that detached from the vessel wall and moved along the bloodstream).
- blood clots in the vessels of the microcirculatory system.
 If in time to identify and properly organize treatment for thrombosis of the veins of the lower limbs, separation of the thrombus can be avoided. How to do this clarifies our article.
If in time to identify and properly organize treatment for thrombosis of the veins of the lower limbs, separation of the thrombus can be avoided. How to do this clarifies our article.
Than the drug Troxerutin is useful and the instruction on the use of the drug has been studied in detail by us and laid out in general access.
Symptoms that should alert the
The visible signs will depend on the location of the thrombus.
50% of people who underwent deep vein thrombosis did not experience any symptoms.
However, the other half of the victims experienced with certain sensations:
- If the thrombus is located in the deep vein of : fever, chills, local pain and blueing, fever at the site of the clot.
- If the blood clot forms in the superficial vein : it can be palpated, the vein will be compacted to the touch, painful touch to the affected area. Part of the body will be swollen, hot, red.
- Thrombus at the foot : cramps in the calf muscle, pain, swelling of the ankle, swelling, which disappears in the morning. One of the late symptoms is brown skin.
- If the vein is inflamed with and contains a thrombus: high fever, pain in the affected area, redness, swelling. The next stage - the skin is covered with cyanotic spots, flakes.
- Thromb in the head : impaired speech, coordination, paralysis of the limbs, facial asymmetry, difficulty in swallowing food. If the clot came off in my head - a stroke.
- Thrombus in the intestinal vessels : manifested, after a certain time, with the disease "peritonitis"( abdominal pain, giving to the shoulder or collarbone, vomiting, stool retention).
- If a blood clot breaks , a heart attack occurs in the heart of the .
- Vienna, carrying blood from the brain : cervical, headache, vision problems.
- Thrombus in the lung : extremely dangerous disease. If a blood clot breaks off in the lungs, the person suffocates, turns blue. Then he stops breathing. And usually no symptoms, before the dying state, is not manifested.
Why does the gap occur?
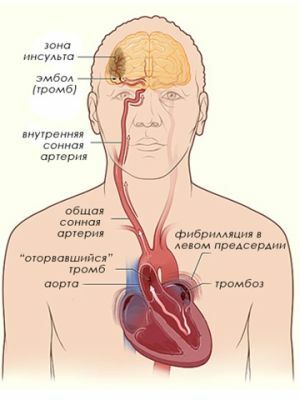
In the photo, the process is visible if the blood clot in the heart of the
has come off. To give an unambiguous answer to the question why the clot breaks off, it is necessary to study a considerable amount of not always unambiguous medical literature.
But in general, you can fairly simply describe the process.
A blood clot forms in the body, waiting for "its time".
Why does a thrombus burst from a person's :
- , it does not completely cover the lumen of the vessel;
- blood flow is fast enough( to tear off the blood clot from the wall).
Therefore, in most cases, a thrombus breaks away from the wall of the artery.
Then the blood clot moves - it can for a sufficiently long distance. Another thrombus can be divided into several particles, which leads to the clogging of several vessels at once.
Symptoms that occur when an thrombus has come off is determined by the affected area.
If is damaged in the artery of , there is a shortage of oxygen and nutrients( an organ that is supplied from this artery).First comes ischemia, after - necrosis of the corresponding organ.
More rarely, a thrombus comes off in the vein of .Symptoms are also determined by the site of the lesion( stagnant phenomena, multiplication of microorganisms, inflammation of tissues, sepsis occur in that region).
Thromboembolism of the lungs - a deadly wandering thrombus
One of the most "unfortunate" places for a thrombus is, perhaps, the lungs.
Pulmonary embolism - is an instantaneous cessation of blood flow in the pulmonary arteries of due to clotting of a blood clot.
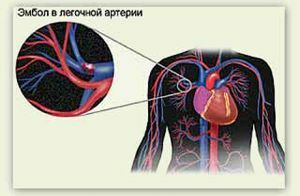 PE is often the result of complications of the postpartum and postoperative period.
PE is often the result of complications of the postpartum and postoperative period.
If the thrombus has come off in the lungs - it's in a third of the cases, the true death of in the first minutes.
More than half of the patients die within 2 hours after the appearance of a thrombus in the arteries of the lung.
Most often, PE triggers blood clots that have fallen from the deep veins of the lower limbs.
PE is manifested through rapid breathing, shortness of breath, improvement in prone position, chest pain, palpitations, cold sweats, coughing, dizziness, convulsions in the limbs, pallor, "blueness".
Diagnosis
Timely detection of a blood clot is an opportunity to avoid surgery and even to save your life.
If you are at a risk of developing thrombosis, it is best to periodically check the status of the coagulating blood function:
- thromboelastography;
- thrombin generation test;
- active partial thromboplastin time;
- thrombodynamics;
- prothrombin time test.
Treatment of various forms of thrombosis
The first step towards cure is the timely identification of the problem.
Treatment for thrombosis is performed by solely under the supervision of a physician, in a steady-state regime.
For diagnosis, it is necessary to consult a phlebologist or cardiologist.
He will perform an evaluation of the thrombus, the possibility of his separation, formulate a diagnosis, select a method of treatment.
There are such ways of recovery:
- medication( anticoagulants, reducing blood clotting, nicotinic acid, statins);
- is an injection into the vessel of a substance that dissolves a thrombus;
- surgically( with severe forms of thrombosis);
- installation of cava filters in the vein( applicable for unilateral thrombi, which are often torn off);
- associated procedures( LFK, massage);
- low-cholesterol diet.
The type of treatment, in the first place, will depend on the type of thrombus and its size.
Also the method of treatment is selected depending on the affected area.
In more inaccessible areas( deep veins, heart, lungs), a drug that dissolves a thrombus is injected.
Surgical intervention is used in the extremely serious condition of the patient.
Prevention of clot formation
- Observance of of the correct diet - minimum of cholesterol( margarine, fatty, "rich" soups), more products that reduce blood clotting( green tea, cherry, tuna, broccoli, spinach, citrus, cowberry).
- Taking aspirin reduces blood clotting( usually, cardiologists prescribe it after 40 years).But do not prescribe it yourself!
- At least 30 minutes per day physical activity ( cardio).Thus, you accelerate blood circulation, strengthen the heart muscle, reduce blood clotting.
- Use special jersey( compression) during trips and flights.
If a blood clot breaks in the heart, lungs or leg, the consequences can be the saddest and following simple recommendations and regular visits to a doctor can save lives!
