What is appendicitis? What are the types of appendicitis? Symptoms of appendicitis in children, adults and pregnant women. Surgery to remove appendicitis.
Contents
- Causes of appendicitis development in adults and children
- Where is appendicitis, how does it look, from which side it hurts?
- Signs and symptoms of appendicitis in adult men and women
- Signs and symptoms of appendicitis in children and adolescents
- Signs and symptoms of appendicitis in pregnant
- Appendicitis chronic
- purulent appendicitis
- Acute phlegmonous appendicitis
- Gangrenous appendicitis
- operation to remove appendicitis: laparoscopic
- How long operationto remove appendicitis?
- What can I eat after the operation for appendicitis?
- How many are in the hospital with appendicitis?
- All about appendicitis: Video
The appendix is a process of the caecum. It is not known for certain why this strange education exists at all. Scientists suggest that the main function of the appendix is to protect the small intestine from harmful organisms that abound in the cecum.
Appendicitis, in turn, is the process of inflammation of this process of the cecum. This inflammation occurs quite often. The operation to remove the inflamed appendix is considered ordinary and fairly simple.
This article will be devoted entirely to the appendix, the causes of its inflammation, signs and symptoms, varieties, as well as the procedure for its removal and recovery period.
Causes of appendicitis development in adults and children
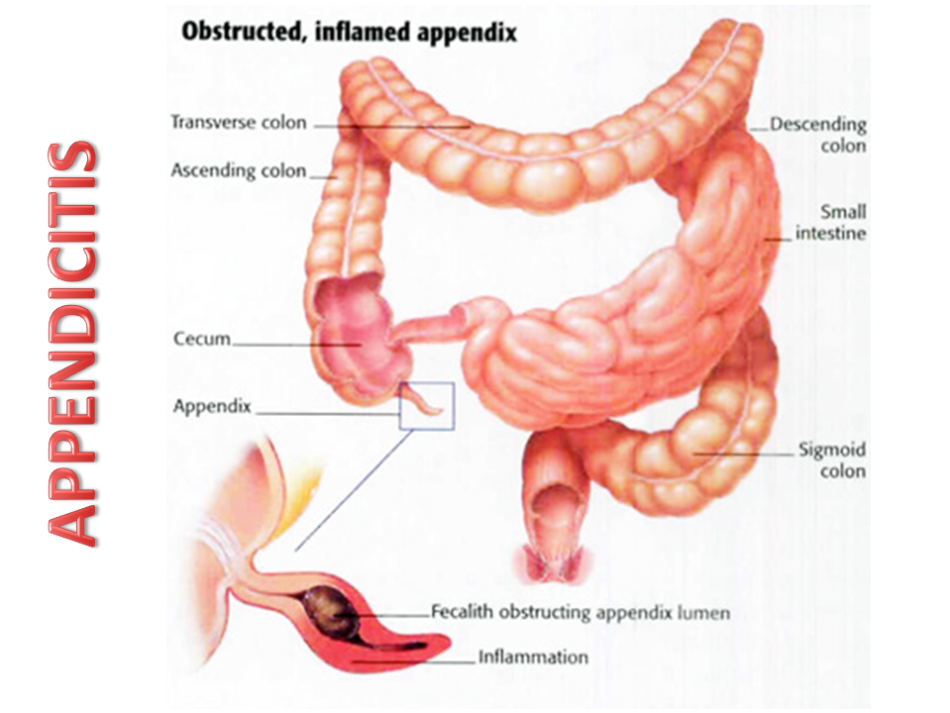 Causes of appendicitis in adults and children
Causes of appendicitis in adults and children It is difficult to name the true causes of appendicitis development in adults and children. There are several theories that try to explain the nature of the inflammation of the appendix:
The mechanical theory of for the development of appendicitis is based on occlusion of the appendix. In consequence of obstruction of the process of the cecum, inside it irreversible processes begin to occur - increased pressure, stagnation of capillary and venous blood, ischemia and activation of conditionally pathogenic flora. The following factors may provoke such a situation:
- parasites - a cluster of helminths( for example, ascarids) is able to clog the passage in the process of
- stool stones - characteristic of people aged
- enlargement of lymphoid follicles
- soldering
- foreign body( bones, seeds)
- scars
- tumors
The infectious theory of explains the appearance of appendicitis by the penetration of infectious agents into the intestine. To diseases that can provoke an inflammation of an appendix include tuberculosis, amebiosis, typhoid fever, etc.
