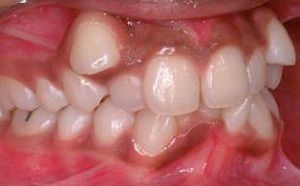
 There are a lot of different dentoalveolar anomalies. This is justified by the fact that the health of the teeth depends on many different factors.
There are a lot of different dentoalveolar anomalies. This is justified by the fact that the health of the teeth depends on many different factors.
The position of the teeth and their shape are affected. Quite common pathology is tortoanomalia.
Contents
- General
- General information
- General information
- Provoking factors
- Manifestations of the violation
- Diagnostic measures
- Treatment and correction
- Preventative measures
- General information
General characteristic
In the case of toroanomalia, the teeth rotate relative to their vertical axis. This deviation has certain characteristics:
- Most often, the side incisors are scrolled, which are located on the upper jaw. Also curved can be canines and mandibular incisors. Other teeth may be exposed to torsion. However, this happens only with certain factors.
- Tortococclusion is diagnosed by the dentist even then, the angle of rotation is only a few degrees. There are several degrees of severity of pathology. The most severe case is a rotation of 180 degrees. A small deviation is observed when the turn does not exceed 45 degrees. Serious cases include cases where the teeth turn to a larger angle.
- Most often only one tooth is subjected to anomalous torsion. Less often, it extends to neighboring. Everything depends on the reasons for the deviation.
Aggravating factors
There are several main reasons that cause an abnormal "dance of teeth":
- The lack of the necessary location for the .This is due to a very narrow jaw or with a microdentium. Because of the
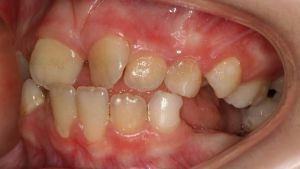 , this tooth does not fit in a row in its normal position. For this, he turns around at a certain angle. Most often it rotates by 45 degrees, since it is in this position that it occupies the least space. Sometimes due to the peculiarities of the jaw, it is impossible to correct such a defect.
, this tooth does not fit in a row in its normal position. For this, he turns around at a certain angle. Most often it rotates by 45 degrees, since it is in this position that it occupies the least space. Sometimes due to the peculiarities of the jaw, it is impossible to correct such a defect. - Constant pressure , which turns out to be "neighbors" along the tooth row, due to the fact that they do not cut right. Because of this pressure, the tooth begins to rotate a little in its nest.
- Incorrect tabulation of the tooth follicle .Even in infancy, begin to develop rudiments of teeth. Sometimes this process passes with deviations, and they initially cut through at the wrong angle.
- Persistence of infant teeth , which manifests itself on the location of the molars. Because of the resistance of the "milk" to the fall of the new root, you have to deviate slightly and change your natural position. The problem is easily eliminated in the initial stages. To do this, it is enough to pry out the baby teeth, which prevent it from growing new.
- Injuries to .Damages that were received at the time of cutting new teeth can disrupt their further growth.
Manifestations of a violation of
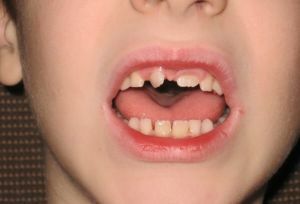 Anomaly does not have a pronounced symptomatology. It manifests itself only by turning teeth around the axis. Often, dentists face an easy stage of tartanomalia. In this case, the angle of rotation is only 45 degrees.
Anomaly does not have a pronounced symptomatology. It manifests itself only by turning teeth around the axis. Often, dentists face an easy stage of tartanomalia. In this case, the angle of rotation is only 45 degrees.
Such a violation is not very serious and the main problem in this case is only an aesthetic aspect. Many patients are concerned not with pain, but with a cosmetic component.
If the incisors and canines turn seriously, mucous membranes can be injured. This can lead to the appearance of stomatitis. But even in such cases, there is no sharp manifestation of an anomaly.
Diagnostic measures
To identify the terto position, it is often enough to perform a visual inspection. Sometimes additional diagnostic methods are used: 
- Anthropometric analysis of .It is carried out to determine the degree of deviation of the teeth from the normal position. During the analysis, special plaster models of the jaws are used. With their help remove the size of the patient's jaws. The obtained data is analyzed and compared with the information in the tables of Wetzel and Ustimenko.
