Hyperplasia is a disease characterized by the proliferation of uterine tissues. This process can lead to many undesirable consequences, including cancer.
Contents of
- What is endometrial hyperplasia?
- Endometrial hyperplasia
- Endometrial hyperplasia symptoms and causes
- Uterine hyperplasia: glandular, cystic, atypical, in menopause
- Endometrial thickness in endometrial hyperplasia
- Endometrial hyperplasia treatment without curettage
- Endometrial hyperplasia
- Video: Endometrial hysteroscopy of the uterus with hyperplasia
- Hyperplasia of the endometrium treatment after scraping
- What is dangerous is endometrial hyperplasia, what are the consequences?
- Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia with folk remedies
- Monthly with endometrial hyperplasia
- Endometrial hyperplasia and pregnancy
- How to take dufaston with endometrial hyperplasia?
- Orgmetrium with endometrial hyperplasia
- Norcolut with endometrial hyperplasia
- Endometrial hyperplasia prophylaxis
- Endometrial hyperplasia:
- reviews Video: How to cure hyperplasia of the uterus easily
Women at any age are susceptible to gynecological diseases .Some of them can secretly flow to a neglected state and become a threat to the reproductive function of women and the even her life. In this article we will consider in more detail such a disease as endometrial hyperplasia and talk about the methods of its treatment.
What is endometrial hyperplasia?
Endometrial hyperplasia is a common disease that affects women of all ages.
 Endometrial tissue can undergo pathological changes in hyperplasia
Endometrial tissue can undergo pathological changes in hyperplasia Endometrium is a membrane covering the uterine cavity and is subject to changes depending on the woman's menstrual cycle. In the second phase of the cycle, the mucosal layer within the uterus expands, characterized by a more active blood circulation, and favorable conditions for the life-support of the embryo are created. In the absence of fertilization, the excess part of the mucous membrane is excreted by the body during menstruation.
If complete destruction does not occur, the endometrial layer expands due to the pathological of amplified multiplication of cells. This process leads to hyperplasia, that is, to an increase in tissues above the norm.
Video: Endometrial hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia symptoms and causes
In the early stages of the disease, the disease can be asymptomatic, which complicates timely diagnosis. Symptoms indicating hyperplasia:
- absence of pregnancy with regular sexual activity
- excretion between menstruation
- frequent delays of the monthly and following abundant discharge
- periodic pain in the groin
 Hyperplasia may be asymptomatic and may manifest itself as unpleasant symptoms
Hyperplasia may be asymptomatic and may manifest itself as unpleasant symptoms The cause of developmenthyperplasia is disruption of the hormonal background of caused by:
- elevated estrogen level
- puberty
- inflammation organin the urogenital system
- genital infections
- high blood sugar
- obesity hypertension
- incorrectly installed uterine spiral
- heredity
- surgery
The exact cause of the disease can be established only after the examination the doctor.
Uterine hyperplasia: glandular-cystic, focal, atypical, in menopause
Depending on the structure, such types of hyperplasia are distinguished:
- glandular-cystic , at which the endometrium thickens evenly. If there is an increase in only the glandular tissue, we are dealing with the most mild form of the disease - glandular hyperplasia. If bubbles filled with fluid( cysts) are formed, this is the development of the glandular-cystic species
- focal , characterized by uneven tissue thickening. Cells multiply more actively in a certain area. This hyperplasia is divided into a simple( increase in the volume of cells) and complex, in which foci with excess tissue serve as the basis for the emergence of single or multiple polyps
- atypical ( adenomatosis), which is the most dangerous form of the disease. The probability of degeneration into oncology is extremely high. The cells not only multiply intensely, but also mutate, changing their structure. Adenomatosis can develop in the functional and basal layers of the endometrium. With this variant of the disease, it is possible to remove the uterus
- endometrial hyperplasia in the menopause associated with the extinction of ovarian activity due to age, which leads to a strong restructuring of the body and hormonal imbalance
Endometrial thickness in endometrial hyperplasia
Ultrasound examines endometrial thickness measurements ,which are the criteria for diagnosis of the disease:
- the norm is the size of from 9 mm to 11 mm
- with the development of glandular hyperplasia thickness of uv up to 15 mm, sometimes up to 20 mm
- on the possible presence of a malignant tumor is indicated by a non-uniform structure of the mucosa thickness over 20 mm
 With hyperplasia, the thickness of the endometrium increases
With hyperplasia, the thickness of the endometrium increases Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia without curettage
At an early stage of development, the disease can be cured with conservative therapy withoutscraping.