The vascular theory of is based on the fact that frequent vascular diseases( systematic vasculitis) caused by a spasm of the blood vessels of the appendix can be the cause of appendicitis.
In addition to the above theories, the causes of appendicitis are also considered:
- Hereditary predisposition
- Improper diet - eating a large amount of meat can trigger an inflammation of the appendix;in people using fasting, appendicitis occurs less frequently
- Anatomical features of the appendix
- Clogging of arteries supplying the appendix
- Immune deficiency states provoked by lifestyle( stress, smoking, drinking alcohol, ecology)
- Infection from nearby genitaliawomen
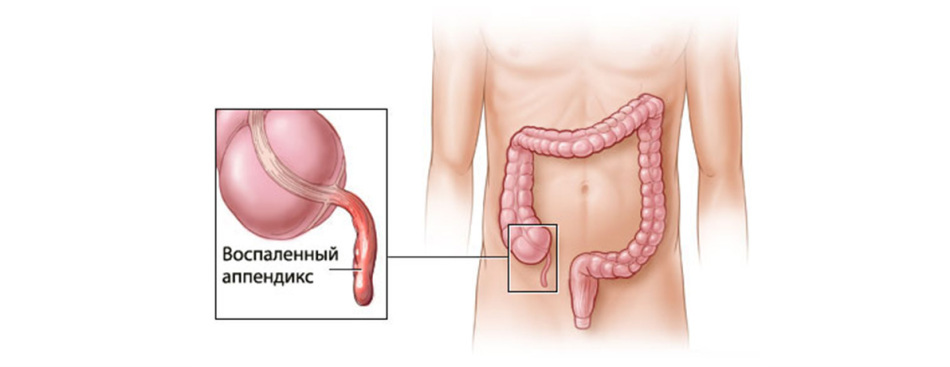
Where is appendicitis, how does it look, from which side it hurts?
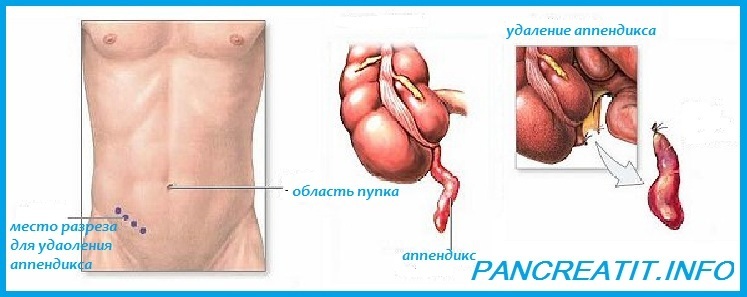 Where is appendicitis located?
Where is appendicitis located? - As described above, the appendix is a process of the cecum. It is located on its dome. The form of the appendix is vermiform. The length of the shoot is 3-5 cm at the birth of a man, and by the age of 10 it reaches 10 cm. The diameter of the appendix is 4-5mm
- The appendix consists of several balls of tissue - serous, muscular, submucosal and mucous
- The appendicular artery carries the necessary nutrition for the process and the outflow of venous blood.
- The appendix has two nervous plexuses - submucosal and muscular
- The appendix contains a largenumber of lymph nodes. This fact at least slightly explains the nature and purpose of this process
- Normally, the caecum with appendix should be located in the right ileal region. However, there are cases when their location absolutely does not meet the standards - the mirror arrangement of the organs. In addition, the appendix can be placed in any part of the intestine
- Appendicitis pain is most often localized on the right side of the abdomen
Signs and symptoms of appendicitis in adult men and women
 Symptoms of appendicitis in adults
Symptoms of appendicitis in adults The main signs of appendicitis in adults are:
- Pain:at first the pain is blunt and extends to the entire upper abdomen - it can be confused with pain in gastritis;over time, pain begins to localize clearly in the right ileal region;the pain gradually begins to increase;at movement, a cough, effort painful sensations can be felt more sharply;at a certain stage of the inflammation of the appendix, the pain can generally subside, which often leads to a late call to the doctor
- Nausea and vomiting. These two symptoms are of a reflex character and can only appear once in appendicitis. Moreover, emptying the stomach through vomiting will not bring the desired relief
- Lack of appetite
- Raise body temperature to 38 degrees
- Dry mouth
- Rapid heart rate
- Weakness and malaise
- Liquid stool
- Frequent urination
All of these symptoms are characteristic of the catarral stage of appendicitis that laststhe first twelve hours after the onset of inflammation.
