 One of the serious and complex directions in dental practice is the prevention and elimination of dentoalveolar deformities and bite anomalies.
One of the serious and complex directions in dental practice is the prevention and elimination of dentoalveolar deformities and bite anomalies.
Many of the patients who turn to orthodontists have different types of progeny.
Contents
- What is physiology, and what is the pathology?
- Related disorders
- Reasons and etiology
- Symptoms and diagnostics
- Features and correction methods
- Helping the smallest
- From 12 and older. ..
- For adult patients
- Retardation period
- Possible consequences
- Preventive measures
What is physiology, and what is the pathology?
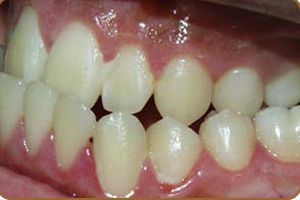
Progenic bite is a maxillofacial anomaly with an unnatural extension of the lower teeth. Progeny is often a violation, observed in one form or another in 1.4-30% of people, leading to aesthetic and functional consequences.
Progenic bite is physiological and pathological. With a physiological type, the jaws are located in a normal dynamic and static state, work adequately and correctly, periodontal tissues are healthy. Also, teeth should have an aesthetic appearance. The jaw joint should have a moderate load and correction of this bite is not required.
The difference between the pathological occlusion is the broken functioning of the jaws, which causes numerous problems in the body, despite the direct rows of teeth. This pathology must be corrected, since it can lead to the appearance of chronic gingivitis, periodontitis, gastrointestinal disturbances.
With pathological prognosis, the full-fledged work of the dentoalveolar apparatus is disrupted, which often leads to problems with other organs.
This anomaly manifests itself for various reasons( as a result of a congenital or acquired defect).The difference between the pathological 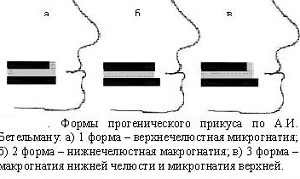 occlusion is that it leads to disruption of the full-fledged operation of the dentogram device, leading to the violation of other body systems.
occlusion is that it leads to disruption of the full-fledged operation of the dentogram device, leading to the violation of other body systems.
Causes may be congenital or consequence of serious diseases( chronic gingivitis, periodontitis).In pathological closure there are several forms of manifestation: when the defect is related to the wrong formation of the bones of the facial region, it is called gnathic. If the normal location of the teeth changes, the disorder is called dental alveolar.  Related disorders
Related disorders
By the terms of prognathism and prognosis is meant the excessive protrusion of the skeletal parts of the skull relative to each other, which is formed during the development of the jaws( one upper or both - prognathic bite, and the lower - progenic).
Progeny is divided into partial and complete, is a change in the development of the lower jaw. Prognathia can be true and pathological, it can spread to the entire jaw or to parts of it.
Causes and etiology of
There are several reasons for the appearance of this form of occlusion, but sometimes it can be associated with genetic heredity. To the factors that provoke the development of the pathological form of the disease, include:
- absence in the upper region of the jaw of the frontal teeth;
- damage to the body by chemicals or heavy metals during intrauterine development of the fetus;
- disease in pregnancy, leading to the development of violations in the dentoalveolar system of the child;
- atypical placement of dental rudiments;
- congenital not fusion of the palate with alveolar processes, short frenum of the tongue;
- mouth breathing with tonsill hypertrophy, chronic ENT diseases;
- trauma of the child while traveling through the birth canal;
- macroglossia or large tongue, the pressure of which increases the parameters of the lower jaw;
- early loss of temporary teeth;
- the remaining mounds on the milk fangs;
- early childhood diseases( rickets);
- incorrect placement of the baby's head in a dream.
 When there are provoking factors, the physiological balance of the muscles of the chewing muscles with the mimic is broken, which causes a strong effect on the lower jaw.
When there are provoking factors, the physiological balance of the muscles of the chewing muscles with the mimic is broken, which causes a strong effect on the lower jaw.
In progenic disorders of the anterior teeth, the factors that result in the development of the upper anterior teeth are in the first place. To this group is:
- an abnormal sequence of temporary teeth replacement by radical;
- adentia lateral incisors;
- supercomponent teeth, which were cut in the frontal part from below;
- early appearance of lower teeth with loss of upper teeth.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Typical symptoms of prognosis are
- formation of the oral slit;
- extension of the lower lip and chin forward with frequent loss of the upper lip;
- large mandibular angle;
- sinking the middle third and increasing the height of the lower third of the face.
With lower macroognathy, the face often contracts, nasolabial folds deepen, and the chin is smoothed.
To an intraoral character, anomalies include a direct occlusion of the anterior teeth, the reverse incisive overlap. When the jaw teeth are joined, a mesial step is formed. Diastemes, trembles, and incline of the teeth of the lower jaw may also appear.
Violated sagittal ratio of the first molars. Dimensions of alveolar arches do not correspond to the norm, functional defects appear with a decrease in chewing efficiency.
By location, pathology is common and partial. For general prognosis is characterized by a discrepancy between the connection of the front teeth and the lateral ones. Partial disturbance is characterized by a lack of closure in only one area. This may shift the jaw.
Given the location and parameters of the jaw, a progenic bite with upper micrognathia, lower macrognathia, lower prognathia, upper retrognathy is distinguished. 
Diagnostic tests are performed by the orthodontist, the research complex includes examination of the profile and facade, visual analysis of the occlusion of the oral cavity and anthropometric data, a functional test for distinguishing false from true prognosis.
