Very often you can observe on the surface of the skin, in addition to the usual moles or eels, strange new growths. The appearance of a build-up of an indeterminate nature should cause anxiety and become an excuse for an immediate visit to the dermatologist. Neoplasms can carry a number of problems, up to the development of skin cancer. Even the most harmless wart should be checked by a doctor for good quality. What are the types of skin growths and what are they threatening?
- Types growths
- Benign
- Atheroma
- Hemangioma
- lymphangioma
- Lipoma or talc
- papillomas and warts
- nevi and moles
- Fibroma
- neurofibroma
- Malignant
- Melanoma
- bazalioma
- Kaposi's sarcoma
- liposarcoma
- Fibrosarcoma
- Precancerous
- disease Bowen
- Pigmentxeroderma
- Star keratoma
- Cutaneous horn
Species of growths
Skin growths are divided into three main groups - goodqualitatively, malignant and premalignant. And each group has its own subspecies.
to contents ^Benign
Such neoplasms on the skin do not pose a direct threat to their carrier, if they do not have various kinds of mechanical effects.
to table of contents ^Atheroma
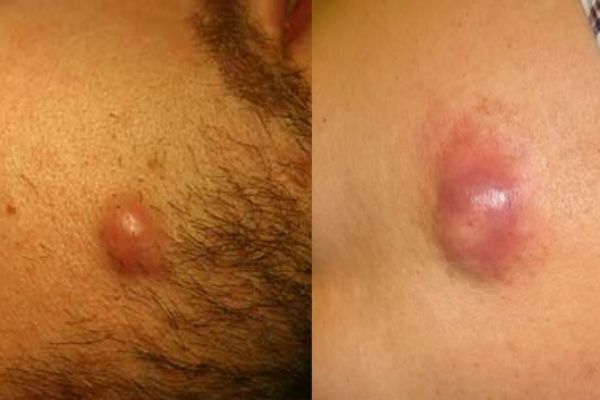
Cutaneous neoplasm, which forms in the process of occluding sebaceous glands. Outwardly, the outgrowth resembles a small dense cone, with a clearly outlined contour. Such a bump to the touch is very elastic and mobile. When palpating, it does not give pain and discomfort. The cone can swell and even break through. With a break from the build-up, purulent-greasy liquid is released. During the period of inflammation, fever rises, atheroma can get sick. The growth is formed in places of a large accumulation of sebaceous glands - on the skin of the head, neck, back, in the groin area.
Hemangioma
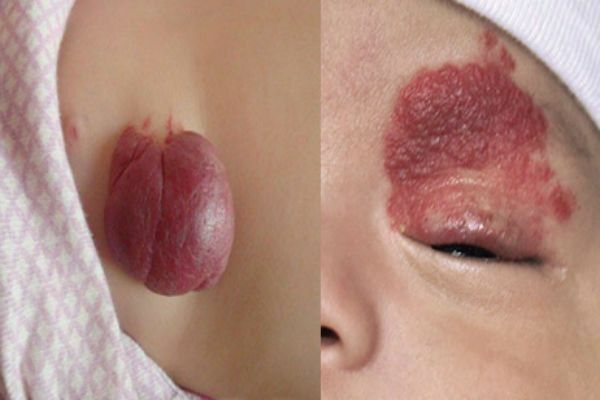
Hemangioma is a vascular tumor that can occur:
- Capillary is an outgrowth on the surface of the skin, can reach large sizes. Color from red to bluish. Often it grows to the sides.
- Cavernous - a limited subcutaneous knotty growth. The skin in the area of a tricky hemangioma usually turns red. Such tumors often appear in newborn children in the neck and head.
- Combination - a neoplasm that combines capillary and tricky hemangiomas in one growth. Such a subcutaneous or external neoplasm is usually cyanotic in color, with a sprawling or limited margin.
- Mixed is a hemangioma, which when spreading affects not only the vessels but also adjacent connective tissues.
Lymphangioma
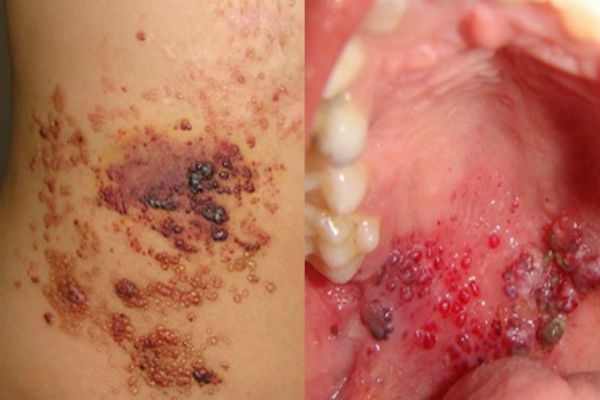
Tumor is a tumor that develops on the walls of the vessels of the lymphatic system. The tumor is characterized by very slow growth. In the area of lymph nodes a bloated cutaneous tumor grows, it is painless. Neoplasm is cystic, consisting of several isolated or combined cysts. The disease mainly affects children, but it can also develop in adults. This disease usually occurs in the fetus even during intrauterine development. The disease is not dangerous, but it has the ability to grow instantly under the influence of unfavorable environmental factors. In this case, immediate surgical excision is required.