Signs and symptoms of appendicitis in children and adolescents
 Signs of appendicitis in children and adolescents
Signs of appendicitis in children and adolescents Symptoms of inflammation of the appendix in children include the following symptoms:
- Pain: the pain is localized in the navel and has a spasmodic, harsh character;after sharp jerks in the abdomen comes relief, but through time everything again repeats;To provoke pain can change the position of the body, walking, lying on the left side;with time, the pain moves to the area below the navel, closer to the right side of the
- Weakness
- Increased body temperature to 37-38 degrees, less often to 39 degrees( in some cases, the temperature increase as a symptom in children is generally absent)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Very rarely problems with stools( diarrhea or constipation)
Signs and symptoms of appendicitis in pregnant women
 Signs of appendicitis in pregnant women
Signs of appendicitis in pregnant women It is extremely difficult to diagnose appendicitis in pregnant women, as in her body there is a mass of variousProcesses that are similar to the symptoms of appendicitis. In addition, in the abdominal area, women in slavery may experience less intense pain because of the stretching of all of their muscles.
However, there are several main signs of appendicitis in pregnant women:
- Pain: the pain can spread throughout the stomach, and can be localized in the upper, lower right or left abdomen;when taking a lying position on the right side, the pain may become worse;over time, pain can completely move to the right iliac region
- Nausea and vomiting
- Frequent urges to urinate
- Increase in body temperature
Appendicitis chronic
 Chronic appendicitis
Chronic appendicitis Chronic appendicitis has recently been isolated in a separate form of appendicitis. This disease has a number of differences from acute or purulent appendicitis:
- Chronic appendicitis has mild symptoms
- Inflammation of the appendix can last for years
- To remove chronic appendicitis - not necessary
- To cause exacerbation of chronic appendicitis may non-observance of the
- diet Pain can occur only during palpation and pressingon the abdominal cavity
- Patients with chronic appendicitis often have constipation or diarrhea
Often doctors, so as not to wait suddenlyth appendicitis rupture and prolonged agony of the patient, offer to remove an inflamed appendix surgically. Such an operation is considered planned and the patient, as well as the surgeon, has the opportunity to prepare for it.
In some cases, it may be decided to fight with chronic appendicitis in a conservative way - taking antispasmodic medications, dieting, special physiotherapeutic manipulation, fighting with digestive disorders.
