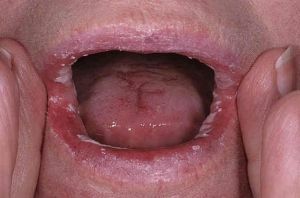
 Dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity is characterized by a change in the normal composition of the microflora in this zone. With a dysbiotic malfunction, harmful organisms begin to attack not only the mucous membranes, but also the bone component.
Dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity is characterized by a change in the normal composition of the microflora in this zone. With a dysbiotic malfunction, harmful organisms begin to attack not only the mucous membranes, but also the bone component.
As a result, the dentition loses its strength, and in the absence of treatment, an active destruction of tissues begins with the defeat of all structures of the oral cavity.
Dysbacteriosis is a violation of the balance between a conditional and pathogenic microflora, when harmful bacteria begin to predominate in a quantitative or qualitative composition, provoking a number of complications.
The growth of pathogenic microflora can be influenced by both external and internal factors. With dysbiosis, active reproduction of microorganisms of opportunistic flora leads to a decrease in the functionality and quantitative composition of bifidobacteria. In this case, representatives of pathogenic flora can produce without changes.
Contents
- Composition of microflora in the mouth
- Reasons for imbalance
- Features of the clinical picture
- Diagnostic criteria
- Treatment methods
- Possible consequences
- Preventative measures
Ingredients of the microflora in the mouth
The most common oral cavity bacteria are bacteria. They number more than 500 strains. In addition, the mucous inhabits protozoa, fungi and viruses. The number and composition of organisms of each human microflora is individual. All inmates of the oral cavity can be divided into 2 groups:
- An oblong or permanent environment .These bacteria are constantly in the mouth of a person. The most common lactobacilli, streptococci, staphylococci, prevotella, bacteroids.
- Optional or non-permanent microflora .Its penetration occurs during food intake, migration of organisms from the nasopharynx, intestines, skin. Typical representatives of this group are pseudomonas, E. coli, Klebsiella.
Causes of imbalance
Several factors, both external and internal, can lead to the development of oral dysbiosis:
- Digestive diseases .With a malfunction in the digestive system, metabolic processes in the body slow down, the absorption of nutrients is impaired. When the internal reserve is depleted, there is an imbalance of the bacterial environment of the intestine, which contributes to the development of dysbiosis in other departments.

- Rinsers for cleaning the oral cavity .Most often, these products include antiseptics and alcohol. These components contribute to the overdrying of the mucous membranes, which breaks their structure.
- The presence of bad habits .Smoking and taking alcoholic drinks affect the functioning of the salivary glands. As a result of prolonged drying or excessive moistening of the oral cavity, the microflora composition changes.
- Decreased immunity to .When the resistance of the organism decreases, it becomes vulnerable to pathogenic microflora.
- Presence of chronic diseases .If you do not deal with the treatment of existing ailments, the focus of the inflammatory process will gradually affect the neighboring organs. Especially if it is located in the oral cavity, for example, caries, stomatitis.
- Incorrect power supply .The lack of vitamins in the diet leads to vitamin deficiency.
- Taking certain medications .Basically, antibiotic and antiseptic agents affect the composition of microflora.

Features of the clinical picture
The appearance of certain symptoms depends on the degree of dysbiosis in the mouth. There are 4 stages of the disease:
- Latent phase .Dysbiotic shift is characterized by a slight change in the amount of one strain of pathogenic microorganisms. There is no symptomatology.
- The subcompensated stage of is characterized by a decrease in lactobacilli. Symptoms of the disease have a washed-out picture.
- Pathogenicity of monocultures .Lactobacilli are diagnosed in minimal quantity, the oral cavity is inhabited by an optional pathogenic environment. Symptoms of dysbiosis are clearly distinguishable.
- Decompensated form of the disease .In this stage, in addition to severe symptoms, yeast-like fungi grow.
The very first sign of the disease is the appearance of bad breath. Then there is an uncharacteristic taste and burning. To these symptoms, a violation of the salivary glands is added.
