 Every day at least one person in serious condition is diagnosed with maxillofacial phlegmon in the departments of maxillofacial surgery of city hospitals. Is this disease dangerous for health and what precedes its development?
Every day at least one person in serious condition is diagnosed with maxillofacial phlegmon in the departments of maxillofacial surgery of city hospitals. Is this disease dangerous for health and what precedes its development?
Maxillofacial phlegmon is an acute, purulent, diffuse inflammation of subcutaneous fat in the neck, mouth cavity, jaws and face caused by the penetration of pathogenic microflora from the affected areas. Most often it develops as a complication of diseases of the oral cavity: osteomyelitis or periostitis of the jaws, or in case of infection with trauma or ENT - diseases.
Precipitating factors
- Content
- Features of clinic and symptoms
- Modern classification
- Maxillary area
- cheekbone and eye socket
- Localization Pterygopalatine-palatine fossa
- buccal region
- Phlegmon mandibles
- defeat bottom of the oral cavity
- neck
Precipitating factors
disease develops underexposure to a number of microorganisms that enter the tissues, cause the development of the pathological process:
- of staphylococci;
- streptococci;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- dental spirochete;
- E. coli.
The most common flora is mixed, with the predominance of anaerobic microorganisms that do not need oxygen. If microorganisms get through the tissues of the teeth, the pathological process is called odontogenic.
Features of the structure of lymphatic and circulatory systems predispose to the development of purulent diseases of subcutaneous fat. In the case of allergic diseases, such as pollinosis, eczema and atopic dermatitis, the likelihood of developing phlegmon increases.
There are 5 main sources of infection, which cause the development of phlegmon of the pterygo-jaw space:
- carious teeth and affected roots;
- inflamed periodontal tissue;
- inflammation of the oral cavity: stomatitis, glossitis;
- inflammation of the salivary glands;
- inflammation of the ENT organs.
The pathogenesis of this disease is caused by the ingestion of a virulent microorganism that releases toxins and causes inflammation with characteristic signs: redness, pain, swelling, fever, dysfunction of the jaw joint.
There is a delay in the formation of soft tissues, limited by the neutrophilic shaft, and mass death of leukocytes with the onset of purulent inflammation.
Clinic features and symptoms
The disease begins quickly with a short period of precursors. Initially, patients noted the presence of headache, increased fatigue, weakness.
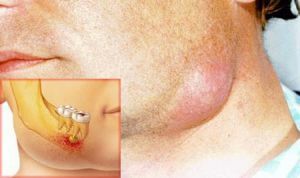 With phlegmons of the maxillofacial region, the pathological process is unlimited from healthy tissues, which causes the development of intoxication of the body. Intoxication syndrome is characterized by an increase in temperature to 38.5-40 C, headache, nausea, vomiting.
With phlegmons of the maxillofacial region, the pathological process is unlimited from healthy tissues, which causes the development of intoxication of the body. Intoxication syndrome is characterized by an increase in temperature to 38.5-40 C, headache, nausea, vomiting.
Subsequently, dense diffuse edema is formed, accompanied by a sharp unbearable pain. At the site of inflammation, a sharp asymmetry of the face is formed, depending on the localization of the pathological process, the process of breathing is difficult with the formation of dyspnea.
Skin over the inflamed area is hyperemic with a characteristic symptom of fluctuations: when you touch the site of inflammation, fluid vibrations are felt. During food intake, saliva production increases.
Modern classification of
Currently the most modern is the topographic anatomical classification, taking into account that the maxillofacial phlegmon can be localized:
- in the region of the maxilla;
- on the lower jaw;
- in the area of the bottom of the mouth;
- on the soft tissues of the tongue and neck.
Because of the appearance, there are odontogenic( dental provoking factor) and non-dentogenic phlegmons. 
The severity of patients is divided into 3 groups:
- mild severity - the pathological process is within one anatomical region;
- mean severity - pathology localized in several anatomical regions;
- severe severity - the process captures the entire maxillofacial region and neck.
Maxillary region
The phlegmons of the upper jaw are most dangerous for the health and life of a sick person, especially the inflammation of the infraorbital area and eye orbit. This is due to the anatomical location of the blood vessels and the possibility of drift infection with the further development of inflammation in the cavernous sinuses and the meninges.
All this leads to the progression of pathology and the development of meningitis and thrombosis of the cavernous sinus of the brain. The disease begins, as a rule, with the edema of the upper lip, which subsequently spreads to the upper jaw.
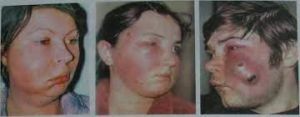 Smoothes the nasolabial fold above the lip. The skin of the infraorbital region is sharply hyperemic, when you try to put a fold into the fold, there is a sharp soreness. The opening of the mouth is not disturbed, during tooth tapping, which caused the pathological process, there is a moderate pain, the folds of the mouth are smoothed.