Treatment with medicaments uses in such cases:
- early stage of
- disease adolescent period in
- patient is excluded the possibility of developing atypical cells
 Conservative treatment method includes treatment with hormonal drugs
Conservative treatment method includes treatment with hormonal drugs This method of treatment is based on in several stages:
- Stop bleeding by balancingbetween estrogens and gestagens. To cope with this task help oral contraceptives that suppress the activity of the ovaries. At the same time, anti-anemic therapy may be performed depending on the magnitude of blood loss
- Taking progesterone medications to suppress proliferation of endometrial tissue. At the same time, drugs aimed at normalizing the functioning of the autonomic and central nervous systems can be used. At the same stage, drugs for gonadotropin-releasing hormones
- are taken. After the main course of treatment, is prescribed an additional therapy, , aimed at restoring the normal functioning of the reproductive system.
Alternative therapies are:
- a special master swirl containing gestagens that exert local influence on the endometrial layer, gradually thinning it
- folk remedies
- homeopathy
Endometrial hyperplasia scraping
The scraping procedure is diagnostic and therapeutic. It is carried out by removing functional layer of the endometrium , which is then quickly restored. Materials removed from the uterus are sent for examination.
 Scraping is carried out with special devices
Scraping is carried out with special devices Indications for curettage:
- polyps in the uterine cavity
- remains of the fetal egg
- malignant tumors
- uterine bleeding
There are several ways of performing the procedure scraping:
- Blinded with the curette
Under general anesthesia. The doctor curette scraps the surface of the walls of the uterus. Reception of food and food before this operation is prohibited. After that, antibiotics and bleeding agents are prescribed.
- Hysteroscopy
Carried out using a small video camera - a hysteroscope. This is a more advanced type of cleaning, since good visibility is provided by means of an optical device inserted into the uterus. The advantage of this method is that the tissue scraping is performed more accurately by the , and at the same time the treatment of hyperplasia is directly performed. Hysteroscope allows you to control the thickness of the removed layer of epithelial tissue. In addition, the process of cleaning small areas is facilitated. In this case, the possibility of accidental tissue damage is practically excluded.
- Separate scraping
Performed in the same way as the above procedures. It differs only in the sequence of cleaning.
 Scraping is not performed during menstrual bleeding
Scraping is not performed during menstrual bleeding During menstrual scraping is not performed , because in the case of self-rejection of endometrial tissue, the results of laboratory tests during its study may be inaccurate.
The operation is performed by on any day of the cycle:
- for bleeding, the cause of which is not known to
- when the fetus
fades. This procedure can not be performed on under the following conditions:
- infectious diseases
- elevated leukocyte count
- inflammation of the genitourinary system
Video: Hysteroscopy of the endometrium of the uterushyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia treatment after scraping
After scraping procedure, the doctor prescribes medical treatment, which is directedto prevent recurrence of hyperplasia. The woman is prescribed hormonal drugs. Duration of the course - up to six months .In case of recurrence, resection of the endometrium is performed.
As a rule, the body of a woman is quickly restored after curettage. Initially, there are small discharge, which can be accompanied by spasmodic pain. The menstrual cycle is restored to within 4 months of .Monthly begins usually after a month.
 Menstruation resumes a month after scraping
Menstruation resumes a month after scraping For rapid recovery and prevention of complications in the first post-operation period:
- do not exercise physical activity
- do not go to sauna
- do not take hot baths
- exclude sexual contacts
- abstain from pregnancy for half a year
Reason for treatmentin the hospital serves:
- elevated temperature
- unpleasant odor of discharge
- absence of secretions
- poor health in general
What is the danger of endometrial hyperplasia, what are the consequences?
In the absence of proper treatment, hyperplasia leads to the following negative consequences for :
- the formation of adhesions
- infertility, since a fertilized egg can not catch on the uterine mucosa due to the altered structure of the endometrium. In addition, the formation of adhesions accompanying hyperplasia, reduces the patency of the tubes, and as a consequence, the ability to become pregnant. Also increases the risk of miscarriage
- menstrual irregularity
- anemia that acquires a chronic
- due to heavy bleeding can be converted to oncological form
 Hyperplasia can develop into cancer
Hyperplasia can develop into cancer Therefore, treatment should be taken very seriously and not let the disease run its course. This will help to avoid irreversible processes. It is necessary to be treated immediately after diagnosis.
