In the article you will find information about the causes, symptoms and methods of treatment of esophageal spasm.
Contents
- Esophageal spasm: symptoms and causes
- Spasm of the esophagus: causes and symptoms
- Segmental spasm of the esophagus
- Spasm of the esophagus on nerves:
- symptoms Esophageal spasm on swallowing: symptoms
- Esophageal spasm of the esophagus: symptoms and causes
- Esophagus spasms in pregnancy:causes
- Spasm of the esophagus with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine: the causes of
- What to do with spasm of the esophagus, how to remove?
- How to remove spasm of the esophagus by folk remedies?
- Esophageal spasm: treatment
- Physiotherapy and massage
- Medication therapy
- Video: Esophageal diseases
The main function of the esophagus is to carry food from the oral cavity to the stomach. During normal operation, the smooth musculature of this organ is waved in a wave-like manner for the translational movement of the food lump.
Spasm of the esophagus - a disease in which there is a difficulty of peristalsis, food ingestion and pain signs of varying severity in the sternum. This condition is associated with the pathology of smooth muscle functioning, expressed in the involuntary painful contraction of the walls.
Esophageal spasm: symptoms and causes
Among the causes leading to esophageal spasm( esophagus), the main ones are:
- Hard, not sufficiently chewed, dry, too hot or cold food.
- Microtrauma walls, which can be formed as a result of damage by stiff food or foreign bodies.
- Alcoholic beverages of increased strength, which can lead to burn mucous.
- Food or chemical poisoning.
- Intercostal neuralgia associated with the work of the digestive system.
- Infectious diseases affecting the mucosa - acute bronchitis, influenza infections, measles, rubella, scarlet fever.
- Inflammatory processes in the internal organs near the esophagus.
- Ulcer of the stomach or duodenum,
stones in the gallbladder. - Gastroesophageal reflux pathology, one of the manifestations of which is the casting of stomach contents back into the cavity of the esophagus.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
- Overstrain, psycho-emotional stress and stress.
Spasms are more often fixed at the entrance or exit of the esophageal tube. These sites are equipped with a large number of nerve endings, so first of all they respond to malfunctions of the nervous system. The function of the sphincter of the esophagus is to prevent the ingress of unsuitable food, in connection with this there is a sharp reduction from contact with hot, acute or stiff food.
Pain symptoms can be acute - in the form of intense cutting pain or a feeling of "lump", compression and severity. The duration of the attack is from a couple of seconds to one hour.
 The main symptom of esophagospasm is chest pain
The main symptom of esophagospasm is chest pain The main symptoms of the attack are:
- Acute pains in the chest and area between the shoulder blades resembling the signs of angina pectoris.
- Pain of the compressive nature behind the sternum, which increases with exercise.
- Dysphagia is a difficulty in swallowing food, both solid and liquid.
The appearance of pain symptoms can be associated with the process of eating and active physical activity, and also arise in a state of rest and even sleep.
Diffusive spasm of the esophagus: causes and symptoms
Appears as a violation of esophagus motility - uncoordinated muscle contraction located along the entire length of the esophagus while maintaining the normal tone of the lower sphincter.
Symptoms expressed as:
- Intense pain in the sternum and the connection zone of the esophagus tube with the stomach. The pain sensation extends upward, it can cover the lower jaw and the shoulder girdle. A sharp pain attack is not associated with eating.
- Disturbance of swallowing, which is more pronounced when trying to swallow puree food or drinks than solid food.
- Regurgitation after cessation of muscle spasm.
- The attack can last from 2 to 3 minutes to several hours.
