 Before talking about the specifics of the development of PE( pulmonary embolism), the causes that contribute to its inception and other facts, it is necessary to clarify what it is.
Before talking about the specifics of the development of PE( pulmonary embolism), the causes that contribute to its inception and other facts, it is necessary to clarify what it is.
This is the condition in which the pulmonary artery is located, when a thrombus clogs its branches.
In addition, in this state, normal circulation of blood and its access to the lung tissues is impossible. As a result of the disease, a heart attack or infarct-pneumonia may develop.
Contents
- What contributes to the development of the disease?
- Mechanism of the development of the disease
- Types and nature of the course of the embryo
- How does the disease manifest itself?
- Diagnosis of the disease
- First emergency care
- Features, methods and effectiveness of therapy
- Danger? !Yes!
- Relapse prevention
What contributes to the development of the disease?
Often the cause for the development of pulmonary embolism( PE), is a deep vein thrombosis that affects the lower limbs. In more rare cases, thromboembolism develops against a background of vein thrombosis.
In addition, people at risk are those who have the following:
- hereditary factor;
- poor blood clotting;
- long-term postoperative period;
- fracture of hip or pelvis;
- heart disease;
- bad habits;
- is overweight;
- varicose veins;
- malignant tumor.
In addition, the disease can develop in pregnant women and women who are in the postpartum condition, women who take oral contraceptives that include estrogen and people who have suffered a stroke or myocardial infarction.
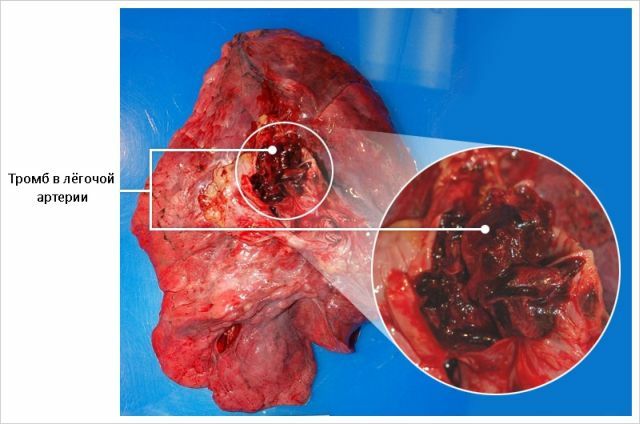
Mechanism of development of the disease
Thromboembolism is the result of embolism by thrombotic masses that have come from elsewhere into the pulmonary artery. The source of the disease is the development of a thrombotic vessel.
Pathology is born on the background of development of thrombotic process:
- in vessels of pelvic organs and lower limbs;
- in the system of the lower and upper genital veins;
- in the vessels of the hands or heart.
If the patient suffers from thrombophlebitis, embologogenic venous thrombosis and other pathologies characterized by the formation of 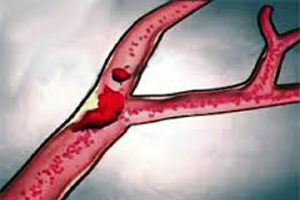 thrombotic masses, the risk of developing thromboembolism of the branches of the pulmonary artery is significantly increased. Trigger mechanism becomes a clot of blood detached from the attachment site and its subsequent migration.
thrombotic masses, the risk of developing thromboembolism of the branches of the pulmonary artery is significantly increased. Trigger mechanism becomes a clot of blood detached from the attachment site and its subsequent migration.
Significantly less often thrombi form directly in the pulmonary artery itself. Thus, there is a birth of thrombosis in the branches of the artery and its rapid spread along the main trunk. As a result, symptoms of the pulmonary heart are formed, and the vascular walls change, which are dystrophic, inflammatory and atherosclerotic.
Types and nature of the flow of the embryo
Doctors distinguish several types of pulmonary embolism. The division into groups occurs when taking into account the volume of the included arterial pulmonary bed.
Thus, the following types of PE are distinguished:
- A small or non-mild form of disease, when small muscle arteries and pulmonary arterioles are affected. It is characterized by stable hemodynamics and complete absence of any signs of pancreatic insufficiency. This species is observed in 50% of patients.
- The submissive form of ( off ½ of the river bed) implies signs of acute pancreatic insufficiency. In this case, arterial hypotension is not observed.
- If is observed as a massive form of , it implies a violation of the respiratory system, hypotension, and shock. At the same time, not less than ½ of the channel and more than two shared arteries are turned off. In addition, acute pancreatic insufficiency is observed.
- For , the fatal form of is characterized by the shutdown of more than ¾ of the vascular bed of the lungs and the destruction of the pulmonary trunk. This type of disease is observed in 20% of patients who make terminal patients, although not infrequently develops in those who have not previously undergone surgery.
How does the disease manifest itself?
The following signs may indicate the development of pulmonary embolism, which are symptoms of acute cardiopulmonary insufficiency:
- appears dyspnea;

- marked pain in the chest, which intensifies during coughing and deep inspiration;
- is an unconscious condition, dizziness and severe malaise;
- sharp drop in blood pressure;
- heart rate increases;
- appears a dry cough, which is followed by the release of sputum with blood veins;
- skin becomes pale;
- upper half of the body and the face becomes cyanotic;
- body temperature rises.
If there is thromboembolism of small branches of the pulmonary artery, the symptoms may be absent or expressed rather poorly.
