 Glossalgia is a secondary manifestation of a neuro-trophic disorder, which is expressed in painful sensations in the area of the tongue, discomfort and burning in the oral cavity, not associated with external stimuli.
Glossalgia is a secondary manifestation of a neuro-trophic disorder, which is expressed in painful sensations in the area of the tongue, discomfort and burning in the oral cavity, not associated with external stimuli.
The disease is more common in women over 40 years of age. Men suffer from this disease much less often, which is explained by the more stable psychoemotional state of the strong half of humanity.
Contents
- Causes much deeper
- Nature of the clinical picture
- Glossology and glossology - is there any difference?
- The approach to therapy is special, as is
itself. The causes are much deeper
Glossalgia is a consequence of the defeat of one of the links of the central nervous system. Violation of the peripheral part of the CNS can be caused by the following reasons:
-
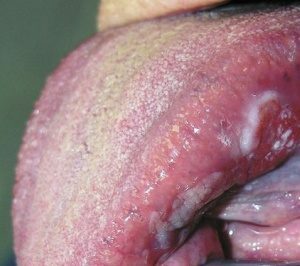
Squamous cell carcinoma
vascular disorder;
- mechanical damage or injury;
- complication of an infectious disease;
- formation of tumors.
It is noted that in patients with increased hypotension, there are more frequent cases of violation. This disorder can develop against a background of ischemic disease with the complete absence of an external stimulus.
Mechanical damage to the tissues of the oral cavity almost never leads to the appearance of glossalgia. The development of the disease is promoted by nervous manifestations, which arise either independently or against a background of other diseases.
Among other factors that provoke the disease:
- encephalitis - regardless of its etiology has a negative effect on the brain and CNS;
-
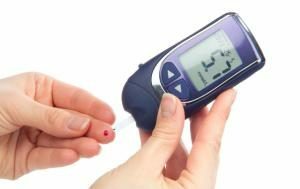 infections of the digestive tract - are accompanied by intoxication, tachycardia, dehydration;
infections of the digestive tract - are accompanied by intoxication, tachycardia, dehydration; - diabetes mellitus - promotes the development of atherosclerotic disorders. Glossalgia is more common against a background of diabetic neuropathy;
- hypothyroidism - decrease in the level of thyroid hormones, accompanied by damage to the nervous system;
- neurosyphilis is a form of syphilis in which cells of the nervous system are destroyed;
- oncology - leads to impaired brain activity;
- genetic diseases - porphyria, Kennedy's disease and other diseases associated with the defeat of the nuclei of the cranial nerves.
Prolonged course of the disease can lead to structural changes in the mucous membranes of the mouth, namely: thinning of the epithelium, hyperemia of the mucosa, slimming cells. In the tissues of the tongue there is a violation of microcirculation, which leads to a deterioration of sensitivity and a violation of taste sensations.
The nature of the clinical picture
The disease manifests itself in various ways, the main sign of glossalgia is the burning sensation of the tip of the tongue or tingling, the tongue hurts, as if burned, pinch or bake. All these symptoms occur without visible mucosal disorders.
If glossalgia is not accompanied by a trauma to the tissues of the oral cavity, then the outward appearance of the disease is practically not manifested.
 The disease begins gradually, and patients often can not name the exact moment of the onset of symptoms, which complicates the clinical picture and facilitates the establishment of false diagnoses. Symptoms can completely go away and suddenly arise again. The disease can develop for many years without causing serious fears in the patient due to the lack of pronounced manifestations.
The disease begins gradually, and patients often can not name the exact moment of the onset of symptoms, which complicates the clinical picture and facilitates the establishment of false diagnoses. Symptoms can completely go away and suddenly arise again. The disease can develop for many years without causing serious fears in the patient due to the lack of pronounced manifestations.
External stimuli can exacerbate symptoms.
These include:
- dental diseases - complicated caries, inflammation of the gums, poor-quality prosthetics;
- trauma of the language - mechanical damage, friction of the tongue about dentures and chipped teeth;
- The use of spicy food - intensifies burning, plaits the tip of the tongue and increases soreness.
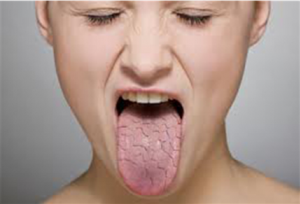 Patients may experience dry mouth, which increases during periods of agitation, stress, and fatigue. Against the background of gastroenterological diseases, there may be a white raid on the root of the tongue.
Patients may experience dry mouth, which increases during periods of agitation, stress, and fatigue. Against the background of gastroenterological diseases, there may be a white raid on the root of the tongue.
In rare cases, there is increased salivation. Violation of sensitivity is often accompanied by pain.
Violation of speech and difficulty in chewing food are also signs of a violation. In 20% of patients, serious violations of diction are noted.
But it happens that during eating, the symptoms completely disappear, which once again proves the connection of the disease with neuro-cerebral activity, and not with external influences. Physicians explain this phenomenon as a priority of the food dominant over the focus of nervous excitement.
 Pain sensations can have a different character: burning in the tongue, tingling, sadening, aching pain. These manifestations often change the localization, can completely disappear or increase, depending on the psychoemotional state of the patient. Discomfort in the tongue can be accompanied by pain in the mouth - baking tongue, burning sensation spreads to the sky, the inner surface of the cheeks and lips.