Smoothes the nasolabial fold above the lip. The skin of the infraorbital region is sharply hyperemic, when you try to put a fold into the fold, there is a sharp soreness. The opening of the mouth is not disturbed, during tooth tapping, which caused the pathological process, there is a moderate pain, the folds of the mouth are smoothed.
Treatment of the maxillary phlegmon is carried out only by surgical intervention by opening the focus and conducting active drainage with the application of Vishnevsky ointment.
Skull area and orbitals
The caries of the upper jaw are also the cause of the development of phlegmon of the malar region. Also, infection can not be excluded with suppuration of hematomas, insect bites, development of furuncles.
Symptoms do not differ from phlegmon of other localization: there is swelling of the cheekbone with possible spread to the orbit region, the skin turns red, soreness develops, mouth opening is not disturbed.
Purulent inflammation located in the orbit most often develops as an exacerbation of chronic sinusitis. In the course of the process, one of the most severe pathologies. It is characterized by severe intoxication, headache, high fever. It is accompanied by intense pain in the orbit.
There is a pronounced edema and cyanotic color of the eyelids. In case of involvement of the optic nerve, various visual impairments are possible:
- reduction in visual acuity;
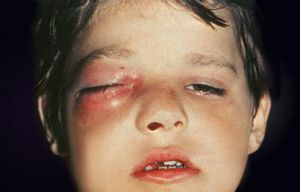
- edema of the conjunctiva of the eye;
- protrusion of the eye from the lesion;
- double vision;
- loss of vision due to compression of the optic nerve.
The main method of treatment is surgical opening with the purpose of penetration into the inflammatory focus, active drainage is carried out with the chlorovinyl tubing and washed with antiseptic solutions in order to prevent the multiplication of microorganisms and the removal of purulent exudate from the focus.
Localization in the pterygoid-palatine fossa
When located in the pterygo-palatine fossa, the main source of the disease is the carious teeth of the upper jaw, in particular the second and third molars. The course is extremely difficult:
- Pain sensations are clearly pronounced. Most often occurs irradiation to the temporal, parietal, infraorbital areas.
- The temperature rises to 39C, there is a severe headache. Absence of treatment adversely affects the general condition of the patient.
- There is edema of the temporal, malar and suborbital areas.
- Opening the mouth and chewing food are difficult.
Treatment is only surgical, the patient enters the department of maxillofacial surgery. The operation is carried out urgently in order to prevent the development of complications. It is mandatory to actively drain the inflammatory focus and rinse with antiseptic solutions.
Cheek area
Soft tissue soft tissue phlegmon on the anatomical location happens:
- superficial;
- deep.
The reason, as in all the cases described above, is carious processes in molars and premolars of the upper and lower jaw. Symptoms typical for this pathology: 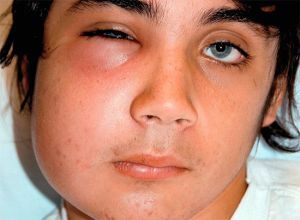
- throbbing pain, prone to strengthening during opening of the mouth;
- swelling of the cheek, expressed by the symptom of fluctuations;
- the skin of the inflamed focus is hyperemic and tense;
- mouth opening is difficult.
Treatment is only surgical with active drainage of the focus and washing with antiseptic solutions at least 3 times a day.
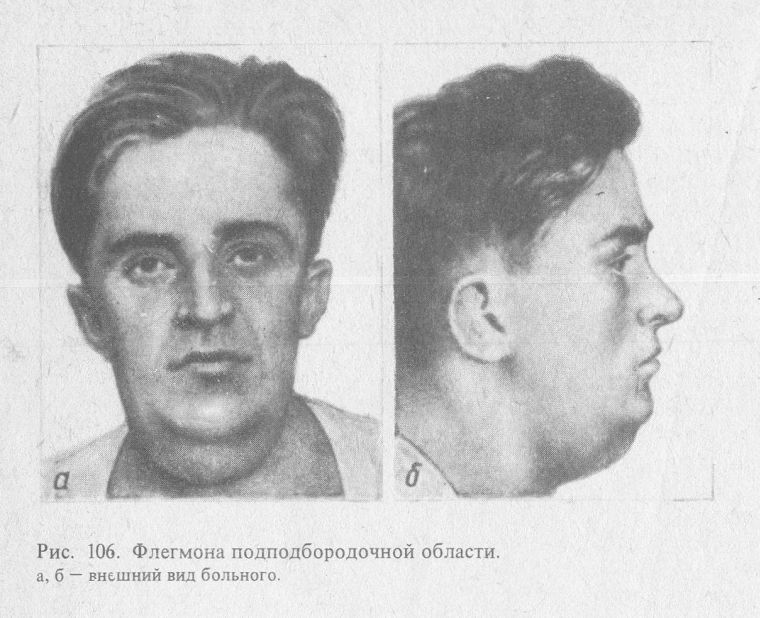
The phlegmons of the lower jaws
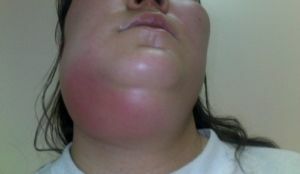
Among all the anatomical areas, the phlegmon developing most in the submaxillary( see photo below), the pterygo-mandibular and perianthal area, poses serious complications: asphyxia, phlegmon of the neck.