- Orthopantomogram allows to determine the quality of dental tissue.
- Radiography of the problem area .Determines the ratio of the damaged root to the neighboring ones.
Treatment and correction of
There are different methods for correcting anomalies. Surgical refers to:
- Extraction .The operation is carried out using an elevator. It is injected into the upper part of the root and the ligament tissues are torn in it. After that, the tooth is pushed out of the hole. This method of treatment is very effective.
- Compostotheotomy .There is a ribbon and latticed view of this procedure. In the first case, the strip of bone is removed, if its width does not exceed 3 mm. Through the grid method, through holes are made in the root region. They are staggered.
- Incomplete dislocation of .The tooth moves to the correct position with the help of special surgical forceps. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
- Fibrotomy of the .A procedure that reduces the resistance of the ligament apparatus. This is done with a small incision periodontal.
Conservative methods:
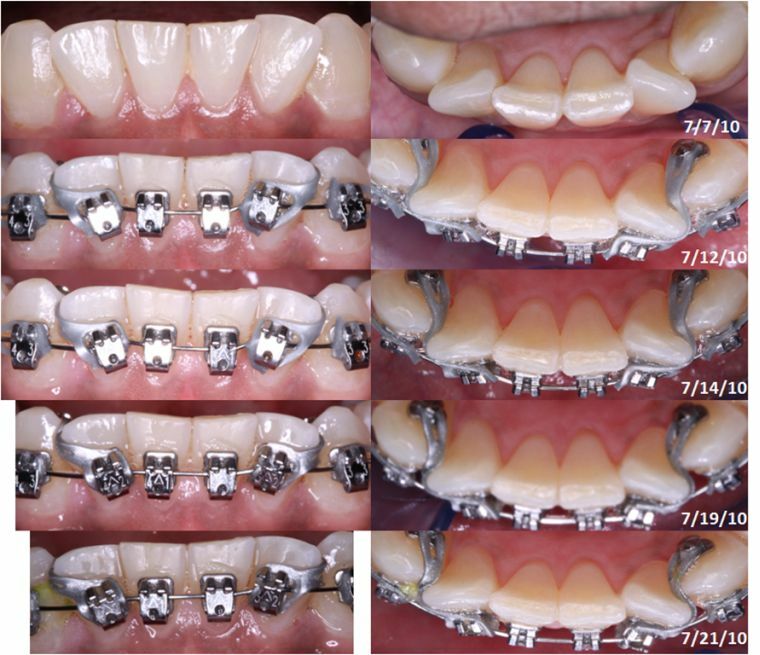
- Brackets .At the initial stage of correction, a nickel-titanium arc is used, which has a minimum cross section. Over time, it is replaced by thicker arcs. In the later stages, instead of the arc, an elastic chain is used.
- Elastopositioners .Applied only with a slight deviation of the crowns. They are presented in the form of double-jawed cap, which have canals for teeth and labial arches.
- Loop of Coffin .It is used for torotocclusion, which appeared because of a narrow jaw arc. The device has two arcs, which are responsible for the correction of teeth. They put pressure on curved teeth.
Preventive measures
There are no specific preventive measures, but simple hygienic procedures will help prevent this anomaly.
In order to timely identify problems in the location of the teeth, you must regularly visit the dentist. Such examinations will help in time to notice the delay in the loss of milk teeth. It is the milk teeth, which do not fall out in time, most often cause the appearance of tartoanomalia.
Other methods of prevention include: 
- regular monitoring of tooth loss and growth, - early diagnosis will help prevent the emergence and development of pathology;
- in the presence of a hereditary factor should be addressed to geneticists;
- needs timely disposal of diseases not only dental, but also general;
- getting rid of bad habits;
- use miogymnastiki if small deviations in the location of the crowns begin to appear.
Prevention is best done in the period of early replacement and sucking. If you discover pathology in adulthood, then her treatment will have to spend more energy, time and money.
If the disease is not cured in time, then serious consequences can be encountered. These include:
- violation of natural occlusion;
- injury of the oral mucosa;
- strong loosening of the teeth.