Treatment of endometrial hyperplasia with folk remedies
Along with traditional methods in the treatment of hyperplasia, folk methods are also used. Such methods are shown only for the lungs, , the initial stages of the disease. The essence of the impact of folk remedies is that toxins are excreted from the body and this ensures the normal functioning of the cells. Non-traditional treatment has several advantages:
- no side effects
- positive tolerability
- possibility of long-term use without harm to health
 Treatment of hyperplasia folk remedies is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor
Treatment of hyperplasia folk remedies is carried out only under the supervision of a doctor
- is considered to be particularly effective:
- alcohol tinctures of medicinal herbs( hemlock, hog pork, pion)
- decoctions of herbs( roots of disco and burdock, plantain, nettle, calf's bark, cuffs)
- syringing with decoctions( celandine, fecessuits)
- use of gauze tampons with garlic
Remember that consultation with a doctor when using folk remedies is mandatory and self-medication is strictly prohibited!
Monthly for endometrial hyperplasia
How menstruation occurs is the main criterion for establishing the disease. All ladies know how they have menstruation, and what kind of discharge with good health. Deviation from the norm should alert the woman and is a signal to call a gynecologist.
 Menstrual discharge in hyperplasia may be different from "healthy"
Menstrual discharge in hyperplasia may be different from "healthy" discharge. The discharge pattern with monthly in case of endometrial hyperplasia may be different:
- scant discharge caused by uneven structure of endometrial changes
- Spotting between menstruations
- heavy discharge with clots and scrapsmucous membranes that often occur after the delay of menstruation
- no monthly, due to the imbalance of sex hormones
- youJelenia after having sex
These factors may be signs of disease development and requires a gynecological examination.
Endometrial hyperplasia and pregnancy
It should be noted that this disease is rare occurs in pregnant women. However, in modern medical practice, such cases are observed. As a rule, the mucosal hyperplasia is focal in this case.
Modern doctors oppose that a woman becomes pregnant with with such a diagnosis of , since the combination of hyperplasia with pregnancy increases the risk of accelerated conversion of benign formations into malignant, that is, cancer.
 Doctors do not recommend pregnancy with hyperplasia
Doctors do not recommend pregnancy with hyperplasia In addition, excessive proliferation of the mucosa inside the uterus adversely affects the fetus itself and can lead to various pathologies of its development. Therefore, pregnancy planning is recommended after treatment and subsequent rehabilitation.
After treatment of the glandular form of endometriosis , pregnancy often occurs without problems , because this is the easiest form. With atypical hyperplasia, the possibility of getting pregnant is complicated by the fact that the treatment requires much more time and effort. In addition, it is often necessary to remove the uterus, due to the lack of results after treatment with medications.
The woman's ability to conceive after treatment is affected by such factors:
- neglect of the disease
- form of hyperplasia
- result of the treatment process
- individual features of
How to take dufaston with endometrial hyperplasia?
Dufaston is a progestational drug that is used in the treatment of hyperplasia in the complex. The main substance is dydrogesterone, , which in its characteristics is similar to natural progesterone. This is the so-called "pure" gestagen, which is used to increase the amount of progesterone in a woman.
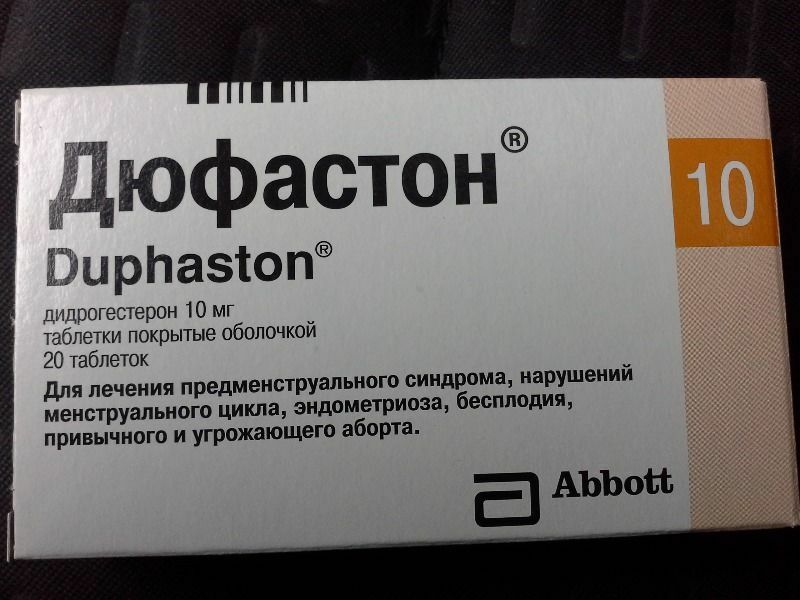 Dufaston with hyperplasia
Dufaston with hyperplasia The drug has proven its effectiveness in preventing endometrial overgrowth, cycle disorders, uterine bleeding. The schedule of taking the tablets is prescribed by the doctor individually. In the presence of bleeding, the dose may be increased.