In a neglected state with a dysbacteriosis of the oral mucosa, symptoms are as follows: 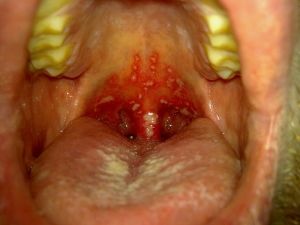
- inflammation of mucous membranes and gums;
- presence of plaque on the surface of the tongue and dentition;
- gum bleeding;
- the appearance of ulcers and vesicles, with a simultaneous increase in body temperature;
- swelling, flushing and soreness of the tongue;
- dryness of the skin of the face, in particular the zone near the lips. Characterized by the appearance of zaed in the corners of the mouth, peeling of nearby surfaces.
Diagnostic criteria
 The diagnosis of dysbacteriosis is often difficult, this is due to the lack of obvious manifestations at the initial stage of the disease and individual differences in the composition of the microflora of the oral cavity of each person. Nevertheless, if a dysbiosis is suspected, the dentist sends a smear from the surface of the mucous membranes or an analysis of the patient's saliva to a microbiological examination.
The diagnosis of dysbacteriosis is often difficult, this is due to the lack of obvious manifestations at the initial stage of the disease and individual differences in the composition of the microflora of the oral cavity of each person. Nevertheless, if a dysbiosis is suspected, the dentist sends a smear from the surface of the mucous membranes or an analysis of the patient's saliva to a microbiological examination.
Material is taken on an empty stomach. On the surface of the enamel there should be no food particles, otherwise the result of the study will be unreliable.
In addition, the patient must donate blood and urine. Additional examinations are appointed according to the testimony. Sometimes, several specialists are engaged in the further course of the disease. It can be a therapist, a gastroenterologist, an immunologist, a nutritionist, an infectious disease specialist.
Methods of therapy
Depending on the indices of examination and the nature of the pathogen, treatment of oral dysbiosis may include:
- Oral sanitation. In this case, it is necessary to remove tartar, seal all the diseased teeth, perform gum treatment and
 mucous membranes.
mucous membranes. - Reception of antiseptics, to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms.
- The use of immunostimulants. Such drugs contribute to strengthening the body's defenses.
- Purpose of probiotics. They restore the balance of beneficial bacteria.
- Admission of vitamin complexes is indicated for beriberi and for general strengthening of the body. Correct selection of appropriate components promotes cell regeneration, strengthening of bone tissue.
- Antifungal agents( with candidiasis) and antibiotics( only indicated for severe dysbiosis) are rarely prescribed.
In addition to taking the appropriate drugs to improve the effectiveness of therapy during treatment, it is recommended that the following rules be observed:
- to abandon bad habits: smoking and drinking;
- to refrain from oral sex;
- to revise the diet, paying special attention to products of plant origin;
- after each meal, you need to clean the oral cavity of the remnants of food.
The duration of treatment depends on the stage of the disease, the presence of foci of inflammation and the existing complications. On average, this period is 2-4 weeks.
Possible consequences of
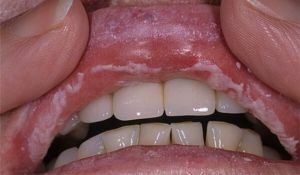 In the absence of timely adequate therapy, the patient begins the process of destruction of bone tissue, caries, pulpitis, cysts appear. Further, pathological changes affect the oral mucosa in the form of stomatitis and gingivitis.
In the absence of timely adequate therapy, the patient begins the process of destruction of bone tissue, caries, pulpitis, cysts appear. Further, pathological changes affect the oral mucosa in the form of stomatitis and gingivitis.
The gums, losing their protective functions, begin to bleed and become inflamed, which is caused by the influence of periodontitis and periodontitis. When a fungal carrier penetrates, candidiasis occurs.
All these pathological changes lead to an early loss of the dentition. In addition to inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, the infection can spread to other parts of the body: the nasopharynx and the gastrointestinal tract, causing various diseases of internal organs.
Preventive measures
To avoid dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity and its complications, it is not enough simply to clean the oral cavity twice a day. To solve the problem it is necessary to approach in a complex way:
- it is necessary to compose a ration of nutrition competently, avoiding forbidden products that destroy the protective shell of mucous membranes;
- is timely to treat internal diseases, any inflammatory process in the body affects the human immune system, which leads to a decrease in resistance to pathogenic microflora;
- should periodically take vitamin complexes;
- is recommended to stop using alcohol and tobacco.
The appearance of dysbiosis in the oral cavity adversely affects the condition of mucous and bone tissue of the dentition. In the absence of proper treatment, you can quickly lose a beautiful and snow-white smile.
