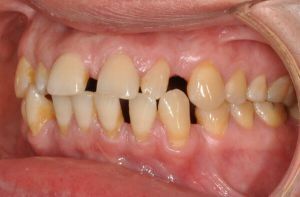
 An abnormality of the development of the teeth is understood as acquired or congenital disorders of their shape or size. These deviations negatively affect both the bite and the formation of the dentition. In addition, abnormal teeth often do not have an aesthetic appearance, cause a person to be uncertain and withdrawn. This disproportion in size( upwards or downwards) occurs in every twentieth person on the planet.
An abnormality of the development of the teeth is understood as acquired or congenital disorders of their shape or size. These deviations negatively affect both the bite and the formation of the dentition. In addition, abnormal teeth often do not have an aesthetic appearance, cause a person to be uncertain and withdrawn. This disproportion in size( upwards or downwards) occurs in every twentieth person on the planet.
The anatomical shape and the size of the teeth can have significant deviations from the norm. In the medical literature, it is customary to distinguish diseases such as microdentity and microdentity, depending on whether the teeth are small or too large.
Content
- Large and giant teeth
- Etiology
- Forms and clinical manifestations
- Correctional
- procedures Small teeth
- Forms
- anomalies Causes pathology
- Hidden and obvious danger
- Correction
- anomalies Preventive measures
Large and giant teeth
rare anomaly, which is characterized by an increase in the sizeteeth 2 to 6 mm from their natural size, is called a macroid. In most cases, it is peculiar to manifest with a replaceable occlusion and is diagnosed in children aged 7 to 9 years.
This pathology can be observed for one or several teeth at once. Most often, the upper central incisors or lower premolars grow large. They are often supercomplex.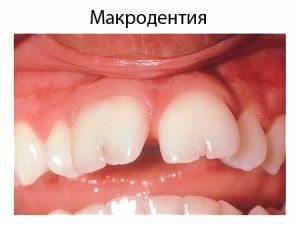
Increasing the size can occur in both width and height. The growth process is often accompanied by a lack of gaps between the bony formations, as well as retention. Insufficient amount of free space in the row causes the large elements to unfold around their axis.
The incisal edge of the central incisor often resembles a screwdriver or has a recess in the form of a crescent. The roots of this anomaly are powerful and short. They are also characterized by associations of several branches.
Etiology
This anomaly is observed due to the fusion of two dental follicles or a normal tooth follicle with superfine or incomplete bone formation. Factors influencing the occurrence of this pathology are:
- improper formation of dental rudiments, caused by a violation of metabolic processes during the maturation of the fetus;
- heredity: every fifth child is diagnosed with a maternity, in the event of such a problem, at least one of his parents;
- problems with the endocrine system, affecting the disproportionate development and growth of the teeth.
Many experts believe that this anomaly is a consequence of the incomplete development of polyiodontics.
Forms and clinical manifestations
In practice, makrodentia can have several forms of clinical manifestations. It is accepted to distinguish five types of this disease:
- Localized .The unit element or a small group that is characterized by enlarged dimensions relative to the rest of the dentition is subjected to change.
- Generalized .Each bone formation has a slight increase( up to 2 mm).The length of the dentition exceeds the size of the jawbone. The cause of the pathology can be the transferred diseases of the future mother in the process of fetal development, as well as the child during the formation and growth of the teeth.
- Absolute .The anomaly is expressed by the excessive length of the incisors. For the upper jaw this figure is more than 3.50 cm, and for the lower jaw it is 2.80 cm.
- Relative .In this case, the upper incisors should not exceed a size of 35 mm, and the lower ones - 27 mm.
- Isolated .The increased size is observed only in one incisor and can reach a deviation up to 6 mm from the norm.
Correction procedures
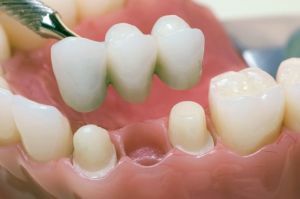 The problems caused by microdentia are easily eliminated thanks to modern methods of orthodontics. The method of treatment depends on the complexity of the pathology and degree of malocclusion. With a slight deviation, grinding of the surfaces of abnormal teeth and their subsequent coating with a fluorinated varnish can be carried out.
