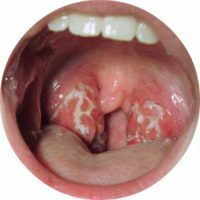
Adenoids in a child - excessive overgrowth of lymphoid tissue of the nasopharyngeal( pharyngeal) tonsil, which is accompanied by a violation of its protective function.
- Causes of
- Degrees
- Symptoms of
- Than
- is dangerous Diagnosis
- Treatment
- No operation
- Removal
- Physiotherapy
- Homeopathy
- Folk remedies
- Prevention
Pathology in children is at one of the top places among all disorders related to the upper respiratory tract. In 60-70% of the diagnosis of "adenoids" is placed at the age of 3 to 10 years;less often - up to 3 and over 10 years. Approximately from the age of 12 adenoid glandular tonsillitis begins to atrophy and completely disappears by 17-18 years. Rarely( less than 1%) pathology is detected in adults.
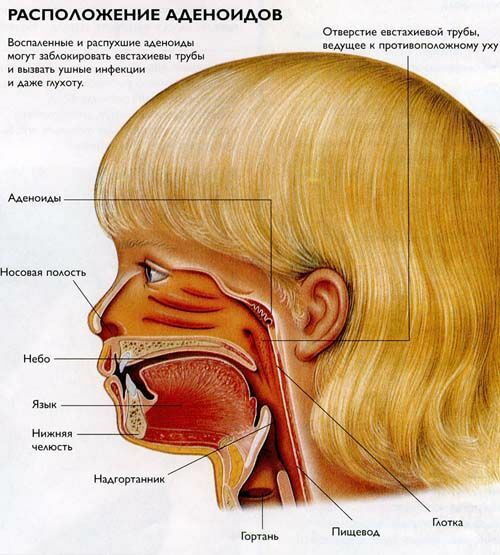
Pharynx( nasopharyngeal) tonsil is located near the artery of the pharynx, on the back and top wall of its nose. Together with other lymphoid clusters of the pharynx( palatine, lingual and tubal tonsils), the pharyngeal tonsil forms the Valdeier-Pirogov ring, which by a protective barrier stops the penetration of the infection into the body.
Normally this amygdala should be small in size and be defined as a small elevation under the pharyngeal mucosa.
Reasons for
Adult addiction in children is promoted by:
- Hereditary factors.
- Complicated during pregnancy. ARVI, transferred by the mother on terms up to 12 weeks, can provoke disorders of the development of internal tissues and organs, including lymphoid. To break the initial formation of the immune organ are able and medical drugs, which the future mother took on different terms of pregnancy.
- Frequent infections of the throat and nose cavity - laryngitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis. In children, many diseases of the oropharynx are provoked by a sharp violation of the microflora balance, when the number of beneficial bacteria decreases, and the number of opportunistic microorganisms increases. With a decrease in immunity, lymphoid tissue begins to expand in order to prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microflora and the spread of infection.
- Mechanical damage to the facial part of the skull during labor. Prolonged finding of the baby in the birth can lead to hypoxia, that is, the lack of oxygen in the body. This, in turn, significantly reduces the body's defenses and increases its susceptibility to any infectious diseases.
- Lymphatic diathesis is an individual feature of the child, which increases the predisposition to the growth of tonsils.
Degrees
- Stage 1 is a slight overgrowth that closes 1/4 of the lumen of the nasal passages. It is characterized by superficial breathing through the mouth.
- 2 stage - sprouting closes 2/3 of the nasal passages. Difficulty breathing not only through the nose, but also through the mouth, speech is broken, the hearing decreases slightly.
- Stage 3 - nasopharyngeal tonsil almost completely covers the nasal passages. Characterized by frequent otitis, a significant decrease in hearing, difficult swallowing.
Symptoms of
- Nasal breathing disorder. Due to the constant shortage of air, the child's mouth can be in a half-open state both during the day during wakefulness and at night. In this case, the lower lip hangs down and a characteristic "adenoid face" is formed, sometimes its structure changes.
- Snoring during sleep.
- Headaches.
- Hearing loss.
- Speech development delay. If the child is small, then he can start talking later than his peers. At children of the senior age the voice becomes nasal, its voicelessness vanishes.