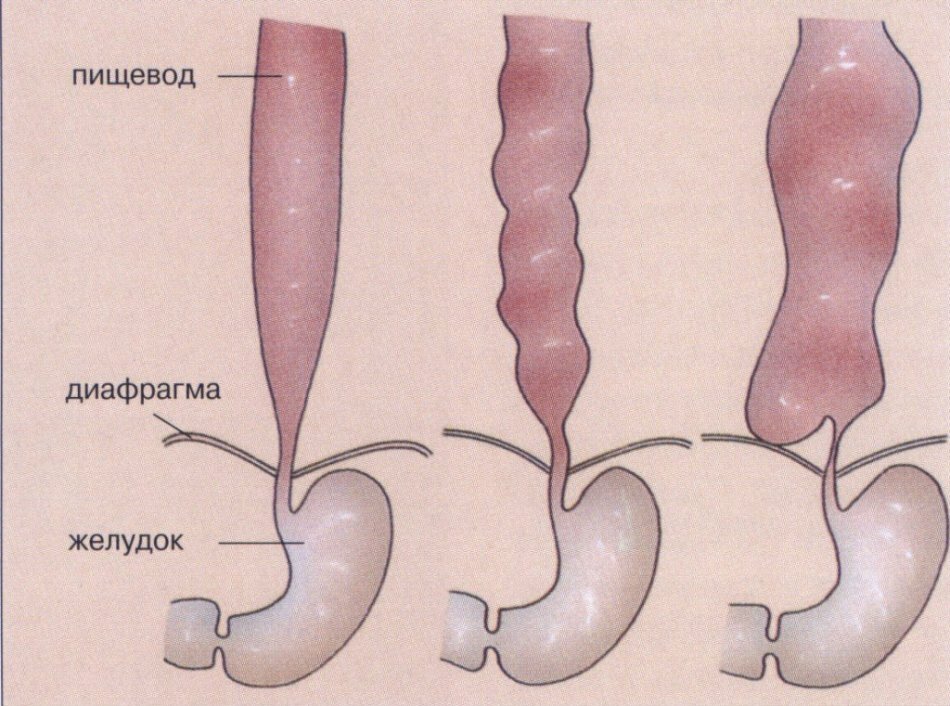 Esophageal deformation caused by spasm of muscle tissue
Esophageal deformation caused by spasm of muscle tissue Segmental spasm of the esophagus
With this type, muscle contractions occur in some areas of the esophageal cavity with high intensity. At the roentgenogram it is possible to see a modification of the esophageal tube like "rosary" or "nutcracker".
Main symptoms:
- Difficulty swallowing foods rich in fiber( vegetable, fruit, wholemeal bread) and soft foods( mashed potatoes, cereals, curds, yogurt).
- Appearance of dysphalgia during fluid intake.
- Pains are characterized as mild, spread in the lower segment, begin and subside gradually.
- Spasm lasts from a few seconds to 2 hours.
Spasm of the esophagus on the nerves: symptoms
In the case of neuromuscular spasm, a convulsive contraction of the smooth musculature of the esophageal cavity occurs.
The reasons for this violation are as follows:
- strong nervous overstrain
- anxiety, fear, sleep disturbance
- stress situations
- depression
Esophageal spasm when swallowing: symptoms
- Appearance of sharp compression of the esophagus muscles during eating.
- Delayed food lump in the cavity with subsequent urge to vomit.
- Difference in the appearance of vomiting - vomit contains undigested food, which did not have time to get into the stomach.
 Difficulty in swallowing with spasm of the esophagus
Difficulty in swallowing with spasm of the esophagus With pathologies of the nervous system and neurological disorders, the attack can develop regardless of the intake of food. The main symptoms are:
- The pains spread in the chest area, reminiscent of the heart.
- The intensity of pain varies from a feeling of slight constriction to acute burning or severe compression.
- Sometimes there are signs of suffocation.
- With neuroses, hysteria, panic attacks, there is a feeling of "coma" in the throat with the inability to swallow even saliva, indicating a reduction in the initial segments of the esophagus.
- Spasms and vomiting can be triggered by fright, anxiety, and abrupt sounds.
- Attacks happen short-term or last up to several hours with different intensity of painful sensations.
Cardiologic spasm of the esophagus: symptoms and causes
Cardiospasm is characterized by signs of widening of the esophageal tube throughout its extent with characteristic changes in its walls and is accompanied by a significant narrowing of the cardial segment. Various factors can serve as the reasons for this state.
- Internal causes include long-term spasms due to the development of peptic ulcer of the stomach or esophagus, traumatic lesions of the mucosa, the presence of tumor formations, toxic effects( alcohol, tobacco, vapors of poisonous substances).Stenosis of the esophagus can also be associated with inflammation of the mucosa in infectious diseases - typhus, tuberculosis, scarlet fever, syphilis.
- External factors are various diseases that cause pathological inflammatory processes near the diaphragm( pleurisy, aortic aneurysm, aortitis).
- Causes of cardiospasm can also be caused by disorders of the central nervous system that result from infectious diseases( poliomyelitis, meningoencephalitis, diphtheria) and intoxication of the body under the influence of certain substances( nicotine, lead, arsenic, carbon monoxide).