The problems caused by microdentia are easily eliminated thanks to modern methods of orthodontics. The method of treatment depends on the complexity of the pathology and degree of malocclusion. With a slight deviation, grinding of the surfaces of abnormal teeth and their subsequent coating with a fluorinated varnish can be carried out.
In complex situations, a decision is made to remove individual units. Prostheses of the required size are installed on the site of the removed teeth using a crown or bridge.
If it is necessary to align or change the position of the teeth, corrective structures such as plates or braces are used.
Small teeth
Abnormal development of teeth, characterized by small dimensions of their crown part, is usually called a microdentium.
Both individual elements and the group in the dentition can be affected by the change. The most common anomaly is observed with the front and side upper incisors. Usually, the pathology develops on both sides of the jaw, that is, it is symmetrical. A deviation is a decrease in bone formation by 1.5 mm or more from its physiological norm.
Forms of anomaly
Manifestation of this disease has an individual character in each case. However, in dentistry it is common to distinguish several types of microdentity:
- The most common is the isolated form of the disease. It is diagnosed in every second patient with such an
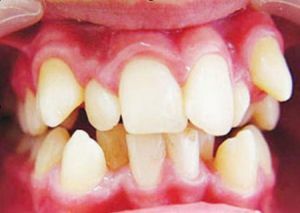 anomaly and is characterized by a change in only a single specimen. In the process of tooth growth, not only its size but also its shape is affected by changes. Outwardly it resembles a narrow conical peg.
anomaly and is characterized by a change in only a single specimen. In the process of tooth growth, not only its size but also its shape is affected by changes. Outwardly it resembles a narrow conical peg. - With generalized , the development of a disorder is detected immediately in several teeth. Pathology is characterized by their uneven growth, curvature and displacement. Often there are irregularities at the edge of the cutting part, as well as a thin layer of enamel.
- With relative , the form of the disease is marked by excessive magnification of the jaw arched with normal tooth size. This problem can be detected with both the upper and lower jaw.
Causes of pathology
The most common cause of microdenism is called genetic abnormalities that provoke an abnormal formation of the tooth germ. In addition, the disease can occur due to a number of external and internal factors: the
- organism in childhood was subjected to radiation therapy or other reception of a radioactive dose;
- early eruption of permanent teeth, caused by premature removal of dairy;
- incorrect arrangement of one or more elements in the dentition;
- deviations in the development of the occlusion due to narrowing of the jaw arc;
- severe illnesses suffered by a child at an early age or by a mother while bearing the fetus;
- problems in the functioning of the endocrine system.
Hidden and overt hazards
Small tooth sizes can cause deformation of the entire bite. In addition to the psychological discomfort caused by the appearance of abnormal bone formations, microdentia can lead to a number of other negative consequences:
- weak stability of small teeth due to lack of contact with adjacent bone elements;
- gum disease caused by the accumulation of microbes in a wide space between the teeth and soft tissues;
- dysplasia of the jaw joints due to improper load distribution during chewing food;
- problems with speech, a clear manifestation of hissing and whistling sounds.
To determine the diagnosis and determine an appropriate treatment course, you should contact a dental clinic.
Correction of anomaly
 Often, the removal of an anomaly of small teeth occurs with the use of orthodontic correction. In the case of abnormal bite abnormalities or irregular shape of individual bone processes, prosthesis is prescribed.
Often, the removal of an anomaly of small teeth occurs with the use of orthodontic correction. In the case of abnormal bite abnormalities or irregular shape of individual bone processes, prosthesis is prescribed.
To align teeth to size, as well as eliminate visual gaps between them, composite or ceramic tabs are installed.
In the case of significant deformation or improper placement of the tooth, the doctor decides to remove it and install the prosthesis using a pin or bridge.
Preventive measures
In order to reduce the risk of anomalies in tooth size, it is necessary for the future mother to monitor her health during pregnancy, as well as the development of the baby's future.
During a period of active growth, a child's nutrition should be balanced, contain vitamins and trace elements.
Children should regularly visit the dentist in order to prevent and detect possible problems in the first stages of the manifestation of the disease.