- Lethargy, weakness.
- Nocturnal enuresis.
- Nocturnal coughing attacks, similar to asthmatic.
- With an exacerbation of the process, the temperature rises, with a burning sensation in the nasopharynx.
- Chronic rhinitis, not amenable to treatment.
- Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes.
- If the disease has passed to a chronic stage, then the following symptoms are observed:
- Frequent colds.
- Vomiting with purulent mucus after ingestion.
- Prolonged cough.
- Pain when swallowing.
- Difficulty breathing.
Than
is dangerous. The increased nasopharyngeal tonsil often becomes the cause of dangerous and severe consequences, as it lowers the immunity and disrupts the proper functioning of systems and organs.
The main complications of adenoids on the part of organs and systems are as follows:
- General symptomatology. Delay in physical development, insufficient weight gain, slower growth, anemia.
- Intellectual development. The development of speech is slow, the formation of correct articulation of speech is disrupted. Weakenedness, absent-mindedness, deterioration of concentration and memory are reflected in school performance. The child lags behind in mental development.
- Mental status. The patient exhibits irritability, apathy, tearfulness, increased fatigue, sleep is disturbed, neuroses appear.
- Immune system. Frequent colds and infectious pathologies are possible. In addition, there may be chronic inflammation( rhinitis, sinusitis, otitis media, tonsillitis, laryngotraheobronchitis).Later there is a tendency to allergic reactions.
- Sense organs. Decreased sense of smell, hearing, taste buds, possibly worse vision.
- Leather. Chronic irritation of the skin of the vestibule of the nasolabial region and nose.
- Teeth. Incorrect development of the upper incisors( project forward, located outside the row).Multiple caries is possible.
- Bone system. The formation of an irregular shape of the chest( "chicken breast") is characteristic. Changes occur with the bones of the facial part of the skull - often there is a defect in the Gothic sky, dysplasia of the jaw, curvature of the nasal septum, dentition.
- Gastrointestinal tract. Soreness during swallowing. Diseases of the stomach and esophagus.
Diagnosis
To determine the consistency and size of adenoids, and the degree of pathological vegetation, use:
- finger examination of the nasopharynx;
- endoscopy;
- posterior rhinoscopy;
- epifaringoscopy.
When viewed, adenoids are identified as pink colorations and soft consistency, having a wide base and irregular shape, located on the nasopharynx arch. The data of the instrumental study are confirmed by CT and side X-ray.
Laboratory diagnostics includes:
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- bakposev( smear) from the nasopharynx to the microflora and sensitivity to antibacterial drugs;
- study of immunoglobulin E;
- cytology of prints from the surface of the adenoid tissue;
- PCR and ELISA diagnostics for infections.
In addition, consultation is required:
- of an allergist-immunologist with assessment and staging of allergic skin tests;
- neurologist( necessary for children with epileptiform seizures and frequent headaches);
- endocrinologist( with signs of thymomegaly and hypothyroidism of the thyroid gland).
Treatment of
Depending on the stage of the pathology and its severity, treatment can be conservative or surgical.
to table of contents ^No operation
Conservative treatment is carried out at I-II degree of hypertrophy or impossibility of their surgical removal. It consists of taking medications that can prevent the growth of lymphoid tissue or reduce its size:
- Antiseptic medications for topical use - Protargol, Collargol, Sialor, Argolife. Drops contain silver particles, due to which the contamination of the tonsils by pathogenic microorganisms participating in the inflammatory process decreases. Symptomatic treatment includes washing the nasal cavity with saline solution( Humer, Aquamaris Baby, Dolphin and others), the use of antiseptics( Miramistin, Okomistin, Ophthalin, Malavit), vasoconstricting drops or sprays( Galazolin, Rinazolinum, Rinofluimucil, Vibrocilum, Nazivin and so on), glucocorticosteroids( Nazonex, Avamis, Flix, Desrinitis, Nazarel, Nasobek and so on), antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs( Isofra, Polidex with phenylephrine, Sofrax, Dioxydin and others).
- Antibacterial drugs. If a bacterial infection is detected, a broad spectrum of drugs is prescribed. Depending on the results of the analysis on the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics, the doctor can prescribe drugs of the penicillin group( Amoxicillin, Amoxicillin and others), macrolides( Sumamed, Azithromycin and so on), cephalosporins( Cefazolin, Cefalexin, etc.) and others.