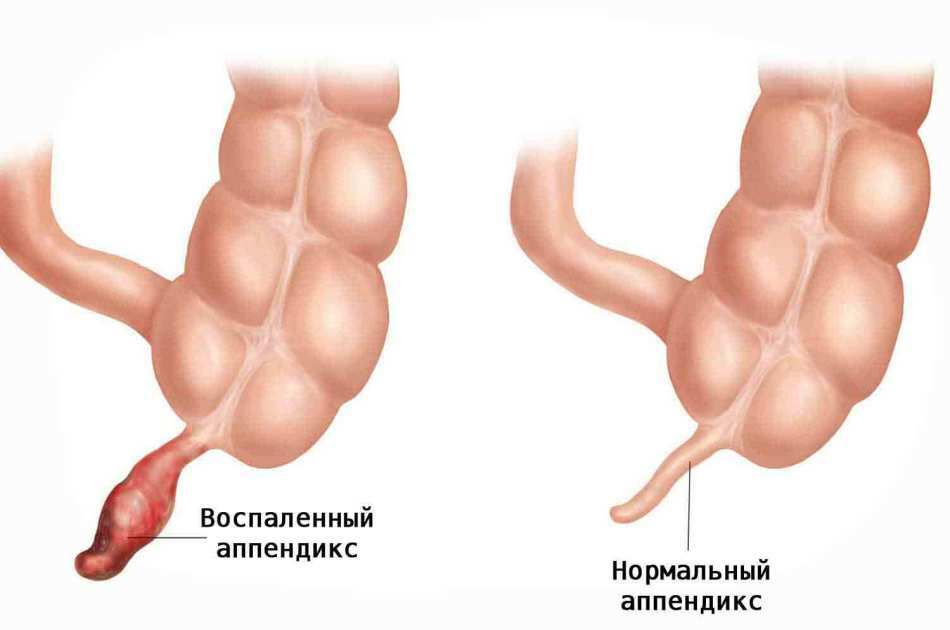
Purulent appendicitis
 Purulent appendicitis
Purulent appendicitis Acute appendicitis, i.e. acute inflammation of the appendix, has several stages:
- The appendix is the initial stage of appendicitis, which lasts up to six hours, and can as suddenly die out, as it appears
- Purulent appendicitis
- Gangrenousstage appendicitis
- Stage of appendix rupture
Purulent appendicitis occurs six hours after the onset of inflammation and lasts up to 24 hours. Purulent appendicitis is characterized by inflammation of the walls of the appendix and accumulation of pus inside it.
Because of the high concentration of pus and its spread throughout the appendage, the appendix starts to increase in size. This leads to an increase in pain in the second stage of appendicitis. In addition, the inflammation is also transferred to the peritoneum, because the pain sensations begin to localize clearly in the right ileal region.
Inflammation and the appearance of pus also can provoke the appearance of additional symptoms of appendicitis - fever, fever, weakness and nausea.
Acute phlegmonous appendicitis
 Acute phlegmonous appendicitis
Acute phlegmonous appendicitis Acute phlegmonous appendicitis is the third stage of appendicitis. This stage comes in a day after the onset of inflammation. It can last only a few hours. During this time, it is simply necessary to remove the ciliated process from the abdominal cavity.
General signs of phlegmonous appendicitis:
- Severe nausea
- Raise body temperature to above 38 degrees
- Severe pain in right side
- Rapid breathing
- Weakness
- Excessive sweating
- Peripheral wall of peritoneum
- Right iliac region somewhat lagging when breathing
- When palpating the right sidebelly pain intensified
The phlegmonous stage of appendicitis is extremely dangerous. Its consequences can be:
- Transplant of appendicitis to the gangrenous stage
- Rupture of the appendix
- Peritonitis
- Peliflebital veins of the liver
- Intestinal obstruction
- Appendicular infiltration
- Infection of the blood
Sometimes with phlegmonous appendicitis the pain subsides - this is the most dangerous condition, as it is deceptive. This phenomenon can delay the patient's treatment to the doctor and lead to the most disastrous consequences.
Gangrenous appendicitis
 Gangrenous appendicitis
Gangrenous appendicitis Gangrenous appendicitis is perhaps the most dangerous stage of appendicitis before the stage of rupture of the process. It comes on the second day after the onset of inflammation.
Gangrenous appendicitis is characterized by the death of tissues, vessels and nerve endings of the appendix. The dead cells of the appendage, along with the blood stream, begin to spread throughout the body of the patient, thus provoking severe intoxication.
It is the gangrenous appendicitis that often causes sepsis and septic thrombophlebitis. Tightening with the removal of the necrosis appendix may lead to its perforation and the ingestion of
pus into the peritoneum.
The main signs of gangrenous appendicitis are:
- Body temperature rise to maximum values is 39-40 degrees( in some cases, the temperature remains normal)
- Significant decrease in pressure
- Heart rate increase
- Weakness
- Frequent vomiting that does not bring relief
- Body dehydration
- Pale skinintegument
- Dry gray
- Abdominal swelling and hardening
Sometimes pain, nausea and vomiting can disappear and a person feels an imaginary relief.
