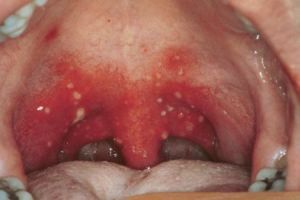
 The most common form of involvement of the oral mucosa is stomatitis. The wounds and ulcers that form in the throat cause severe discomfort and pain, especially during swallowing.
The most common form of involvement of the oral mucosa is stomatitis. The wounds and ulcers that form in the throat cause severe discomfort and pain, especially during swallowing.
Treatment of this pathology is difficult due to the location of the lesions.
Contents
- Provoking factors
- Types and symptoms of the disease
- Bacterial form
- Viral form
- Fungal form
- Diagnostic methods
- Methods of treatment
- Consequences and prevention
Provoking factors
Factors affecting the development of stomatitis in the throat are quite diverse. The most common causes of the disease are:
- receiving injuries to the oral mucosa, here include scratches from a hard toothbrush or dry food, thermal and chemical burns;
- inflammatory processes caused by pathogenic bacteria, viruses and fungi;
- hormonal imbalance;
- deficiency in the body of vitamins and trace elements;
- various diseases of the digestive system, HIV, development of tumoral neoplasms;
- allergic reaction to food, medical products, materials of dentures.
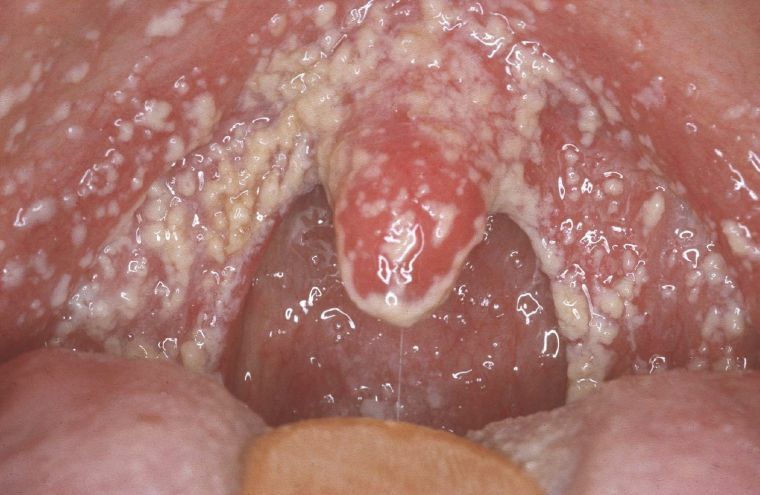
In the photo the curdled plaque in the throat, characteristic for candidal stomatitis
Types and symptoms of the disease
The occurrence of stomatitis in the throat is due to the atypical reaction of the immune system to stimuli, resulting in the formation of sores.
Therefore, the disease often manifests itself against the background of the infection in the body. In this regard, experts identify the following types of pathology.
Bacterial form
Most often the disease is provoked by staphylococci and streptococci. They live in the mouth with diseases of teeth and gums, tonsils and nasopharynx.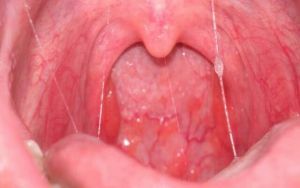
The inflammatory process also develops due to poor oral hygiene or angina.
Often, microbes fall on the wounds of the lips or skin of the face, and then move into the mouth.
Sometimes a dentist can infect an infection during treatment. The first manifestation of bacterial stomatitis in the throat are painful sensations when eating acidic or spicy foods. In the future, the problem area becomes saturated red, cracks and ulcers are formed, the salivary secretion increases, and an unpleasant odor from the mouth appears.
In the absence of timely treatment, soft tissues begin to die, body temperature rises, general weakness appears, severe sore throat, migraine.
Viral form
The herpes virus is considered to be quite common, once it has been ingested into the body, it remains there for life. The disease is transmitted by contact with the carrier of the infection.