- Antihistamines ( Aleron, Cetrin, Eden, Erius).Helps reduce edema of the nasal passages, the severity of inflammatory reactions, reduce the secretion of mucus, the allergic component of inflammation.
- Immunostimulating and immunomodulating medications increase local immunity and reduce the severity of inflammation in the amygdala. Immunal, Ribomunil, Cycloferon, Respibron, Polyoxidonium, Broncho-Vaxom, Derinat, IRS 19 and others.
- Inhalation by nebulizer is one of the best methods to reduce the inflammatory process, the procedures are shown in both exacerbation and during remission of the disease. Inhalation will help to eliminate swelling of tissues, stop inflammation, strengthen local immunity, normalize the outflow of blood and lymph, and stop coughing. Among the pharmacy drugs for the disease is most often recommended mineral water "Borjomi" and saline for inhalation nebulizer. In addition, the doctor can be prescribed: Lazolvan or Ambrobe for liquefaction of mucus;Derinat - as an immunomodulating drug, Pulmicort, Hydrocortisone - for the removal of edema and inflammation. It will also help to remove swelling and eliminate inflammation of Aminocaproic acid and Tonzylgon.
Removing
Surgery to remove adenoids in children is called adenotomy.
Main indications for operation:
- ineffectiveness of conservative techniques in adenoids II, hypertrophy of grade III;
- marked violation of nasal breathing;
- recurrent( chronic) adenoids;
- delayed breathing in sleep or sleep apnea syndrome;
- chronic otitis media, sinusitis, pharyngitis, pneumonia and others;
- maxillofacial deviations, provoked by enlarged adenoid tissue;
- is a cancerous tumor.
Contraindications to surgical intervention:
- bronchial asthma;
- blood disease;
- myocardial diseases.
Adenoidectomy is performed under local anesthesia or general anesthesia.
There are 4 main methods of surgical treatment:
- Removal with adenotom , a knife shaped like a ring. The disadvantages of this method are a strong bleeding during the operation and a poor view, because of which it is not always possible to remove the adenoid tissue qualitatively. If even a small part of the tissue is left, then there is the risk of its re-growth.
- Laser treatment. Instead of a knife, various lasers are used, selected depending on the complexity of the intervention. This method is considered high-precision and low-traumatic. Regeneration of tissues after surgery is faster.
- Endoscopic removal. The main advantages of the method are the visibility of the operating field.
- Cold-plasma method or cobulation. Advantages: painless, bloodless, reducing the risk of postoperative complications, careful removal of the overgrown tissue, rapid recovery after the intervention. The only negative is the high price.
In the postoperative period after removal:
- If necessary, the doctor prescribes vasoconstrictive and astringent drugs in the nose.
- It is necessary to observe a diet: to exclude hot, irritating mucous membrane, solid food.
- Pain in the throat during swallowing can last 3-5 days. To ease them, prescribed painkillers and anesthetic.
- For 7 days it is forbidden to take hot baths, visit the sauna, sauna pool, solarium, beach, gym.
- Possible increase in body temperature to 38 degrees. In this case, it is forbidden to take antipyretics, which include acetylsalicylic acid, since it can provoke bleeding.
- Vomiting with blood impurities is possible if the child swallows blood during a surgical procedure. For the same reason, there may be disorders of the stool.
- Special respiratory gymnastics is useful after removal, which the doctor will tell.
- Nasal congestion and nasal congestion appear due to swelling of the mucous membranes, which go through 7-10 days.
Physiotherapy
Adenoids in children in pediatrics also use methods of physiotherapy:
- UFO.
- Laser therapy.
- UHF on the nose area.
- Electrophoresis.
- EHF-therapy.
- Magnetotherapy.
- OKUF-therapy.
- Climatotherapy.
Physiotherapy methods have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect and reduce the common cold.
to the table of contents ^Homeopathy
Homeopathic remedies can improve the effectiveness of primary treatment methods at I and in part II stage, but they can not replace the drugs of official medicine.
