The DTP vaccine is used to exclude the risk of contracting life-threatening infections: tetanus, pertussis, diphtheria. Many parents do not want to vaccinate their child, but doctors consider this vaccine to be the most important and necessary for immunizing children. Read more about DTP - decoding, from what and why do it?
- Decoding and composition
- Mechanism of Action What is the
- Types
- Vaccines
- DTP
- Bubo Kok
- Infanrix
- Infanrix IPV
- Infanrix HEXA
- Pentaxim
- Tetrakok
- Schedule
- vaccinations Preparation
- recommendations after
- vaccinations Where do
- Contraindications
- Side Effects and Complications of
- When Pregnant
Decoding and Composition
DTP contains components from 3 severe bacterial infections - diphtheria, whooping cough and tablewheatgrass. Therefore, its full decoding is an adsorbed( pure) pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus vaccine.
The composition of 1 milliliter DTP is approximately:
- 20 billion microbial pertussis cells;
- 10 anatoxin-uniting units of tetanus toxoid;
- 30 flocculating units of diphtheria toxoid.
Mechanism of action
The vaccine contains dead bacteria that, when ingested, induce an immune response: they activate the production of antibodies and resistance to diseases.
The immune response of the body to pertussis-diphtheria-tetanus toxoid is very strong, therefore it is the most serious vaccination in the schedule. After vaccination, approximately 94-97% of vaccinated children form antibodies to dangerous diseases.
to contents ^Why
- Pertussis .It is dangerous mainly for children up to 3-4 years. Very hard for children to 1 year. It affects the respiratory system and is characterized by a strong, dry cough, convulsive syndrome, often with pneumonia. At the beginning of the 20th century, whooping cough was one of the main causes of infant mortality.
- Tetanus .An infection that penetrates the body through wound injuries( burns, frostbite, splinters, prickles with plant thorns) of the skin. The disease primarily attacks the CNS, causes convulsive syndromes and leads to tonus every muscle of the body. The patient sweats, increases body temperature to 40 and above degrees, violates vital body functions( in particular, swallowing and respiratory), which threatens with coma and paralysis of the heart muscle. Without timely treatment, there is a risk of death.
- Diphtheria. Severe infectious inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. In the trachea and larynx, fibrinous films and effusions form which can lead to suffocation and death.
If the child is not vaccinated, the course of the disease and its consequences can not be predicted. The organism of the vaccinated child will not miss the disease or it will pass in a mild form and without complications.
Types of
In medicine, DTP vaccines are divided into 2 types:
- Whole-cell. The vaccine contains whole cells of dead viruses, bacteria containing an anatoxin. The vaccination is very difficult to tolerate and can cause side effects.
- Cell-free. Contains particles of dead viral, microbial organisms. This type of vaccine is weaker than the first and is used to vaccinate children whose health does not allow the use of a full-fledged formula.
Vaccines
In Russia, tetanus adsorbed DTP suspension produced by the company "NPO Microgen" is used most often for immunization. Demand for imported analogs is Infranix and Pentaxim.
to contents ^DTP
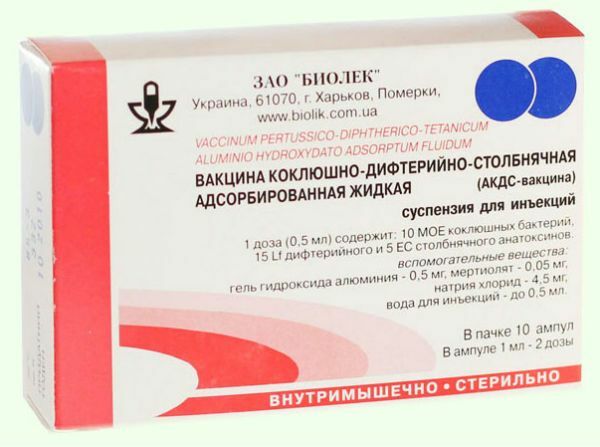
The whole-cell vaccine consists of 3 main components: tetanus toxoid toxicity, diphtheria and dead pectoral rod cells.
In addition, whole pertussis cells have a significant stress on immunity and the body as a whole, as a result of which children and adults with weak immunity can get sick or undergo post-vaccination reactions.