Pain sensations can have a different character: burning in the tongue, tingling, sadening, aching pain. These manifestations often change the localization, can completely disappear or increase, depending on the psychoemotional state of the patient. Discomfort in the tongue can be accompanied by pain in the mouth - baking tongue, burning sensation spreads to the sky, the inner surface of the cheeks and lips.
Symptoms may worsen after prolonged conversations. On the background of allergic reactions, irritation and swelling of the tongue may occur.
 In fact, glossalgia is not an independent disease, which means that its symptoms are closely related to the underlying disease, in the role of which vascular or endocrine disruptions, diseases of the digestive system, which have a clearer symptomatology, can play a role.
In fact, glossalgia is not an independent disease, which means that its symptoms are closely related to the underlying disease, in the role of which vascular or endocrine disruptions, diseases of the digestive system, which have a clearer symptomatology, can play a role.
Get a complete clinical picture will help a neurologist who will determine the exact cause of the appearance of symptoms characteristic of glossalgia.
Complications of the diagnosis of the presence of such neuralgic diseases as inflammation of the glossopharyngeal or trigeminal nerve. Glossalgic syndrome is usually not accompanied by acute pain, while with neuralgic disorders there is a pronounced pain syndrome.
Painful seizures are localized in that part of the oral cavity where the innervation of the nerve is broken. Soreness goes along with an attack, which, as a rule, is accompanied by nervous twitching, facial muscle cramps and muscle spasms. Glossolgia and glossodynia - is there a difference?
Glossalgic syndrome is often confused with glossodynia. Medics themselves do not seek to share these concepts, although these are different types of functional disorders.  Both these manifestations are associated with impaired sensitivity of the language, which leads to frequent confusion.
Both these manifestations are associated with impaired sensitivity of the language, which leads to frequent confusion.
It is believed that glossalgia is directly related to the disruption of the central nervous system. Glossodynia is a consequence of somatic disorders, including hormonal disorders and diseases of internal organs.
Glossalgia often passes against the background of of the osteochondrosis of the cervical department of .Disturbance of blood supply in this area, as well as possible jamming of nerve endings leads to paresthesia of the tongue and tissues of the oral cavity.
 The disorder develops in the presence of phobias and experiences, which explains why the disease affects women more often. Many of them have a pronounced carcinophobia, which is expressed in a constant fear of finding an oncology in the oral cavity.
The disorder develops in the presence of phobias and experiences, which explains why the disease affects women more often. Many of them have a pronounced carcinophobia, which is expressed in a constant fear of finding an oncology in the oral cavity.
Increased suspiciousness of such patients leads to the inevitable appearance of false symptoms, which eventually develops into a serious pathology requiring psychoanalytic and neurological treatment.
Glossalgia is more closely related to CNS lesions, which are more often organic. Such phenomena can be rooted in the peculiarities of intrauterine development, the effects of radiation, age-related atrophic processes. In connection with this, the disorder is accompanied by the following disorders and disorders not directly related to the oral cavity:
-
 loss of orientation;
loss of orientation; - low working capacity;
- weak concentration of attention;
- reduction of active vocabulary;
- memory degradation.
It is noted that the syndrome often occurs in women in menopause, which is due to hormonal changes and age-related changes.
The approach to therapy is special, as is
itself. Treatment of glossalgia is determined based on the causes of the disease. It is necessary to exclude all extraneous factors for establishing a complete clinical picture and the appointment of adequate treatment. Preventive measures are carried out to eliminate possible inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
 In the presence of vegetovascular disorders, preparations containing B vitamins and sedative therapy are prescribed. With significant pain, analgesics of local action, as well as novocain blockades, can be recommended. To reduce pain, rinses with anesthetic drugs are prescribed.
In the presence of vegetovascular disorders, preparations containing B vitamins and sedative therapy are prescribed. With significant pain, analgesics of local action, as well as novocain blockades, can be recommended. To reduce pain, rinses with anesthetic drugs are prescribed.
Glossalgia, accompanied by loss of language sensitivity, often indicates iron deficiency anemia. To eliminate it, prescribe drugs with iron content. To improve capillary blood flow, patients are prescribed intravenous injection of nicotinic acid and injections of no-shpy.
Patients with characteristic symptoms are recommended physiotherapy, including transnasal electrophoresis. Good results can be achieved using a galvanic collar. To eliminate dry mouth, drugs that increase salivation are recommended.
 Patients with strong phobias and neurotic conditions are prescribed tranquilizers and hypnotics. A huge role in the treatment of glossalgia is played by psychoanalytic therapy. By its results, the patient can be recommended autogenic training, hypnotic effect.
Patients with strong phobias and neurotic conditions are prescribed tranquilizers and hypnotics. A huge role in the treatment of glossalgia is played by psychoanalytic therapy. By its results, the patient can be recommended autogenic training, hypnotic effect.
In the treatment of glossalgia, acupuncture has demonstrated its effectiveness, which also helps to cope with neuralgic manifestations that are not amenable to drug treatment. Laser therapy is also useful when there is paresthesia of the tongue.
Patients who develop glossalgia against allergic reactions are recommended antihistamine therapy. In the presence of dysbacteriosis and fungal infections of the oral mucosa, initially, these manifestations that prevent the treatment of the syndrome are eliminated.
Glossalgia, which arose against the background of diseases of the digestive system, requires a preliminary cleansing of the gastrointestinal tract, elimination of toxins and toxins. In this case, a patient may be recommended a short-term fasting and taking diuretics. Also, the methods of traditional medicine will be useful, in particular, a positive effect gives a rinse with a decoction of sage and celandine.