Surgery for appendicitis removal: laparoscopy
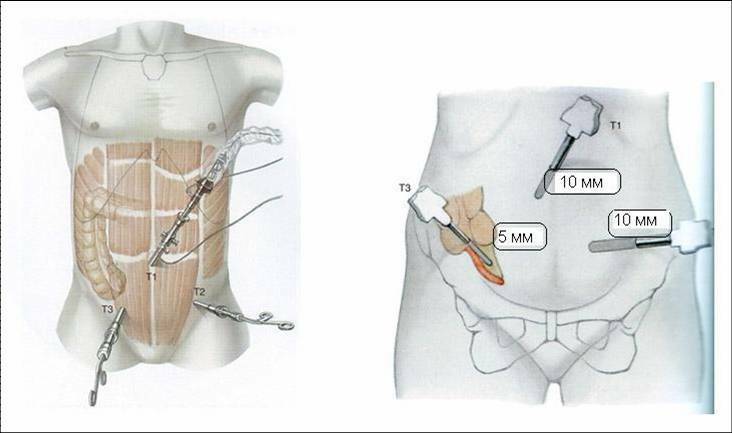 Removal of appendicitis with
Removal of appendicitis with laparoscopy Until recently, appendicitis was removed by the usual surgical procedure using a cut in the anterior part of the peritoneum. This surgery is called appendectomy. Apply it to this day.
However, in some cases, in order to avoid the formation of a rather noticeable scar on the abdomen and a quicker recovery, a new procedure for appendectomy - laparoscopy - is being used today.
The essence of laparoscopy is to remove the appendix by doing just two microscopic holes in the front of the abdomen. A chamber and a surgical instrument are inserted through these openings into the abdominal cavity.
Laparoscopy has several advantages over appendectomy:
- Short rehabilitation after operation
- More accelerated recovery of intestine
- No strong pain after procedure
- Short stay in hospital
- Aesthetic appearance of cuts
- Reduction in the number of complications after surgery
- The period of disability is several times shortened
RemovalThe appendix with laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia. Preparation for the operation takes no more than two hours. At this time, the patient is provided with antibacterial and analgesic therapy.
In cases with acute appendicitis, preparation is much faster.
As a rule, laparoscopy is indicated in the catarrhal, phlegmonous and purulent stage of appendicitis. In rare cases, gangrenous appendicitis is removed by laparoscopy. When ruptured appendicitis, peritonitis, or appendicular abscess, only an open operation is indicated.
How long does it take to remove appendicitis?
 How long does it take to remove appendicitis?
How long does it take to remove appendicitis? - Normally, the operation to remove appendicitis lasts up to 40 minutes - one hour. However, the surgeon will need this much time only if there were no consequences of appendicitis
- . In case of peritonitis or other complications, the operation for removal of appendicitis can last for more than two hours.
What can I eat after the operation for appendicitis?
 What can I eat after the operation to remove appendicitis?
What can I eat after the operation to remove appendicitis? - Recovery period after surgery for appendicitis removal can last from a week to three
- During the first 8-12 hours after surgery, the patient can not eat and drink - you can only wet your lips
- After this time, you can use only light liquid food - chicken broth, kissel, rice broth, tea with sugar
- On the second or third day the patient is allowed to switch to puree and porridge - potatoes, pumpkin, zucchini, rice
- The first week after surgery is the most ascetic. Of the permitted products - porridge on the water, dried fruits, cream soups, vegetable purees, low-fat fish, meat, dairy products. Prohibited foods are fatty, fried and sour food;milk products;foods rich in fiber;pickles, spices, spices;alcohol
- In the second week of rehabilitation, you can enrich your diet with the following products: mushrooms, casseroles, omelettes, beets, soups, puree without roasting. Prohibited at this stage products - mayonnaise, ketchup, sauce, bakery products, legumes
- You can consume baked goods and legumes only a month after the operation.
- . Ideally, you need to keep the indicated diet for up to three months.
How many are in the hospital with appendicitis?
 How long does it take to stay in the hospital after an operation to remove appendicitis?
How long does it take to stay in the hospital after an operation to remove appendicitis? - After removal of appendicitis by laparoscopy, the patient may stay in the hospital for about 3-5 days. Children are recommended to stay in the hospital for two to three weeks.
- When appendectomy, the postoperative sutures are removed on the tenth day, the subsequent finding of the patient in a hospital is regulated exclusively by the decision of the doctor
