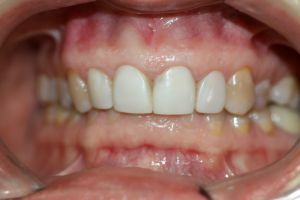
 A deep bite is an abnormal tooth-jaw development, in which the incisors of the upper jaw enter the incisors of the lower one by more than a third of the level of the crowns.
A deep bite is an abnormal tooth-jaw development, in which the incisors of the upper jaw enter the incisors of the lower one by more than a third of the level of the crowns.
This type of pathology is most common in orthodontic practice and accounts for almost 50% of all cases.
In medicine, a deep bite has different terminology:
- deep frontal overlap;
- deep incisal overlap;
- traumatic bite;
- deep incisal occlusion;
- Deep incisal dissoclusion.
Contents of
- What is the cause?
- Classification of anomalies and types of disorders
- Causes of pathology and risk factors
- How to identify a violation of
- About possible problems
- Diagnostic approach
- Prevention and therapy disorders
- Possible complications
- Preventive measures
What is the cause?
Depending on the vestibular deviation of the upper incisors, the depth of the incisal overlap occurs. Often a deep occlusion can manifest in combination with the distal.
The reason for this is:
- uneven development of the upper and lower jaws;
- shortened branches of the lower jaw;
- distal position of dentition relative to each other;
- later teething;
- delay in the appearance of permanent teeth.
The bite pathology disrupts the functionality of the jaw, reducing chewing efficiency. The aesthetic appearance worsens - the lower part of the  of the face is shortened, and the lips take an ugly position.
of the face is shortened, and the lips take an ugly position.
The anomaly also affects the overload of the front teeth and damages the mucous membrane, which provokes oral diseases that complicate the treatment process.
Classification of anomalies and types of disorders
The deep bite has a different pattern of tooth interaction and is classified according to several basic features. According to the type of interaction of the frontal teeth are distinguished:
- vertical violation( overlapping the lower part of the jaw);
- horizontal violation.
By the type of interaction of the lateral incisors, two basic forms of occlusion are distinguished:
- The neutral form of the is almost never visually distinguished. Even in adulthood, a person with permanently formed bones of the face pathology is difficult to notice. Specialists determine the deviation from complete overlapping of the upper teeth of the lower teeth and the presence of a supramental fold.
- The distal form of the , on the other hand, is very visible in both children and adults. The pronounced disproportionality of the face is accompanied by an unnaturally small chin, as if shifted to the side of the neck. With a smile, as a rule, a large part of the gums is exposed.
Causes of pathology and risk factors
The following factors can influence the incorrect development of the occlusion:
- hereditary predisposition;
- severe infectious diseases transferred by a pregnant woman;
- birth complications.
In addition, the anomaly can be caused by various diseases at an early age:
- by impaired functions of the respiratory and endocrine systems;
- with diseases of the ENT organs;
- with gastrointestinal problems;
- violation of the functions of metabolic processes.
The development of pathology is also affected by disorders of the musculoskeletal system:
- incorrect posture;
- disorders in the development of the spine;
- hereditary diseases of bone and connective tissues.
In infancy, the abnormality can be caused by bad habits of the child constantly sucking a finger or a nipple.
Among other causes of pathology are: 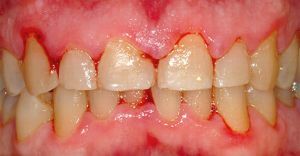
- traumatic dislocation of the jaw or damage to the functions of the temporomandibular joint;
- absence of some teeth, contributing to involuntary tilt of neighboring teeth towards the defect;
- improper dental treatment;
- development of gingivitis and periodontitis.
How to identify a violation of
It is easier for an adult to determine if he has problems with bite or not, rather than a child. Specialists diagnose a dentoalveolar anomaly for several characteristic symptoms:
- enamel of anterior teeth is prone to rapid abrasion due to increased load on them, which usually leads to the formation of caries;
- chewing functions are broken and there are problems with chewing and swallowing food( especially in young children);

- may cause breathing problems;
- dyslalia or paralysis( speech disorders);
- violation of the proportions of the face;
- inflammation on the mucosa of the mouth due to constant mechanical action of the teeth.
Detection of at least one of these symptoms in children or adults is the reason for contacting an orthodontist. The sooner a diagnosis is made, the easier it will be to undergo treatment.
It is easier to fix a deep bite in children under the age of 13, since the position of the teeth is not completely formed.
On possible problems of
A deep bite not only negatively affects the aesthetics of the face, but also significantly harms the entire human body. The presence of a defect causes such problems:
- violation of spoken language;
- damage to the mucous membranes of the mouth, causing inflammation of the gums and periodontitis;
- increased load on the front teeth, detrimental to tooth enamel;
- aesthetic drawbacks;
- difficulty in breathing and swallowing processes;
- regular headaches.
