
Almost every one of us at least once noticed that after a long reading, a long work at the computer or needlework, pain and burning in the eyes, temporarily deteriorating eyesight, the image becomes vague.
It is known that the intense tension of the eye muscles leads to their immobility and atrophy. Because of this, the natural mechanisms of focusing the eye on objects of the surrounding world located at different distances are violated.
These mechanisms are called accommodation of the eye, and failures in their work are violations of accommodation. In this article we will try to disassemble in detail the mechanism, how it works and what violations are possible.
- 1. How does it work?
- 2. Types of accommodation
- 3. Checking the accommodation of
- 4. Why is the accommodation disturbed?
- 5. What are the violations of accommodation?
- 6. Treatment of accommodation disorders
- 7. Prevention of accommodation disorders
- 8. Conclusion
- 9. Video
How does it work?
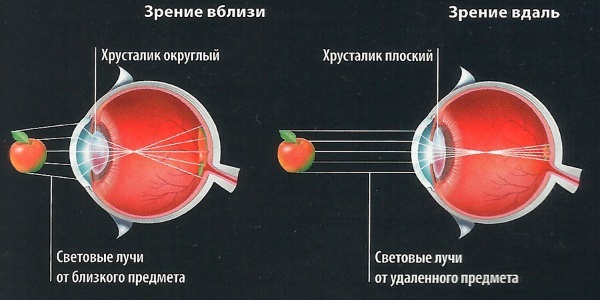
Accommodation - the ability of the human eye to refract light rays in such a way as to see equally well at both close and medium and long distances.
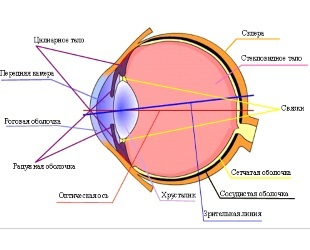
The accommodation unit incorporates 3 basic elements:
- Lens.
- Ciliary muscle. CINNOVA bunch.
If there is a need to view an object at close range, the ciliary muscle strains, and the zinnic ligament relaxes. At the same time, the lens is curved. When focusing on objects in the distance, the opposite happens: the ciliary muscle relaxes, and the lens becomes more flat.
The process of accommodation is controlled by the nervous system. For the ciliary muscle meets the parasympathetic department, and for the cynic ligament - sympathetic. This means that a person can not control this mechanism independently - all actions take place automatically, without our knowledge.
The distance between the nearest and furthest object, which can easily be considered by a person, is called the accommodation distance.
Types of accommodation

Absolute accommodation is a device for focusing at a certain distance, carried out by one eye without any second participation.
Relative accommodation - the process of adaptation, which is carried out by both eyes together with each other.
Reflective accommodation is an automatic refractive adjustment that supports the ability of the eye to see the surrounding objects without interruption.
Proximal accommodation is the adaptation process that is triggered if the object in question is approaching at least 2 meters.
Tonic accommodation is a process that occurs with an accommodative device in the absence of any stimulus.
Test of accommodation
To check if the accommodation process is normal, several tests and samples have been developed:
| Name | Description |
| Accomodation | This is a hardware method. The test is conducted on a special device, which is fully automated. The meter checks the adequacy of the accommodative response to artificially created stimuli. Accomodometry can evaluate the absolute and relative accommodation of |
| Proximetry | The test is also performed by an ophthalmologist using a ruler and a table for checking eyesight. It helps to determine the distance to the nearest object that the eye clearly sees. |
| Sivtsev's tables | The subject is given sheets with text written in small print. Then the doctor slowly begins to approach the sheets until the image is completely blurred. The distances from the eyes to the sheets are measured by the |
| ruler. The DuDan test | The nearest point of the vision is determined by approximating the figure drawn on the paper to the eye until the middle line of the figure is spread out. |
| Ergography | This method helps to determine how mobile the ciliary muscle |
| Biomicroscopy | The ocular bottomLooking through the slit lamp |
Why is the accommodation disturbed?
