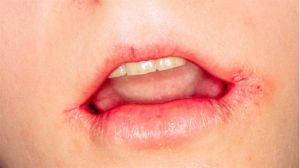
 Zaeda is an inflammatory process of the skin in the corners of the mouth and mucous membrane, caused by streptococci or yeast-like fungi of the Candida family, - candidamycotic jaeda.
Zaeda is an inflammatory process of the skin in the corners of the mouth and mucous membrane, caused by streptococci or yeast-like fungi of the Candida family, - candidamycotic jaeda.
Favorable environment for their development is:
- lack of vitamin B2;
- diabetes;
- maceration of the skin near the mouth and mucous saliva due to the formation of deep folds with a declining bite;
- continued therapy with antibiotics, cytostatics and corticosteroids.
Contents
- Ordinary blow
- Why jumping so love "children"
- Symptoms and Diagnosis
- A child needs help - everything is not that easy!
- First aid at home
- Further therapy
- Possible complications
- Prevention of violation
Oral shock
Features of development of the disorder depending on its kind:
- Streptococcal form - begins by forming a bubble in a corner with a thin coating, in a short period the bubble turns intoerosion of the slit-shaped form, which is covered by a purulent and bloody coating. When you try to remove the crust, a red surface is exposed with a crack in the center, after a couple of hours, the jaeda is covered again with plaque. This process causes small pain and burning sensation.
- Candidamycotic - has the form of red lacquer erosion with macerated epithelium. Sometimes the resulting grayish-white coating is easily removed. The cork is absent from the top and in general the formation is often masked under the wrinkles in the corner of the mouth. The disease can be chronic.
In the presence of syphilis, the area of erosion has seals, studies of the detachable tissue reveal pale treponemes and positive serological responses to the disease.
Why snacks so love the "children"
In children, jaunts occur mostly because of the pathogens that are always present on the skin - streptococci and fungal, but to start the inflammatory process there must be a push and this:
- dirty or strange dishes;

- unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- biting and licking of the lips, what often children do;
- poor oral care;
- squeezing pimples in adolescents;
- use of fluoride-containing toothpastes;
- combing the skin in the corner of the mouth;
- predisposition to colds and frequent hypothermia;
- in babies toys and pacifiers, on which remain the particles of dried saliva;
- poorly treated breast nipple;
- constant licking and biting of objects.
Many pediatricians agree that the cause of erosion is the lack of riboflavin, which is responsible for the growth of hair and nails, as well as the normal state of the skin. The impetus to fungus activity may be a decrease in immunity and certain diseases:
- chronic tonsillitis;
- caries;
- helminthic invasion;
- any of the types of cheilitis - angular, eczematous, exfoliative, stomatitis;
- liver pathology;
- diabetes mellitus;
- pathology of hematopoiesis;
- allergic reactions;
- is a chronic inflammation of the tonsils.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The first signal of the occurrence of a problem is the occurrence in the child in the corner of the mouth:
- a small bubble or papules;
- swelling and redness;
- after a certain period of formation bursts, and at this point there are microcracks, erosion and bloody discharge;
- the entire period of wound healing is accompanied by its ruptures and subsequent tightening, while the baby feels tolerable pain, burning, all this prevents talking and eating.
With these symptoms, you should act immediately, so as not to run the whole process, and the disease does not acquire a chronic stage.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to identify the etiology of the origin of formations and to help the child with drugs that do not cause 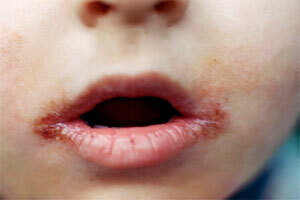 to allergic reactions. It is also important in the future to carry out prophylaxis in order to prevent new outbreaks.
to allergic reactions. It is also important in the future to carry out prophylaxis in order to prevent new outbreaks.
For the purpose of diagnosing snoring, a laboratory scraping from damaged tissues and the resulting fluid is taken to determine the type of pathogen.
In order not to be mistaken in the conclusions, since the seizure is externally very similar to herpes, additional studies are being performed:
- takes a smear from cracks and mucous mouth to identify herpes, yeast and streptococcal fungi, viruses;
- at certain times a blood test is done;
- also additionally conduct tests at the endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, pediatrician.
A child needs help - everything is not that simple!
During the treatment of seizures, it is necessary to fight the disease or factors that led to the formation of cracks, and not with the formations themselves.
The wound therapy in any case is associated with the cause of their development, it has a complex character and includes three types of effects:
- local;
- medication;
- restorative.
First aid at home
Than and how to quickly cure zaeda at the corners of the mouth in your child's parents at home, depending on the reasons that they are provoked:
- in children under 2 years of age when cheilitis , you must use a fatty infant creamor petroleum jelly, which protect the lips from the effects of saliva and painful manifestations;
- exfoliative type - softening creams, rosehip oil, retinol, wheat germ, tea tree oil;
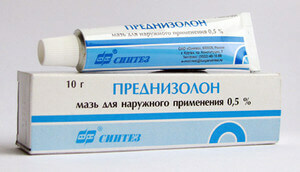
- eczematous - anti-inflammatory cream, prednisolone ointment;
- staphylococcal, streptococcal formations - ointments with antibiotics, hormones, combined antibacterial;
- mycotic - must be treated with local antifungal drugs.
It also follows from the first moments of the occurrence of wounds to use traditional medicine:
- wetting the cracks with cucumber juice;
- lubricating the wound with essential oils of avocado and tea tree;
- impregnation of the damaged site with soluble vitamin A and E;
- application of infusions for the purpose of disinfection - a turn, a bark of an oak, a camomile, a calendula, a sage, a celandine. Also the use of aloe, calanchoe, psyllium juice;

- topical application of rose oil and rose petals;
- smearing with honey or a mixture of honey and butter;
- with a fungal form of the disease rinsing with a solution of soda - a teaspoon to ½ cup of water, you can add vitamin B12.
Further therapy
In the future, depending on the type of formation used:
- antihistamines;

- Gluconate and calcium chloride to relieve allergic complications;
- Stomatidin;
- Metrogil Denta;
- healing and disinfecting medications, for example, Bepanten;
- immunomodulators for the purpose of increasing the body's resistance;
- vitamin complexes.
It is also necessary to treat dysbacteriosis and correction of nutrition, so as not to irritate the damaged areas.
Possible complications of
Even one wound disturbs the baby with painful sensations, but if they are not treated in time, you can completely deprive the child of peace and appetite.
The launched form turns into a solid wound with crusts, ulcers and ulcers, which constantly bleeds and secrete purulent formations.
The result is:
- the general resistance of an organism goes down;
- infected contacting babies;
- depletion;
- abundant salivation;
- occurrence of an abscess due to deeply penetrated microbes.
Prevention of
violation Since most species of zaed are infectious, it is necessary:
- prohibit children from kissing each other;

- use common utensils or linen;
- to control the purity of hands;
- to soften if necessary lips of children's hygienic lipstick or children's cream.
Prevention of re-infection consists in:
- reception of iron-containing preparations for a long time;
- content of B vitamins in the diet;
- strengthening immunity;
- protects the skin of the lips from frost and ultraviolet radiation;
- hygiene compliance.
If treatment in a home does not bear fruit, you need to seek the help of a specialist, since the occurrence of ulcers may be a signal of more serious diseases.