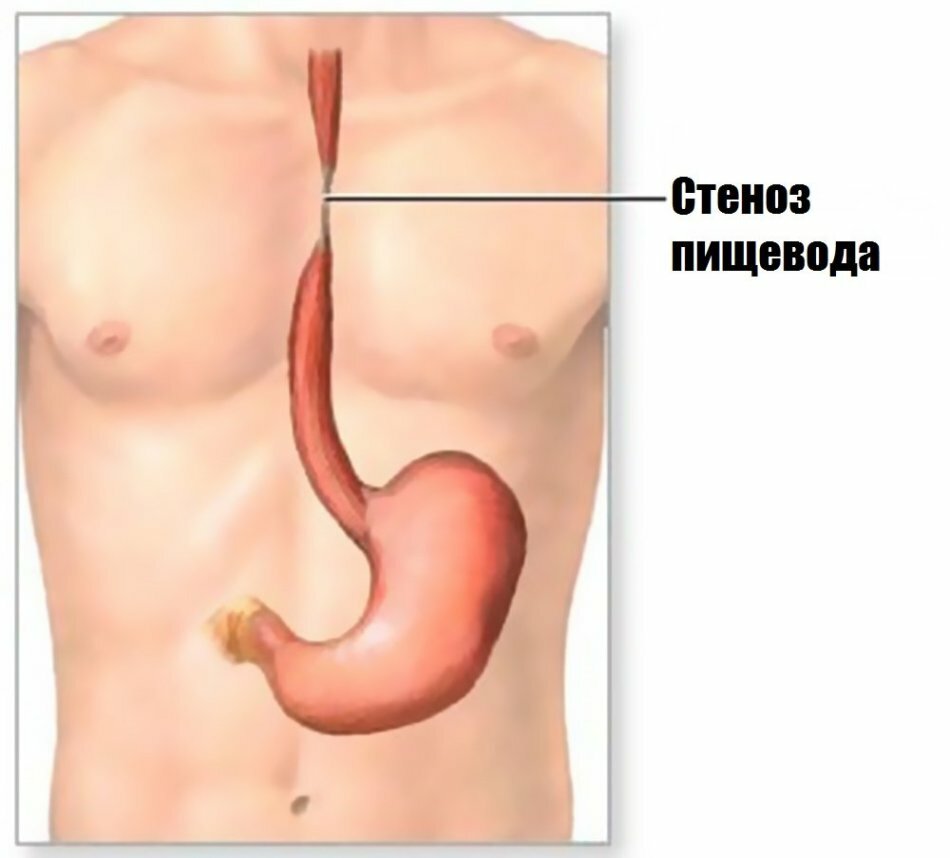 Esophageal constriction
Esophageal constriction Esophageal spasms in pregnancy: causes of
Esophagospasm in pregnancy is not always associated with a pathological lesion of the esophageal cavity. Most often, the causes are physiological and hormonal changes in the woman's body:
- The gradual increase in the size of the fetus puts pressure on the abdominal organs and sternum. As a result of compression of the digestive system, the contents of the stomach can be forced back into the esophagus, irritating its walls and causing stenosis.
- During pregnancy in the body of a future mother, the production of the hormone progesterone increases dramatically, which leads to muscle relaxation. Thus, the tone of the musculature of the sphincter of the esophagus is weakened, which allows the gastric juice to enter its cavity.
- Under the influence of hormones, the nervous system of a pregnant woman becomes more excitable, which can trigger spasmodic attacks.
 Spasms of the esophagus - a frequent phenomenon in pregnancy
Spasms of the esophagus - a frequent phenomenon in pregnancy Spasm of the esophagus with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine: causes
Spasms of the esophagus may be one of the symptoms of osteochondrosis. This type is called vertebrogenic esophagospasm and is observed with osteochondrosis of the thoracic or cervical spine due to infringement of nerve endings( radicular syndrome).
- Digestive organs, like other internal organs, depend on the spinal cord. By means of vegetative nerves there is a regulation of work of bodies.
- Symptoms caused by esophagospasm in osteochondrosis are sometimes difficult to distinguish from signs of other diseases. Diagnosis of this condition includes a number of examinations.
 Osteochondrosis can provoke convulsive muscle contraction of the esophagus
Osteochondrosis can provoke convulsive muscle contraction of the esophagus What should I do if I have esophageal spasm?
To help quickly remove the pain, you can do the following:
- During an attack, the patient is usually able to take a few sips of warm liquid - best of all milk, chamomile broth or mint. This will help the food to move forward, relieve acute pain.