The signs of pathology depend on the patient's age and the level of immunity. Often manifested such a stomatitis in the form of vesicles, localized in groups, reddening of the mucous membrane and the formation of wounds, increased lymph nodes, rapid fatigue, increased temperature.
The chronic form of the disease is expressed in frequent relapses. Children and pregnant women are at greatest risk of disease.
Fungal form
The most famous representative of this species of fungi is Candida. In small amounts, this fungus can be found in the body without causing harm. However, with a weakening of immunity, the use of hormonal drugs or antibiotics, it is 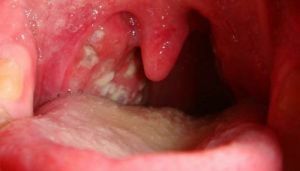 active growth. As a result, a white coating forms on the throat, sky and tongue.
active growth. As a result, a white coating forms on the throat, sky and tongue.
When it is removed, reddened and inflamed spots remain. The first sign of candidiasis is dysbiosis. The middle stage of the development of the disease is characterized by the presence of deposits, in appearance resembling cottage cheese. When the disease is neglected, a film is formed covering almost all soft tissues in the oral cavity.
Treatment can last from a week to a month. Young children tend during this period to refuse food, be irritable and nervous. To determine the exact type of the disease, it is necessary to undergo diagnostic procedures in a medical institution.
Diagnostic methods
When a patient visits a doctor, he examines the oral cavity, establishes symptoms, and specifies the timing of the illness. To determine the causes of throat stomatitis, it is necessary to find out whether the patient has allergic reactions, possible trauma or transferred infectious diseases, whether the rules of hygiene are regularly observed.
The severity of the disease depends on the number of ulcers and the area of the lesion. In medicine, there are no tests that confirm a certain type of stomatitis. However, to establish the diagnosis, it is enough to pass a number of laboratory tests:
- Blood test for glucose .This test allows you to identify diabetes, which can be a concomitant
 disease and increase the likelihood of developing stomatitis.
disease and increase the likelihood of developing stomatitis. - Analysis for bacterial culture .With its help, the type of infection in the body that causes the onset of the disease is established. This will help to prescribe the correct treatment and neutralize the pathogen.
- Polymerase chain reaction .It is an accurate diagnostic method that identifies types of sources of the disease, such as influenza and herpes viruses, varicella and enterovirus.
The physician should also conduct differential diagnosis to exclude similar types of diseases, such as shingles or candidiasis. Frequent relapses of stomatitis cause suspicion of HIV infection.
Treatment methods
If stomatitis occurs in the throat, treatment should be comprehensive and include:
- taking anti-inflammatory and analgesic medications;
- restriction of physical activity and overheating of the body, exclusion of hot baths;
- frequent drinking, including herbal tea;
- is an exception to the diet of sharp, acidic and hot dishes that promote irritation of the oral mucosa;
- regular rinsing of the throat with salt solution with the addition of iodine;
- with a severe course of the disease is an intravenous injection with an antibiotic.
Consequences and prevention of
 In the absence of adequate and timely treatment of stomatitis of the throat, the infection can spread to neighboring tissues, and even organs.
In the absence of adequate and timely treatment of stomatitis of the throat, the infection can spread to neighboring tissues, and even organs.
There is a high risk of blood poisoning. Inflammatory process promotes increase in body temperature and general weakening of the body. Bacteria that move to the gums may cause tissue death, tooth loss and destruction of the jawbone. The swelling of the throat and trachea leads to complicated breathing and asphyxia.
To prevent this disease,
- should be regularly cleaned and rinsed;
- systematically visit the dentist, in time to eliminate diseases of the teeth and gums;
- to avoid damage to the oral mucosa;
- does not contact with carriers of infection;
- refuse to eat food that causes an allergic reaction;
- not to allow the occurrence of stressful situations.
In addition, children and pregnant women should promptly treat various infectious and viral diseases, eat right and maintain immunity at a high level.