DTP of Russian or Ukrainian production is available in ampoules of 5 or 10 pieces in a carton. Each ampoule contains a single dose of the vaccine - 0.5 milliliters of the drug. In the kit there is an instruction for use and a tool for opening ampoules.
to table of contents ^Bubo-Kok

Combined vaccination consisting of hepatitis B pathogen antigen, dead pertussis pathogens, diphtheria and tetanus toxoid.
Infanrix
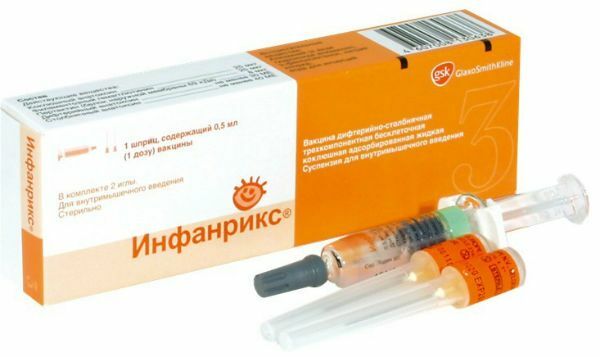
The most popular vaccine for children and adults produced by the Belgian company GlaxoSmithKline. From domestic differs cell-free manufacturing technology and the absence of merthiolate and formalin. This composition minimizes the possible consequences( puffiness, fever, convulsive syndromes, rashes and others).
The drug is available in special syringes complete with needles. Packing of syringes is hermetically sealed, which completely excludes the possibility of infection with non-sterile medinstrumentami.
Infanriks IPV
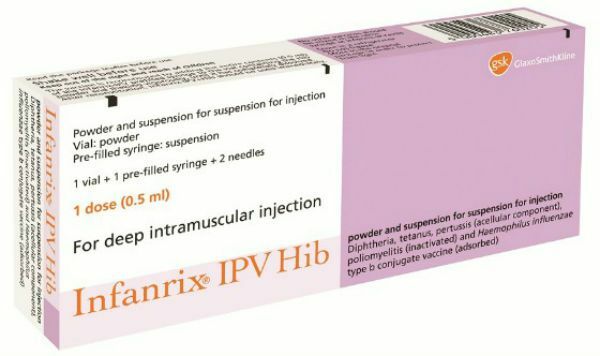
A variant of the complex Infanricks vaccine with the addition of a component against poliomyelitis for children from 2 months.
Infanriks IPV can also be used for revaccination.
Infanriex HEXA
The vaccine contains components against 6 diseases: tetanus, whooping cough, diphtheria, hemophilia, poliomyelitis and hepatitis B. Such a complex is very convenient because it is possible to confine one injection and not to worry about the interaction and qualityindividual preparations.
The antihepatitis substance in the package is kept dry and mixed in the same syringe with the main drug immediately before the injection.
to contents ^Pentaxim
A cell-free vaccine of French origin against 5 diseases: pertussis, tetanus, diphtheria, poliomyelitis and hemophilic infection. All components are already in the prepared form in the syringe.
Tetrakok
A complex whole-cell DTP containing an additional component of poliomyelitis. Packed in dosed, sealed syringes, 1 dose per package. It is considered one of the safest whole-cell vaccines and rarely provokes the development of complications. Country of origin - France.
to table of contents ^Schedule of vaccinations
All DPT vaccinations have a feature - after some time the immune defense gradually weakens and a revaccination is needed.
In the absence of contraindications, the vaccination schedule looks like this:
- I inoculation - 3 months;
- II inoculation - 4-5 months;
- III inoculation - 6 months.
The first 3 doses are recommended to be placed with an interval of not less than 30-45 days. With the introduction of the following doses, the allowed interval between injections should be 4 weeks.
- IV inoculation - 18 months;
- V inoculation - 6-7 years;
- VI inoculation - 14 years.
The vaccination should be carried out once every 10 years. If the schedule of vaccination is not respected, it is necessary to administer with the observance of the specified rule: 3 injections in 45 days, and the next not earlier than after 1 year.
to contents ^Preparation of
The vaccine has a strong strain on the body, therefore, before the procedure the child needs to be properly prepared in order to reduce the risk of complications after vaccination:
- Before immunization visit children's doctors, including a neurologist, as often the effects of DPT are observed in childrenwith violations of the central nervous system.
- Hand over general tests of urine and blood to make sure there are no pathologies that can complicate the condition of the child or adult after the injection.
