 Untimely treatment of caries can cause the development of various complications, one of which is flux. The second name of this disease is periostitis or inflammation of the periosteum.
Untimely treatment of caries can cause the development of various complications, one of which is flux. The second name of this disease is periostitis or inflammation of the periosteum.
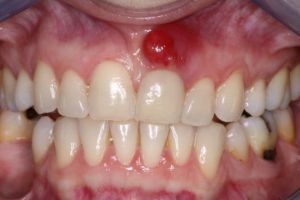
Flux is a powerful inflammatory process, the site of which is the root of the tooth. Such a pathological state of the oral cavity causes the appearance of a strong tumor of the gum at the site of the diseased tooth.
Contents
- How the disease develops
- Causes of the development of the pathology
- Clinical picture
- Approach to therapy
- Than it is dangerous?
How the disease develops
The main reason for the formation of flux on the cheek is the penetration of infection from the carious cavity into the pulp, and as a result of it becomes its strong inflammation.
Progression of the pathological process in the pulp is accompanied by the appearance of severe pain, but with the death of the pulp there is a significant reduction in pain. Such a phenomenon does not mean at all that the inflammatory process has died down, but its current has simply become a latent form.
The disappearance of pain in the area of the aching tooth leads to the fact that the patient is not in a hurry to seek help from a specialist and the result is a lack of effective treatment.
Gradually, the infection spreads to the root of the tooth and the inflammation develops in the jaw bone. The result is a congestion of a large amount of pus under the periosteum, which tries to come to the surface.
This pathological condition is called flux and, in the absence of effective treatment, many complications may develop.
Causes of the development of the pathology
Most often, the development of the flux occurs as a result of tooth decay, which was not cured in time.
This leads to the fact that the infection flows to the root of the tooth and causes the development of the inflammatory process in a number of located tissues.
After this, leukocytes, which are protective blood cells, flow to the source of the infection. There is a gradual withering away and the result is the formation of flux on the gum.
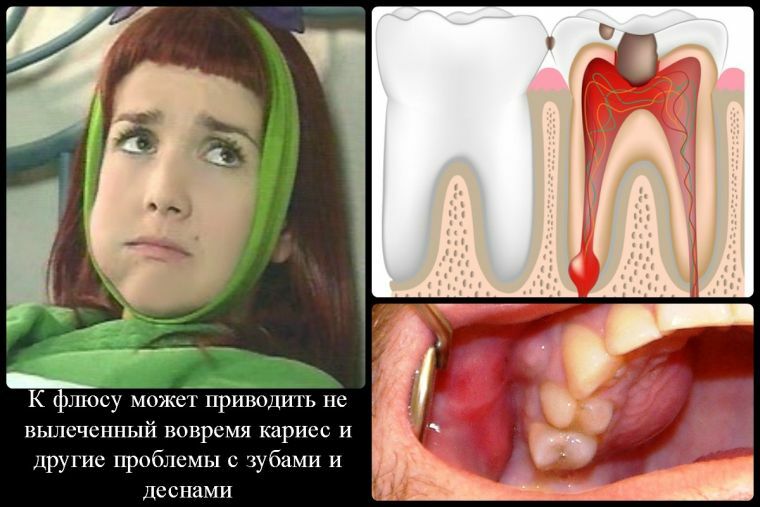
In addition, the development of dental flux may occur for the following reasons:
- Often the treatment of dental diseases is performed using anesthesia, which is injected into the gum. If the precautions of are not observed, penetration of pathogens into the gingiva of is possible, which leads to the development of a disorder.
- Non-compliance with the hygiene rules for the care of the oral cavity , and periodontal disease lead to the penetration of food and plaque residues into the gingival pocket. In addition, there is also the entry of pathogens into this area, which ends with the development of inflammation of the periosteum.
- Flux development can occur as a result of progression in the oral cavity of such a disease as angina .This pathology is accompanied by the accumulation of a large number of pathogenic microorganisms in the area of glands, and gradually the inflammatory process flows onto the periosteum.
- Various kinds of injuries and fractures of , which are accompanied by the development of the inflammatory process in the periosteum, can provoke the development of the disease.
- In some cases, the appearance on the gums even of a small scratch can become a breeding ground for bacteria and cause the formation of a flux.
The reasons for the development of periostitis are quite diverse, but the leading place among them is not caries that are cured in time.
Clinical picture of
The main symptom of the flux is a strong toothache, the location of which becomes the jaw.
Gradually, unpleasant feelings begin to occur in the neck and ear, and near the lesion there is a slight swelling in the form of a cone.
In addition, the acute shape of the flux is accompanied by the appearance of the following features: 
- pain enhancement when pressing or tapping on the tooth, which is located above the focus of inflammation;
- body temperature rise;
- staining the gums at the lesion in a bright red color;
- is a strong swelling of the cheeks;
- worsening the overall well-being of the patient.
Acute form of the disease is accompanied by a strong swelling of the gums, which can gradually pass to the upper lip and nasolabial fold.
In the event that the flux proceeds in a chronic form, the jawbone thickens over the diseased tooth. This form of pathology proceeds slowly, however, the inflammatory process gradually affects the gingival tissue.
Approach to therapy
Flux is a complex and dangerous disease, the consequences of which are very deplorable, its proper treatment should be carried out only under the supervision of a specialist.
It is important to understand that it is impossible to cure such pathology independently at home without qualified medical care.
If the infringement has caught the patient unexpectedly, and there is no possibility to seek help from a doctor, then treatment at home should consist of taking antibacterial drugs and painkillers.
 It is for this reason that when the first signs of the disease appear, seek help from a specialist.
It is for this reason that when the first signs of the disease appear, seek help from a specialist.
In the event that the inflammatory process has not yet gone too far, the treatment may be limited to the use of conservative therapy without surgical intervention.
The specialist will clean the tooth and seal or remove it. After this, a course of antibacterial drugs is usually prescribed, which can suppress the further spread of the inflammatory process.
If it is impossible to get rid of the flux with the help of medical treatment, an autopsy is performed with the release of accumulated pus.
If it is necessary to quickly close a section, drainage is inserted into it. After some time, the specialist conducts the treatment of the cavity with antiseptics and removes the drainage.
After such surgical intervention, the patient is prescribed the same tooth therapy as after the drug therapy.
Than it is dangerous?
Many patients mistakenly perceive the flux for ordinary toothache and hope that eventually it will subside.
This opinion is erroneous and, in the absence of necessary treatment, the pathology can be transferred to the chronic form of the flow, which significantly complicates its treatment.
Often, after the periostitis, various complications develop in which there is an outgrowth of pus from the inflammatory focus in the periosteum and spreading it to nearby tissues.
In the event that during this time will not be provided with medical care, this will cause the transition of the inflammatory process to the facial tissues. Gradually, the infection spreads throughout the body with the blood flow and the result is sepsis. 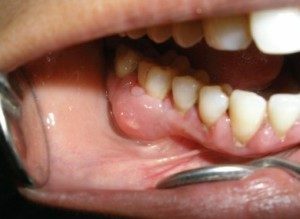
The defeat of the upper jaw can provoke the spread of inflammation to the meninges and the brain itself.
The most common complications after the flux are:
- abscess;
- phlegmon.
Periostitis gives a lot of anxiety and discomfort to its owner, therefore it is best to avoid the development of such pathology.
It is important to pay attention to the prevention of this disease and, above all, to observe the rules of hygiene in oral care.
It is necessary to visit the dentist for prevention at least twice a year, and also to treat various diseases of the oral cavity in time.