The process of accommodation of the eye can be disturbed both for natural and for pathological reasons. Natural causes of disorders of accommodation:
- is a natural aging process( after 45 years the lens tissue loses its elasticity.) The lens ceases to take the desired shape, and the light rays fall on the retina at the wrong angle);
- a disturbance of a diet( insufficiently diverse food causes deficiency of vitamins and microcells, and also protein, because of it there is a coarsening of a ciliary muscle);
- sedentary lifestyle( lack of physical activity leads to a violation of normal blood supply first in the cervical arteries, and then - in the vessels of the eyes);
- high load on the organs of vision;
- lack of sleep and rest.
To , the pathological causes of include:
- , traumas of the eyes and head;
- surgical interventions on vision in the past;
- chronic diseases associated with metabolic disorders;
- autoimmune processes;
- hemorrhage in the brain;
- volumetric neoplasms of the brain;
- vascular disorders;
- wearing incorrectly matched glasses or contact lenses.
What are the violations of accommodation?
We will dwell in detail on the main types of accommodation disorders that have the greatest clinical significance.
Spasm of accommodation - involuntary contraction of muscles responsible for focusing on near objects, even when there is no need for it. This condition is also called false myopia due to the complete similarity of symptoms. Unfortunately, without timely treatment, false myopia is transformed into a true one.
Spasm of accommodation is the second most common ophthalmic disease after myopia, and it accounts for about 20% of people who seek medical advice.80% of the sick are schoolchildren of junior and middle classes.
This is associated with both high eye strain in the school and with the physiological characteristics of the adolescent visual organs. The disease is treated medically and surgically.
Astromotion astenopia is a condition characterized by excessive ciliary muscle tension when trying to focus on nearby objects.
Violation is manifested by the inability to read text written in small print, constant headaches, noise in the ears, dizziness, accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
People suffering from astigmatism are most prone to this disruption of accommodation. Correction of the state is carried out by wearing special glasses.
The accommodation clock is accompanied by the inability to focus on closely located objects. When proximetry is detected, the nearest point of clear vision is too far away.
Paresis of accommodation develops due to the paresis of the ciliary muscle. Usually this disorder is associated with neophthalmological causes: brain trauma, voluminous formations, toxic poisoning.
Paralysis of accommodation occurs for the same reasons as paresis, but the ciliary muscle becomes completely immobile. Patients suffering from this form of the disease, completely lose the ability to read. Paresis and paralysis develop rapidly, and in the absence of treatment, normal vision becomes impossible to restore.
Presbyopia is a natural age-related disorder in the accommodation mechanism, which is also commonly called age-long-sightedness. Presbyopia develops because the lens loses its elasticity and can no longer project rays of light onto the retina. The age-related farsightedness is corrected by the selection of special contact lenses or glasses.
Treatment of accommodation disorders
In general, the treatment methods for all accommodation disorders can be divided into four main groups:
- spectacle correction( wearing individually selected glasses);
- lens correction( wearing individually selected contact lenses);
- laser microsurgery of the eye( change of the shape of the cornea by a beam of a medical laser);
- drug therapy( effective only in conjunction with other measures).
Prevention of accommodation disorders

To reduce the likelihood of the development of accommodation disorders, it is necessary to follow simple rules:
- perform work related to visual loads only in conditions of sufficient illumination;
- , during intensive visual work, take small breaks, do not overload your eyes;
- do special exercises to relax the eye muscles;
- wear only those glasses that are selected for on-site consultation by a qualified ophthalmologist;
- lead an active lifestyle, go in for sports, be out in the open air;
- discard bad habits;
- try to eat properly and in a balanced manner, replenish the vitamin deficiency with special complexes;
- undergo a preventive examination from an ophthalmologist at least once a year.
Conclusion
- Accommodation is one of the most important mechanisms of vision, allowing a person to see the objects of the surrounding world clearly and clearly.
- The accommodation process is triggered involuntarily, it is controlled by the nervous system.
- Visual and hardware techniques are used to diagnose disruption of accommodation.
- Disturbances in accommodation can lead to persistent deterioration of vision and a decrease in the quality of life.
- Preventative measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of the development of accommodation disorders.
Video
We present to your attention the following video:
