 When treating stomatitis, antibiotics are not always used. Most often, the therapy is carried out with the help of local anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and wound-healing agents.
When treating stomatitis, antibiotics are not always used. Most often, the therapy is carried out with the help of local anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and wound-healing agents.
Antimicrobials are prescribed in certain cases, depending on the type and form of inflammation. Antibiotic can also be used in the treatment of major diseases that cause the appearance of stomatitis.
Contents of
- When is therapy supplemented with antibiotics?
- What is prescribed for adult patients?
- Amoxiclav - he is all familiar Ampicillin
- Medication with a broad profile of exposure Azithromycin
- Amoxicillin
- Sumamed for adults and children
- Augmentin - a modern replacement for Amoxiclav
- Clarithromycin
- Lincomycin - effectiveness proved!
- New generation antibiotic Kanamycin
- What is used to treat children?
- Precautions
In which cases is therapy supplemented with antibiotics?
Antibacterial drugs for the treatment of stomatitis are rarely used, and for many types of the disease, antibiotics are useless and even harmful. In some cases, stomatitis even develops after taking antibiotics, especially a similar situation in children.
For example, antibacterial agents provoke the development of a fungal infection.
The antibiotic is not effective, and it does not need to be prescribed for:
- viral and allergic stomatitis;
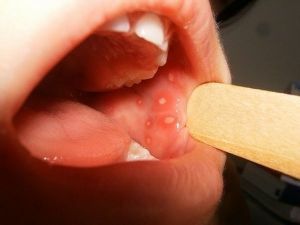
- candidiasis and aphthous form of inflammation;
- mucosal damage caused by injuries, cuts or burns.
Antibiotic therapy is carried out if any associated bacterial infections in the body are detected:
- ;
- blisters and sores with purulent contents;
- bacterial appearance of stomatitis;
- acute and severe forms of inflammation( ulcerative-necrotic).
In these cases, the use of an antibiotic is advisable and brings definite benefits. Antibacterial drugs are prescribed either orally, or in the form of ointments or powders locally, applying them directly to the affected mucosa.
For successful treatment with antibiotics, it is necessary to examine the culture from the oral cavity in order to identify the specific type of causative agent of the infection. Correctly selected drug acts narrowly, without disturbing the microflora.
What is prescribed for adult patients?
There are many varieties of antimicrobials. For the treatment of adult patients with bacterial stomatitis or with infection, the following antibiotics are prescribed as a concomitant problem.
Amoxiclav - he's all familiar Ampicillin
 This is an antibacterial combination. The basis of the drug is ampicillin, which refers to antibiotics of the penicillin series, which has a wide spectrum of action.
This is an antibacterial combination. The basis of the drug is ampicillin, which refers to antibiotics of the penicillin series, which has a wide spectrum of action.
The active substance acts depressingly on a number of bacteria, directly suppressing their synthesis. The clavulanic acid included in the composition ensures the stability of the drug to enzymes released by microorganisms to destroy the active components of the drug.
Medication is prescribed for adults and children when local therapy for stomatitis is ineffective. Dosages are as follows:
- adults 375 mg / 3 times daily;
- children( 7 - 12 years old) 250 mg / 3 times a day;
- children( up to 7 years) 125 mg / 3 times a day( syrup).
The course of treatment - 6 - 7 days. The medication is taken regardless of the food intake.
When taking medication, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and headache are possible. Contraindications - individual intolerance, severe liver and kidney damage.
Medication with a broad profile of exposure Azithromycin
This is an antibiotic from a new group of macrolides. Has a wide range of action. The composition of the drug includes azithromycin - a semi-synthetic representative of the group of azalides.
The principle of action is based on bacteriostatic action. It suppresses the growth and multiplication of bacteria. It has activity against streptococci, staphylococci and some anaerobic bacteria. The medicine is prescribed to adults: 2 times a day for 500 mg, taking it between meals. The duration of the course is 3 days. Children over 12 years - 250 mg / 2 times a day.
Amoxicillin
A penicillin antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action. It has good bioavailability. There is a destructive effect of  on bacterial walls. The active action begins 15 to 20 minutes after application and lasts up to 8 hours. The substance does not degrade in the acid of the stomach.
on bacterial walls. The active action begins 15 to 20 minutes after application and lasts up to 8 hours. The substance does not degrade in the acid of the stomach.
The drug is prescribed only for systemic action to stop the development of the underlying infection in the body.
The drug is used when local therapy for 5 to 7 days has been unsuccessful. The main therapeutic dose for adults is 1 tablet( 500 mg) / 3-4 times a day.
Sumamed for adults and children
 Antibiotic from the group of macrolides. The composition includes the azithromycin dihydride. The active effect is manifested in the suppression of the synthesis of bacteria. Has a wide range of action. Well absorbed, accumulating in the source of infection. Valid for a long time.
Antibiotic from the group of macrolides. The composition includes the azithromycin dihydride. The active effect is manifested in the suppression of the synthesis of bacteria. Has a wide range of action. Well absorbed, accumulating in the source of infection. Valid for a long time.
Antibiotic is prescribed for adults and children from 6 months with severe bacterial infections that provoke stomatitis.
The medication is taken in the form of tablets or a syrup suitable for children. The daily adult dose is 1 capsule( 500 mg), which is taken 1 hour before meals. Course - 3 days. Babies are prescribed a suspension, 10 mg / kg per kg, for 3 days.
Augmentin - a modern replacement for Amoxiclav
A drug based on a semisynthetic antibiotic from the genus penicillins. Has a pronounced disastrous effect on different microorganisms. It consists of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, has a mechanism of action similar to Amoxiclav.
For bacterial stomatitis, the drug is prescribed when the local treatment is unsuccessful. Take it in tablets, suspension or syrup. Can be prescribed to children after 12 years.
Does not require long-term treatment, appoint for a period of no more than 4 - 5 days. The medicine stops the inflammatory process in the first 3 days.
The exact dosage is selected by the doctor, based on the severity of the infection and the form of leakage. The usual dose with an average degree of disease is 1 tablet / 2 times a day. With a complicated infection - 1 tablet / 3 times a day.
Clarithromycin
Antimicrobial agent from the macrolide group. The composition includes active substance - clarithromycin, which has  bactericidal action on certain types of bacteria. It is characterized by good bioavailability and rapid absorption. The half-life is 4 to 6 hours.
bactericidal action on certain types of bacteria. It is characterized by good bioavailability and rapid absorption. The half-life is 4 to 6 hours.
Contraindicated in susceptibility to macrolides. Do not appoint children under 12 years. The drug is taken: adults - 500 mg / 2 times a day, with meals. Children after 12 years - 250 mg / 2 times a day. The duration of the course is 6 - 10 days.
Side effects are manifested mainly in disorders of the digestive tract, dizziness, insomnia.
Lincomycin - effectiveness is proven!
This is an effective antibiotic based on an active substance - lincomycin hydrochloride from the group of lincosamides. Has tropism to soft tissues. Good accumulation. It is indicated for purulent ulcers caused by bacterial stomatitis. Oppressing the development of gram-positive microorganisms sensitive to lincomycin.
The drug is prescribed to adults at 500 mg / 4 times a day. Children after 12 years - 500 mg / 3 times a day. The medicine is taken 1 to 2 hours before meals.
New generation antibiotic Kanamycin
 Antibacterial preparation of the first generation, consisting of a complex of three components of kanamycin. Has a high penetrating ability. Violating the structure of the protein of a microbial cell, causes her death.
Antibacterial preparation of the first generation, consisting of a complex of three components of kanamycin. Has a high penetrating ability. Violating the structure of the protein of a microbial cell, causes her death.
Is active against many kinds of bacteria. Apply in injections, intramuscularly. Assign only with obvious severe forms of bacterial infection. The dosage will be determined by the doctor.
What is used to treat children?
Treatment of antibiotics of stomatitis in children is carried out only in severe cases and strictly according to indications. Antimicrobials are prescribed in the case when bacterial stomatitis is detected, as well as when infection is attached to other forms of the disease.
Drugs are selected individually, depending on the type of pathogen. The doctor assesses the degree of inflammation, the nature and possible complications, then appoints an adequate treatment. The medicine is selected according to age. Effective and relatively safe antibiotics that can be used for children of children are: 
- Amoxicillin is a penicillin antimicrobial agent with a broad spectrum of action;
- Sumamed is a medicament based on azithromycin, which is well tolerated by children and does not have strong side effects;
- Augmentin - a strong antimicrobial drug that allows you to achieve a quick result, can be used at the age of 2 months.
All antibiotics intended for children are released in the form of syrups. They have a pleasant taste, which facilitates their reception.
Antimicrobials are used when there is no positive result from topical treatment with antibiotic-containing ointments. Treatment is carried out in conjunction with other ancillary drugs.
Precautions
In order for the treatment to yield positive results with the least side effects when taking antibiotics, certain rules must be observed:
- the kind of medication and treatment plan is chosen by the doctor only;
- course of therapy can not be interrupted, even after obvious improvements;
- it is necessary to strictly observe the prescribed dose without changing it on your own;
- combine the use of antibiotics with drugs that repair the intestinal microflora;
- take drugs with a prolonged period of action;
- use first local antimicrobial agents( ointments, powders, gels);
- should not be taken with antibiotics that reduce the effect of the antibiotic.
Any antibiotic has a dual effect, it brings both benefit and harm, you need to correctly assess the degree of need for its reception and whether it is necessary at all. Sometimes it is the only help in the fight against infection.