Assessment of the level of severity of pathology is based on the results of the study of diagnostic models, teleradiography, the use of bite rollers to determine the anomaly of occlusion. The doctor also performs orthopantomography, tomography and radiography.
Additionally, the patient can be sent to a speech therapist and an otolaryngologist for a consultation.
Features and correction methods
Occlusion disorders can be corrected in different ways. The choice of technique for the treatment of progenic occlusion depends on the degree of symptomatology and age of the patient.
The main direction of orthodontic treatment is stimulation of growth and development of the upper jaw, delay in the development of the lower teeth and distal movement, optimization of the occlusion height. Also, the doctor corrects the position of the rows.
Assisting the smallest
Therapy and prevention of temporal occlusion disorders should stimulate the proper development of the dental arches, remove obstructions for distal displacement of the lower region.
 The basis of therapy is timely sanation;normalization of swallowing, language and breathing functions( lip activators and circular muscle training);myofunctional gymnastics, use of the extraoral bandage.
The basis of therapy is timely sanation;normalization of swallowing, language and breathing functions( lip activators and circular muscle training);myofunctional gymnastics, use of the extraoral bandage.
Also a small patient should get rid of bad habits through the vestibular plate. When the children develop a changeable occlusion, the doctor conducts therapy using intraoral devices( arches, plates, cap) and orthodontic devices. If necessary, plasty of the bridle can be performed.
From 12 and older. ..
Treatment of progeny in adolescents involves the use of more powerful methods and equipment, sometimes using the same devices as in the temporary bite:
- plates with springs, located in the sky or in the vestibular incisal area;

- occlusal patches with reverse overlapping of incisors up to 0.2 cm;
- Hoffman or Wunderer activator, Schwartz plate, Buli or Bashirova apparatus, Frenkel clasp device, etc.;
- device Brukle;
- extraoral bandage for delaying the growth of the lower jaw and distal fixation;
- the chin with a rubber pull for moving the lower part of the face( at night).
For adult patients
If a permanent occlusion is established, braces are recommended. Together with orthodontic therapy, speech therapy exercises are performed to correct dyslalia. With excessive growth of the lower zone, surgery can be performed with the removal of teeth or osteotomy of the branch in the upper jaw.
Treatment of pathology in adult patients can be based on the use of arc devices with intermaxillary traction, Brukle apparatus and braces.
The following procedures are also performed:
- shortening the length of the lower row of teeth by removing some of them or removing gaps between nimes, extending the upper region by moving the front row forward;
- sigittal displacement of the upper and lower rows in the required direction;
- is a labial displacement of the upper row and a lingual displacement of the lower row( using a wire ligature or protracting springs).
 If necessary, combined hardware-surgical treatment with extension of the upper jaw can be performed. Prosthetics can also be used.
If necessary, combined hardware-surgical treatment with extension of the upper jaw can be performed. Prosthetics can also be used.
Cost and duration of correction depends on the structures and methods used, the choice of which depends on the form, manifestations of pathology and age of the patient.
The duration of treatment also depends on the severity of abnormal development. On average, correction of occlusion in children takes 1-2 years. In adults, the timing is different based on the stage of development( vary within 1.5-4 years).
Retention period
An obligatory stage of therapy is the consolidation of the results. Correction of rows of teeth by hardware methods is not completed after their removal. After the main therapy, the patient passes the retention period with the use of orthodontic structures for a long time( from six months to 2 years).
The doctor personally sets the exact time limit individually. To fix the result, the following devices are used:
- .They are non-removable devices, they have the form of a small arc from a special fiber or metal. Fastening
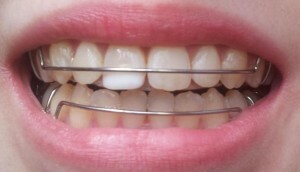 design is carried out with the lingual part of teeth composite. They maintain the correct position of the dentition, while remaining invisible.
design is carried out with the lingual part of teeth composite. They maintain the correct position of the dentition, while remaining invisible. - Trainers .Such devices are used to correct and fix the bite. Special models are used, which are worn at least 8 hours a day. In the future, the duration of socks is reduced to 1-3 hours.
- Individual mouthguards made of silicone, replicating the relief of teeth. The duration of their socks with retention is at least 20 hours a day, after which time is shortened.
Possible consequences of
If a person does not pay due attention to their health, in a timely manner does not correct the pathological progenic bite, serious problems may appear. These include difficult chewing and eating, speech disorders and dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint.
With incorrect distribution of the chewing load in the front teeth, periodontal tissues are overloaded, periodontal disease with early tooth loss appears. Due to improper chewing food there are disorders of the digestive tract, difficulty with swallowing and irritation of the stomach from rough food. Migraines and tinnitus appear. A person can have aesthetic and emotional discomfort.
Preventive measures
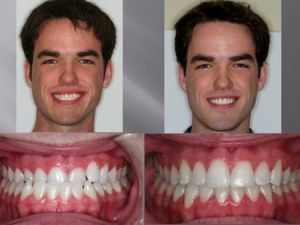
In the photo the patient before and after correction of the prognosis
According to medical data, the prognosis is not always manifested due to genetics. To prevent or prevent an anomaly of development of an occlusion, it is recommended to treat diseases that violate the maxillofacial apparatus in a timely manner, to visit the dentist regularly when changing temporary teeth in a child.
Prophylactic measures include the correct position in a dream, the normal course of pregnancy and childbirth, breastfeeding, elimination of bad habits( thumb sucking, etc.).
Progenic bite is a serious orthodontic defect, which can be corrected by a timely appeal to experienced professionals.