- If a child has had an acute respiratory viral infection or other disease, after the illness should pass at least 2 weeks before the day of vaccination.
- For children prone to allergies, approximately 3 days before the procedure, it is necessary to start taking antihistamines( Claritin, Fenistil, Suprastin, Zirtek, Zodak and others).The medication should be continued for 3 days after vaccination.
- Immediately before immunization, you need to visit a pediatrician who will conduct an examination of the child and will give an opinion of whether it is possible to vaccinate.
Recommendations after vaccination
- If a child has a fever, he needs a bed rest, plenty of drink and febrifuge( Nurofen, Paracetamol, Cefekon D and others).Also help to ease the baby's state of the Viburkol candle. If the mercury column has exceeded the 39 degree mark, you need to call an ambulance.
- On the day of the procedure, it is advisable to refrain from bathing. In the first days it is advisable not to wet the injection site.
- If the baby has formed a seal in the area of the injection, the doctor may recommend that the Troxsevazine gel be applied on the swelling. The lump and seal should dissolve for 2 weeks.
- A child may feel pain in the leg where the injection was made. Sometimes because of this, the baby can begin to limp. To ease his condition will help applying ice to the area of the injection. If the pain does not last a long time, you need to contact the doctor.
- If the child has an allergic reaction in the form of a rash or urticaria, the reception of antihistamines( Eden, Claritin and others) is indicated.
Where to do
The vaccine is given intramuscularly, but if earlier injections were placed in the buttock, then the inoculation is done in the thigh. If you plant a child in the gluteus muscle, there is a high risk of suppuration, there is also the possibility that the medicine will enter the fatty layer and its effectiveness will be reduced to zero. The eldest children are placed in the upper part of the shoulder.
to table of contents ^Contraindications
There are temporary and general contraindications to vaccination with DTP vaccination.
The mediator for vaccination is placed at:
- violation of the CNS;
- afefrilnyh convulsions( provoked not by high temperature);
- severe reactions to previous vaccination;
- immunodeficiency;
- intolerance to any of the components of DTP.
Temporary contraindications to the procedure:
- encephalopathy;
- small weight;
- prematurity;
- diathesis.
With such diagnoses, it is allowed to do import vaccinations with a high degree of purification, but only when the child's health is normalized.
Also temporary contraindications are:
- infectious diseases;
- elevated temperature;
- exacerbation of chronic pathologies.
In this case, vaccination can be carried out 2 weeks after the child's recovery.
to table of contents ^Side effects and complications of
The effects of vaccination on average appear in 1/3 of patients, with most reactions occurring after the third vaccination, when the most intensive development of immunity occurs.
To normal reactions of the body to the prick, which take place 2-3 days after taking antiallergic and antipyretics, include:
- Behavior change. The child can become whiny, anxious and even start screaming. Such a reaction is due to pain after the injection. In other situations, the toddler, on the contrary, becomes lethargic and slightly inhibited.
- Temperature rise up to 38 degrees. To prevent her doctors recommend 2-3 hours after the procedure to give the child an antipyretic drug.
- Swelling and redness at the injection site. A normal reaction is an edema less than 4 centimeters and redness is not more than 7 centimeters in diameter.
- Allergic reaction( rash, urticaria), it is not dangerous for life and after a while will pass.
To side effects of moderate severity are:
- Increase in body temperature to 40 degrees and above.
- Edema and redness more than 4 and 7 centimeters in diameter.
- Diarrhea, repeated vomiting.
In these cases, seek medical attention.
The rare and most dangerous consequences are:
- Anaphylactic shock is a dangerous consequence that can occur 20-30 minutes after the injection. The first symptoms: noise, headache, itching of the skin, cold effusion, loss of consciousness;
- Acute Quincke - hives of enormous size, which is accompanied by swelling of subcutaneous fat and dermis, special fear causes swelling of the larynx. When it develops, emergency medical care is needed to avoid possible death.
- Violation of a neuralgic origin is a rare but dangerous complication that can lead to the death of nerve cells. It is characterized by high fever, convulsions, immobility, vomiting, an increase in coma.
In focal lesions of the brain, paresis of limbs, hyperkinesis, seizures, aphasia and cranial nerve damage may occur. If the child immediately after the vaccination shrieked began to cry, then its cause may be intracranial hypertension.
When pregnant
Women in the DTP do not.