Diagnostic approach
Specialists diagnose abnormal development of the jaw by several basic criteria and with the help of additional survey methods. 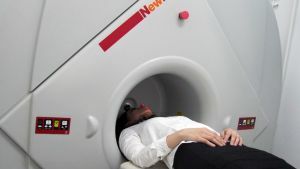
Diagnosis includes:
- oral interrogation to identify problems associated with anomalies and assessing the standard of living with this diagnosis;
- general clinical examination;
- study of patient diagnostic models;
- tomography.
Prevention and therapy of disorders
Prevention and correction of deep occlusion is recommended to be carried out at an early age, while the tooth-jaw system has not yet fully formed.
The defect can be corrected at a later age, however it will require more effort and the duration of treatment will increase significantly.
Treatment of the distal bite is to restrain the development of the upper jaw to allow the lower row of teeth to develop freely.
Special orthodontic constructions are used for this:
- trainer( soft elastic tire, adaptable to any jaw);
- tooth edema;
- braces system with facial arches( for more mature age).
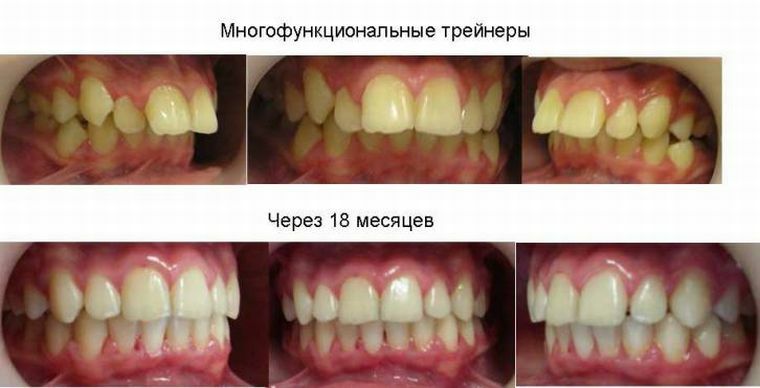
In the photo, a deep bite before and after correction by trainees
Temporary systems require careful care, which consists in the regular removal of the device to clean it.
Mesial bite is corrected by stimulating the development of the upper row of teeth by restraining the growth of the lower jaw. For the treatment of this form of pathology, similar structures are used, as in deep bite. In addition, at an early age, in order to form a proper occlusion, the general gymnastics of the muscles participating in the formation of the dentoalveolar system is additionally carried out.
It helps to restore normal bite systematically by performing a massage of the gums with a slight pressure on the teeth.
In adulthood, treatment methods with the use of trainers or cap is ineffective, therefore, to fix the bite, immediately fix the bracket system, or correct the anomaly surgically. In modern medicine, a deep bite is successfully treated with a laser.
This innovation allows you to effectively and quickly cope with the disease. The problem is solved in just one visit after a preliminary consultation with an orthodontist.
Possible complications of
 Untimely treatment of deep bite can provoke unpleasant complications. The most common - bruxism( gnashing his teeth).
Untimely treatment of deep bite can provoke unpleasant complications. The most common - bruxism( gnashing his teeth).
Permanent clenching and grinding of teeth between themselves can adversely affect tooth enamel and jaw joints. In some cases, the habit does not go away even after correction of the occlusion, so it is recommended to seek treatment as early as possible in order to avoid its appearance.
Malocclusion, due to a constant load on the dentition, promotes loosening of teeth by 30-40 years. It is also possible to significantly denude the dental necks and the appearance of gaps between the teeth.
A deep bite can cause a pathology of temporomandibular joints. The ailment is accompanied by frequent attacks of headaches, a characteristic click at the time of opening the mouth and the pain of the masticatory muscles.
Preventive measures
Correction of an incorrect bite with the help of a bracket system is a rather long process, which can drag on for several years.
Therefore, in order to avoid serious problems, it is recommended that early prevention be carried out at an early age to help prevent functional disorders.
Prevention includes:
- monitoring the position of the infant during the feeding;

- control over the position of the child during sleep;
- weaning from bad habits of sucking a finger or other objects;
- development of a correct posture;
- timely treatment of caries and other dental diseases;
- prevention of rickets and diseases of the bone system.
To make it easier for a child to follow preventive measures to prevent a violation, one should follow simple recommendations:
- , to obtain the necessary load, the child can be offered to bite hard apples, carrots or croutons;
- regularly drive a child to the dentist for preventive examination to detect any damage to the teeth in time.
It is impossible to cope with curvature of teeth on your own, therefore it is strongly recommended to consult a specialist for any degree of deviation.
An orthodontist will conduct a thorough examination, make an x-ray, examine the oral cavity and nerve endings. Further, depending on the degree of development of the anomaly, the specialist will prescribe the necessary treatment.