At reception may occur side effects:
- spotting
- allergic reactions
- dizziness
- hypersensitivity breast
- chloasma
Contraindications to receive:
- intolerance dydrogesterone
- high sensitivity to dydrogesterone
Orgametril with endometrial hyperplasia
Orgametril - contraceptive having monogormonalnycharacter. The main active ingredient is linestrone. It has proven itself with hormonal therapy and is assigned as an aid to .It is especially effective in combating the atypical form and is often prescribed in malignant formations. The organometr is taken according to the scheme drawn up by the doctor.
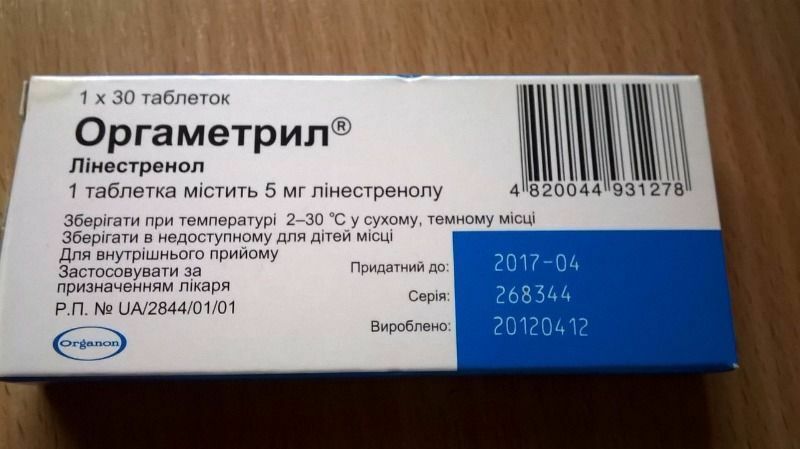 Orgametril hyperplasia
Orgametril hyperplasia Possible side effects:
- diarrhea
- headache
- decreased libido
- allergic reactions
- weight gain
- swelling
not assigned with such factors:
- idiosyncrasy
- jaundice
- disease
- liver diabetes
- disorders cholesterol
- thromboembolism
Norkolut with endometrial hyperplasia
Norkolut has an antiestrogenic effect, although it is not gestagenactive type. Active ingredient - norethisterone is a gestagen with the characteristics of estrogens and androgens. This drug is prescribed only after a complete examination of the patient for the presence of malignant tumors.
 Norkolut with hyperplasia
Norkolut with hyperplasia The duration of admission of Norcolut depends on:
- the nature of the
- pathology of the presence of bleeding
- of other factors.
Possible Side effects:
- Asthenia
- Headache
- Dyspepsia
- Changing structure of lipids
- Chloasma
Applying the drug is not recommended while taking:
- steroids
- drugs affecting the functioning of the kidneys, liver
- drugs that reduce sugar levels
Contraindications:
- the presence of malignant tumors
- the period of puberty
- polycystic ovary
- bronchial asthma
- blood clotting disorders
- epilepsy
Prophylaxis of endometrial hyperplasia
The main preventive method for preventing endometrial hyperplasia remains regular examination of a woman at a gynecologist. Everyone knows that it is necessary to visit a "female" doctor at least twice a year, but not everyone follows this rule.
 Regular examination of the gynecologist - the best prevention of hyperplasia
Regular examination of the gynecologist - the best prevention of hyperplasia In addition, doctors recommend such basic preventive measures:
- regularly undergo medical examination
- in time treat diseases of gynecological and hormonal nature
- watch your weight
- exercise
- avoid abortion, as they significantly increase the riskpathologies
- choose oral contraceptives, consulting a doctor
Endometrial hyperplasia: reviews
Many womenDoubts about the effectiveness of treatment. Some even fall into depression, believing that this is an incurable disease. Especially strongly worried about women, who plan to have a baby.
However, numerous reviews of women who have received treatment indicate that timely diagnosis and subsequent competent treatment of gives positive results to .Sometimes there are relapses, but in no case should not give up and stop treatment.
According to women, treatment with hormonal drugs helps not only stop the growth of the endometrial layer , but also normalizes the cycle, has a positive effect on the hormonal background.
Video: How to cure uterine hyperplasia easily