- You can perform breathing exercises for Z-5 minutes: take a deep breath with abdominal breathing, count down to 5, hold breath for a couple of seconds and exhale slowly.
- A quick relaxing effect is provided by nitroglycerin, the tablet of which the patient must dissolve under the tongue.
- To remove muscular spasm will help the injection of the drug atropine( can be administered intravenously or intramuscularly).
 A few sips of warm drink will help to take off the attack
A few sips of warm drink will help to take off the attack How to remove spasm of the esophagus by folk remedies?
For repeated seizures, you can use home recipes:
- Prepare the broth by adding 1 gallon of water to 0.5 liters of water.a spoonful of flaxseed, 1 teaspoon of anise, 1 tbsp.spoon of natural honey. Bring the mixture to a boil, let it brew for 15 minutes, strain and take it warm 2 to 3 times a day.
- Boil 5 tbsp.spoons of dried leaves of plantain and 2 tbsp.spoon peppermint into 1 liter of water over low heat. Add 3 tbsp.spoons of honey and boil for another Z-5 minutes. Obtain the resulting broth and drink on an empty stomach for 1 tbsp.spoon.
- With neurological spasms, accompanied by insomnia, increased heart rate, a violation of the cardiac activity will help tinctures of valerian, motherwort or peony. These herbs have a mild sedative and spasmolytic effect. Dilute 15 drops of tincture of Valerian root or motherwort in a glass of warm water and take 100 ml of Z times a day for half an hour before meals. Dilute in 1 tbsp.spoon of warm water 10 drops of pion tincture and take Z times a day before meals.
- A good soothing and relaxing remedy are herbal baths - with decoction of pine or fir branches or gathering of herbs( motherwort, linden flowers, valerian, lemon balm).In addition, essential oils of ylang-ylang, tea tree, and orange can be used for 5-10 drops. The optimal duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes at a water temperature of 37-40 ° C.
 Herbal tinctures for calming the nervous system
Herbal tinctures for calming the nervous system Spasm of the esophagus: treatment
Folk methods are applicable if the seizures are caused by fatigue, fatigue or nervous breakdown. If the disease is chronic and caused by the presence of any pathology, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of the underlying disease, and adhere to a sparing diet.
Proper nutrition regimen plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of digestive tract diseases.
- Food should not irritate the esophagus and stomach mucosa - the basis of nutrition should include boiled, stewed or steam dishes of semi-liquid consistency. Take the food should be divided - 4-5 times a day in small portions. The last meal should be no later than 3 hours before bedtime.
- It is necessary to completely eliminate carbonated and alcohol-containing beverages, dark chocolate, strong coffee, fried, spicy and spicy dishes, salty and acidic foods, canned food and smoked products. Ensure that food and beverages are not too hot or cold, optimally at 36-38ºC or at room temperature.
Physiotherapy and massage
Methods of physiotherapy help to stabilize the nervous system, have a relaxing effect on muscle tissue.
In case of spasmodic attacks the following procedures are recommended:
- inductotherapy
- microwave therapy
- electrophoresis
- carbon dioxide, rhodonic baths
An important component of therapeutic therapy is physical activity. If you have sedentary work, you should take breaks every 2 hours and perform a 5-minute set of exercises to strengthen the spine and stabilize the functions of the central nervous system. In his spare time, walks, running, swimming, moderate power loads are recommended.
General massage will help restore normal muscle tone, relieve tension, will have an additional relaxing effect on the entire body.
 Exercise and respiratory gymnastics can help prevent esophageal spasms
Exercise and respiratory gymnastics can help prevent esophageal spasms Medical therapy
The medical treatment of esophagospasm is aimed at eliminating all the attendant symptoms and alleviating the general condition.
- To reduce the acidity of gastric juice, the following drugs are prescribed: Creon, Famotodine, Omeprazole.
- For the removal of spasms, suppression of nausea and the urge to vomit: Drotoverin, Cerucal.
- To protect mucous esophagus and stomach from irritation: Almagel, Rennie, Gastal.
The dosage of medications is prescribed by a doctor depending on the symptoms and causes of the esophageal dysfunction.
The following habits will help to reduce the frequency of attacks:
- sleep and rest on the high headrest
- refusal from alcohol and smoking
- weight loss
- development of correct posture( to prevent curvature of the esophagus)
The basic principles of treating a patient from spasm of the esophagus should include setting the right diagnosis anda combination of a set of procedures for successful therapy.