At the initial stage of the pathology of homeopathy:
- optimizes tissue metabolism and biochemical reactions;
- strengthens local and general immunity;
- activates the body's resources to fight the disease;
- accelerates the process of tissue regeneration;
- reduces the number of respiratory diseases, including exacerbation of adenoiditis;
- improves the outflow of lymph, resulting in reduced edema, allergization and body contamination with toxins.
Most often in adenoids, children are prescribed the following remedies:
- Thuya oil for instillation into the nose.
- IOV-Kid( granules) with thuja, iodine, barberry and other components for oral administration.
- Euphorbium Compositum, Delufen is a nasal spray with herbal and mineral constituents.
- Lymphomyosot - drops for oral use.
- Cinnabsin - tablets for resorption.
These drugs help slow down the growth of adenoid tissue, remove swelling, stop the inflammation in the nasopharynx and drain the mucus down the back wall of the pharynx. The course of homeopathy therapy can be from 6 to 12 months.
to contents ^Folk remedies
As a complex treatment for the treatment of adenoids, prescriptions for traditional medicine can be used, but only with the permission of the doctor. Before using any product, it is necessary to rinse the nose with salt water.
- Aloe vera juice or Kalanchoe. Effective agent with bactericidal action, anti-edema and resorption effect, which is useful in acute and chronic phase of the disease. From the leaves of plants squeezed juice, which is buried in the nose for 5 drops for 2 months. Juice can wash the nose, diluting it with water in a proportion of 1: 3.On the day you need to do 2 washing procedures, the course - not less than 14 days.
- Sea buckthorn oil. Helps strengthen the vessels of the nose, reduce mucus secretion and resolve adenoid formations. The oil is used in its pure form, it is necessary to instill in each nostril 3 drops 2 times a day for 21 days. In the acute phase of adenoiditis, the following recipe is recommended: squeeze juice from garlic, add 3 drops of garlic juice to 1 teaspoon of oil and stir. With a mixture of burying the nose 2 drops 4 times a day until the symptoms are eliminated.
- Beet and honey. It takes 1 part of natural honey and 2 parts of fresh beet juice. Ingredients carefully mix and bury in each nostril for 5 drops to 4 times a day for 15-20 days. The mixture should not be kept in the cold for more than 2 days.
- Eucalyptus leaves have vasoconstrictive and bactericidal action.2 tablespoons of raw material pour 500 milliliters of boiling water and insist in a thermos for about 2 hours. Water infusion is followed by gargle rinsing after eating three times a day. Before rinsing it must be diluted with hot water. The product should not be stored in the refrigerator for more than 2 days.
- Purity. The plant is effective in the complex treatment of adenoids.1 teaspoon dried herbs pour a glass of milk, boil, cool and strain. Decoction to dig in a nose on 2 drops in each nostril up to 5 times a day.
- Eucalyptus, chamomile and birch leaf. 1 tablespoon of eucalyptus leaves and chamomile flowers and 1 dessert spoonful of birch leaves to gently mix.1 tablespoon of herbal mixture pour 200 milliliters of boiling water and insist for about 1 hour. With a ready broth bury your nose 2 times a day in each nostril for 3 drops.
- Field horsetail. A fresh or dry plant is used to treat adenoids. It is necessary to pour 2 tablespoons of herbs with 350 milliliters of hot water, bring to a boil, warm in a water bath for 8-10 minutes, then insist 2 hours and take 100 milliliters 3 times a day for 10 days. Such therapy is contraindicated for children under 3 years.
- Propolis tincture. It is recommended to wash the nose with the product. In a glass with warm water, add ¼ teaspoon of soda and 20 drops of the ready-made pharmacy tincture of propolis, the resulting solution to wash the nose of the baby 2-3 times a day. For convenience, you can use a syringe or syringe.
Prevention of
To prevent the development of adenoids in children, following the following recommendations:
- Complete nutrition - a balanced intake of vitamins and minerals from vegetables and fruits into the children's organism will allow the immune system and ENT organs to develop properly.
- Early hardening - wiping the body( starting with the legs and handles) with a wet towel, contrast shower, frequent walks, airing the room.
- Complex and timely treatment of acute inflammatory diseases of the oropharynx and throat( pharyngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, rhinitis and so on).
- Treatment and preventive measures of chronic foci of infection in the nasopharynx of the child's relatives.