In PE, pathophysiological changes are observed. This is indicated by pulmonary arterial hypertension and pulmonary arterial resistance. In turn, the result of these processes is increased stress on the right ventricle, in some cases it is accompanied by acute insufficiency.
In addition to the above processes, cardiac output decreases as a result of pulmonary arterial occlusion. Also, patients experience a drop in blood pressure and a decrease in cardiac output.
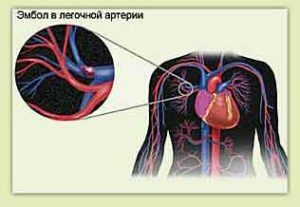 During the development of the disease, vascular obstruction adversely affects pulmonary gas exchange, disrupting its habitual structure. In turn, this leads to arterial hypoxemia, an increase in the gradient of alveolar-arterial oxygen tension, and shunting from right to left with insufficient oxygenated blood.
During the development of the disease, vascular obstruction adversely affects pulmonary gas exchange, disrupting its habitual structure. In turn, this leads to arterial hypoxemia, an increase in the gradient of alveolar-arterial oxygen tension, and shunting from right to left with insufficient oxygenated blood.
The result of numerous processes is a decrease in coronary blood flow, which in turn is the main reason for the failure of the left ventricle, and also leads to pulmonary edema. The patient has a correlation between the area of the blockage, the violation of blood gases and hemodynamic changes in the small circle. With regard to systolic pressure, it rises to 12 kPa, and the average pulmonary arterial to 5 kPa.
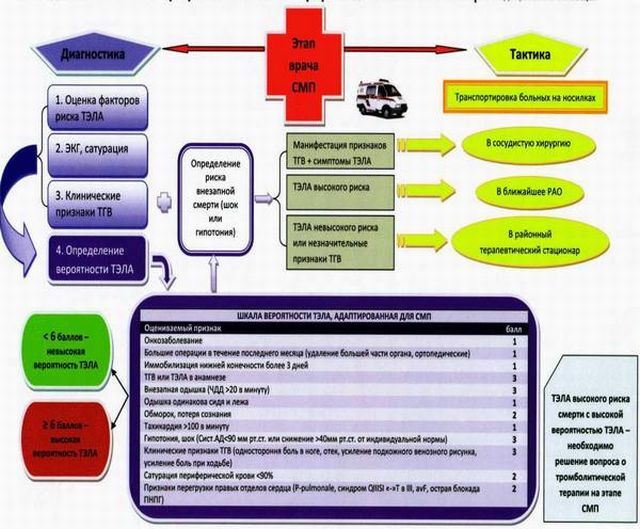
Diagnosis of the disease
Specialists, conducting diagnostics of the disease, primarily direct all efforts to establish the localization of thrombi in the pulmonary vessels. It is also important to assess the severity of violations of hemodynamics and lesions. Also, the source of the disease is established, in order to avoid relapse in the future.
Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism includes a number of activities:
- assesses the patient's condition, clinical symptoms and risk factors;
- are taken for biochemical and general analysis of blood, urine, while the gas composition of blood and D-dimer in blood plasma is studied, and also the coagulogram of the second;
- is an obligatory ECG;
- X-ray of the lungs in order to avoid primary pneumonia, tumors, fractures and other pathologies;
- echocardiography determines the pressure in the pulmonary artery, thrombi in the heart cavity and the load on the right heart;
- lung scintigraphy reveals a violation of blood perfusion;
- angiopulmonography helps to determine where the thrombus is located and what size it is;
- UZDG veins in the lower extremities and phlebography, in order to identify the source of the disease.

First Aid
Emergency care for a patient with suspected pulmonary embolism involves the following:
- bed rest;
- intravenous injection of anesthetic and other drugs to restore pressure;
- provides respiratory failure therapy if symptoms are present;
- antiarrhythmic therapy is performed;
- in the case of clinical death, resuscitation is carried out.
Mechanism of action for pulmonary embolism
The possibilities, methods and effectiveness of
The main goal of specialists in the treatment of a patient is the preservation of life and the prevention of pulmonary hypertension of chronic form. Therefore, first of all, the patency of blocked arteries is restored.
For the treatment of a patient, a medicamental and surgical method is used. The second is used in case of development of acute heart failure or more serious violations.
The choice of treatment methods is affected by the volume of the vascular lesions of the lungs and the state in which there is heartbeat, blood pressure and so on.
In general, treatment for pulmonary embolism involves the following activities:
- Oxygenotherapy , which is the body filling by inhaling mixtures of gases enriched with oxygen
- To reduce the risk of new blood clots, specialists deteriorate blood coagulation with anticoagulants .
- It is mandatory to administer thrombolytics in case of severe pulmonary dysfunction or with a massive disease form.
- Surgical removal of blood clots is used in case of severe disease. In this case, the closure of the pulmonary artery trunk and necessarily the two main branches.
- If the disease is recurrent, then specialists resort to setting up the cava filter .
- And of course, antibiotics are prescribed if the patient has a lung infarction.
Danger? !Yes!
Possible complications of the disease:
- if pulmonary embolism is massive, death is very likely;
- there is a lung infarction;
- possible pleurisy;
- lack of oxygen;
- probability of recurrence of the disease.
Prevention of relapse
Prevention is aimed at preventing risk factors, and implies the following measures:
- taking anticoagulants for the first six months;
- requires continuous monitoring of blood clotting;
- in some cases, when there are lumens in the inferior vena cava, experts recommend the installation of a cava filter;
- wearing special elastic stockings or elastic bandaging of legs.
