What useful properties and contraindications does arachidonic acid have, in which products it contains, and in what cases is it recommended for admission? Read about this in our article.
Contents
- Arachidonic acid: benefit and harm, biological role
- Useful properties of arachidonic acid
- Side effects and contraindications
- Cycle, metabolism, synthesis of polyunsaturated arachidonic acid in the human body
- Biosynthesis
- Regulation of
- Metabolic disorder of arachidonic acid: body reaction, pseudoallergia, treatment of
- Where arachidonic acid is contained, what kind of food: table
- Video: Nutritionist Svetlana Kashitskaya: Salo with his small uselening is a useful product!
Polyunsaturated fatty acids have an active effect on the human body, participate in most metabolic processes, normalize the hormonal background, stimulate the growth and development of muscle and bone tissue, and help in the prevention of many diseases.
Arachidonic acid: benefit and harm, biological role
- Arachidonic acid is a group of omega-6 fatty acids and is widely known in the sports environment, as it is part of high-performance complexes for people engaged in intensive training - bodybuilders, bodybuilders, weightlifters. It helps quick recovery after strength training, increases endurance and strength of muscles.
- Arachidonic acid is an essential fatty acid. This designation implies that the human body is capable of producing the substance itself in quantities that are not sufficient for full provision. Therefore, it is necessary to fill the deficiency of acids from food products or using complex food additives.
- Arachidonic acid is considered one of the most important of the omega-6 group. The greatest concentration of this substance is observed in the tissues of the brain, liver, intestines, breast milk.
Useful properties of arachidonic acid
- Takes part in the process of constructing cell membranes of organs.
- Promotes development and restoration of skeletal muscle tissue in childhood and adolescence during a period of active growth.
- Responsible for the production of prostaglandins - substances involved in protein metabolism and providing elasticity and endurance of muscles. They regulate the contraction of muscle fibers and their further relaxation at the end of the load.
- Normalizes blood circulation, cardiovascular system, increases blood coagulability.
- Stabilizes the work of the central nervous system.
- Responsible for ensuring the full operation of the brain for large physical and psychoemotional loads. Helps prevent the development of such age-related diseases as dementia or Alzheimer's disease, slows down the aging process.
- Participates in the work of the kidneys, organs of the gastrointestinal tract, helping to protect the walls of the stomach and intestines from the corrosive effects of hydrochloric acid during digestion.
- Supports the suppression of inflammatory processes in the body.
- Influences the restoration and regeneration of skin.
- Along with other polyunsaturated fatty acids is part of the vitamin F, the beneficial properties of which are to strengthen bone tissue and immunity, regulate cholesterol metabolism.
- Arachidonic acid preparations are used as a remedy to relieve severe muscle pain.
 Arachidonic acid is recommended for intensive physical activities
Arachidonic acid is recommended for intensive physical activities Side effects and contraindications
Despite numerous useful properties, there are also contraindications to the administration of arachidonic acid. The expediency of using complexes containing this substance must be agreed with the attending physician.
- Side effects from taking can be fast fatigue, sleep disturbance, brittle nails and hair, increased cholesterol, arrhythmia, allergic reactions, depressive conditions.
- In high concentrations it is a very toxic substance and can cause severe poisoning, up to a lethal outcome.
In these cases, the reception of this substance is prohibited:
- hypertension
- acute heart failure
- cancer formation
- asthma
- elevated levels
- cholesterol pathology prostate
- pregnancy and lactation
 control over the content of arachidonic acid should be carried physician
control over the content of arachidonic acid should be carried physician cycle, metabolism, metabolism, the synthesis of polyunsaturated arachidonic acid in the human body
Biosynthesis
Linoleic acid - is indispensableThe omega-6 fatty acid is essential in the body for conversion to arachidonic acid. This process occurs under the influence of certain enzymes.
Arachidonic acid can be synthesized as an anadamide catabolite or when cannabinoids are destroyed.
Regulation of
It should be noted that according to studies, with age, there is a decrease in the human body and neurons( plasma membranes) of the level of arachidonic acid obtained with food.
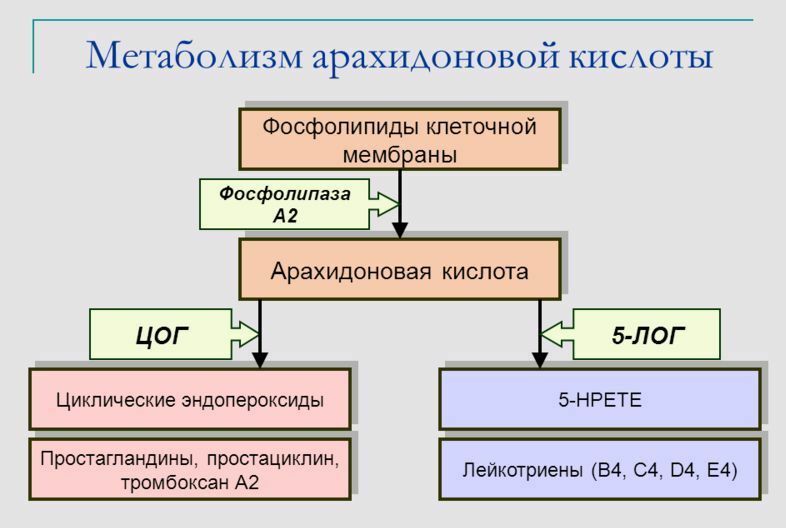 Diagram of arachidonic acid metabolism
Diagram of arachidonic acid metabolism Metabolic disorder of arachidonic acid: body reaction, pseudoallergia,
treatment Disruption of the metabolism of arachidonic acid leads to an allergic-type reaction - pseudoallergia.
- One of the main reasons is the intake of drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Among such analgesics, the greatest number of reactions was noted in connection with the intake of aspirin( acetylsalicylic acid).
- Symptomatic of the disorder may be different - skin manifestations, respiratory reaction, conjunctivitis, Quincke's edema.
- The clinical picture of pseudoallergic conditions is similar to the development of allergic diseases. Usually they are characterized by inflammatory processes, swelling, spasms of smooth muscles, destruction of blood cells.
- Processes can occur locally, affect individual organs or body systems. They are diagnosed by the regular appearance of rhinitis, dermatitis, edema, head and joint pain, impaired function of the gastrointestinal tract, development of signs of bronchial asthma.
Treatment of the patient consists in the establishment and elimination of the cause that caused the pseudoallergic reaction and is carried out strictly under the supervision of the doctor.
 Pseudoallergies in metabolic disorders
Pseudoallergies in metabolic disorders Where arachidonic acid is contained, which foods: table
The daily dose of polyunsaturated fatty acids omega-6 for an adult is 10 g, including 5 g of arachidonic acid.
The richest source is ordinary lard. Although the question of whether arachidonic acid is contained in lard fat, supporters of a healthy lifestyle give a positive response, do not try to recruit omega-6 from this product alone. After all for this purpose it is necessary to eat not less than 250-300 g of fat delicacy in day.
You can supplement the deficiency of arachidonic acid by adding the following products of animal origin to the diet:
- beef liver
- beef
- lamb kidney
- chicken thigh
- chicken or turkey breast
- fatty fish - salmon, trout
Omega-6 are also found in vegetable oils -sunflower, corn, linseed, soy.
 Fatty acid content in
Fatty acid content in Many people mistakenly believe that fatty acids are "useful fats" for the body. In fact, excessive consumption of animal products with a high fat content leads to a significant increase in body weight due to the increase in fat cells. Therefore, regular physical exertion is needed, burning excess fat and aimed at developing and strengthening muscle tissue.