The main source of such purulent inflammation is the carious lesion of the mandibular wisdom teeth. The most often pathological process develops in persons with weakened immunity after 25 years.
Patients complain of swelling of the lower jaw. There is no possibility of making any movement with the jaw. The main complaints of soreness in movement, eating, talking and swallowing. The skin in this place is reddened.
Treatment is carried out by a wide opening of the focus by cutting up to 6 cm. The skin and all the layers following them are cut through the layer. Then drainage is installed, most often it is a chlorovinil tube, afterwards it is washed with antiseptics.
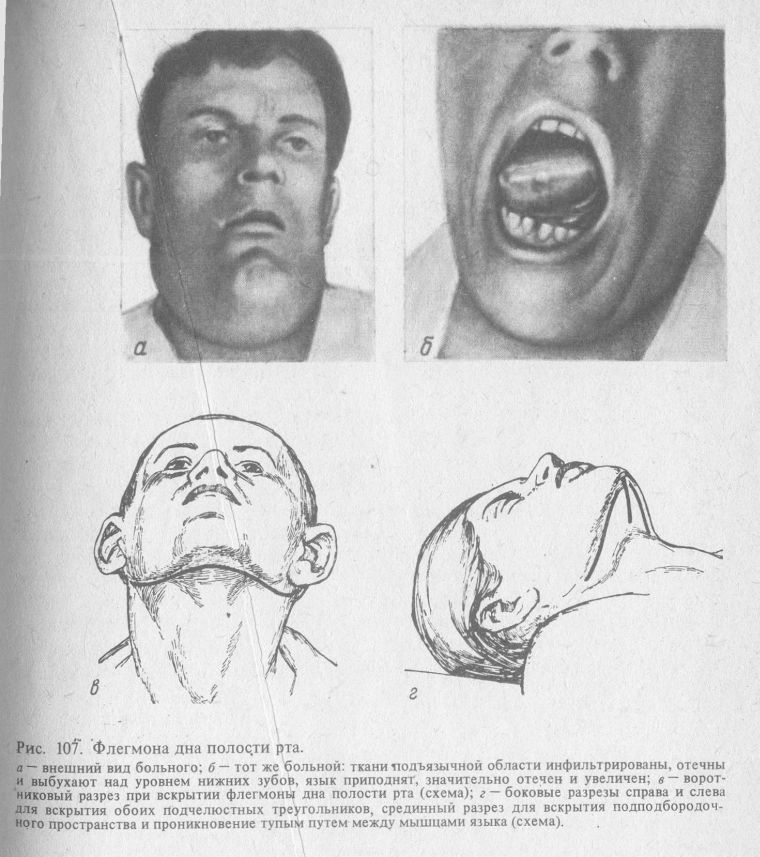
Oral cavity lesion
The bottom of the oral cavity is much less likely to become a place of purulent inflammation of subcutaneous fat. The most frequent cause of development of phlegmon of this localization are carious teeth and other inflammations of the oral cavity, such as glossitis.
Clinical manifestations are very diverse. A special feature is the proximity of the larynx, in consequence of which the development of mechanical suffocation due to the development of edema. Therefore, the person is in a sitting position with the head tilted forward.
The condition of the patient is of medium severity or severe due to the following symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- swelling of the chin and lower jaw;
- tongue is covered in white;
- bad breath.
Treatment is exclusively surgical, has no special features.
Neck area
Develops the phlegmon of the neck, as a complication of most dental diseases. A sedentary infiltrate is defined.
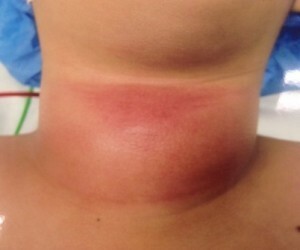 The patient complains of weakness, a strong increase in temperature, there is hoarseness of the voice, difficulty breathing. When phlegmon is localized in the esophagus, eating difficulties may occur.
The patient complains of weakness, a strong increase in temperature, there is hoarseness of the voice, difficulty breathing. When phlegmon is localized in the esophagus, eating difficulties may occur.
Treatment is only surgical, with numerous cuts on the surface of the neck and the establishment of multiple drains. It is necessary to constantly wash the hearth at least 4 times a day.
Prevention is the premature treatment of tooth decay and diseases of the oral cavity. A visit to the dentist must be at least once a year.
At the first symptoms of the disease, you should immediately contact the maxillofacial surgeon for timely treatment.