Lipoma or adipo
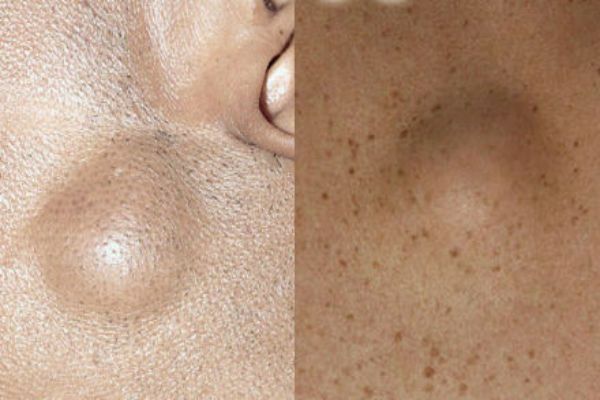
Neoplasm, which develops under the skin from fat cells cells. Outwardly, the adipose is similar to atheroma. The subcutaneous cone is completely painless. It feels like a solid and moving ball when probed. Lipoma can develop on any part of the body where there is a subcutaneous fatty tissue. The growth can be single or multiple. One fatty can grow in size from a large pea and to an apple of medium size. The tumor brings its owner aesthetic discomfort.
Papillomas and warts
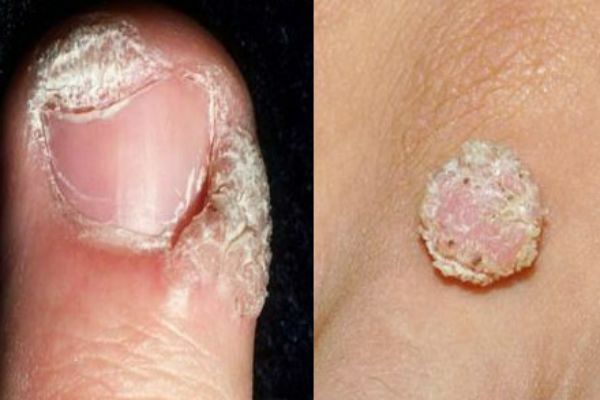
Skin accretions that are formed from epithelial tissue. Such growths can be spherical( in the form of a papilla), horny( filiform) or flat. Neoplasms small, painless. They can develop on any part of the body. The color of the growth can be bodily, brown, red and even black. The appearance of warts signals the presence in the body of HPV - the human papillomavirus.
Nevus and birthmark
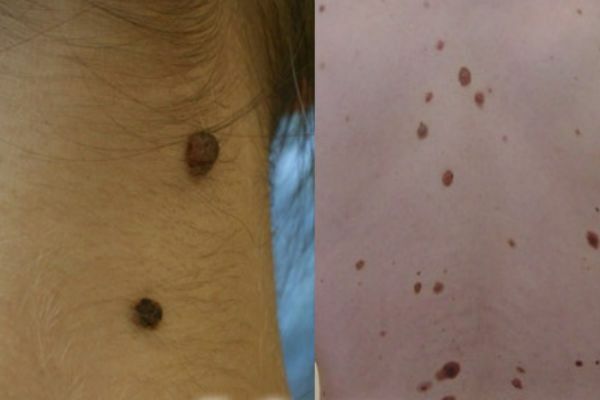
These are congenital or acquired flat lesions in the form of one or more spots. Such outgrowths represent a small or large accumulation of cells that are overcrowded with a natural pigment, a melanin. Neoplasms can be different in color( from beige to dark brown), texture, shape and size. Such growths do not cause special damage to health.
Fibroma
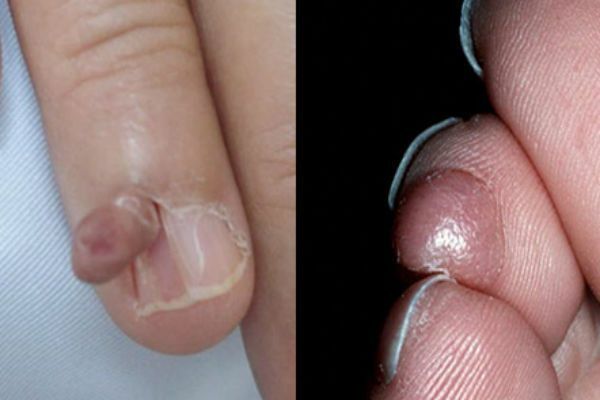
A growth that forms from a cluster of connective tissue. Externally, the fibroma resembles a wart on a thin stalk. The build is similar to a cluster of small dermal spherical knots. The surface of the fibroid may be smooth or loose. The color of the build-up varies from body pink to dark brown. Fibroma grows very slowly, does not cause discomfort( except for mechanical discomfort caused by clothing or its location).If there is no effect on fibroids, it is safe.
Neurofibroma
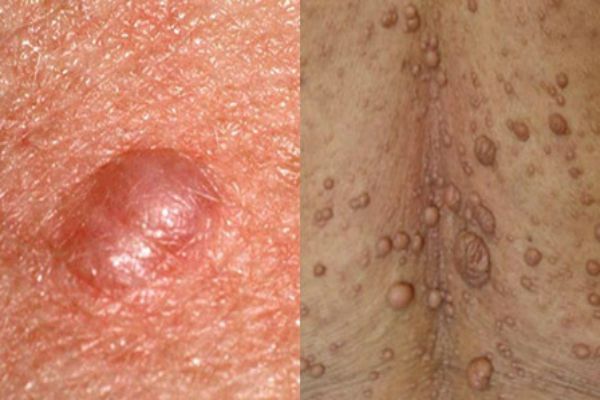
Cutaneous neoplasm, which is formed from nerve cells. Most often it develops on the basis of stress and nervous overexcitation. Often the build-up is located in the area of fatty subcutaneous tissue and under the skin itself. Outwardly, the neoplasm is a dense tubercle, with a pigmented outer skin globule. The growth rapidly spreads over the skin, very rarely lonely. Most often, the back, neck, elbows and knees are affected.
Malignant
This category of neoplasm on the skin often appears by degeneration of a benign growth into a malignant growth. Such growths require immediate detection and disposal.
to table of contents ^Melanoma
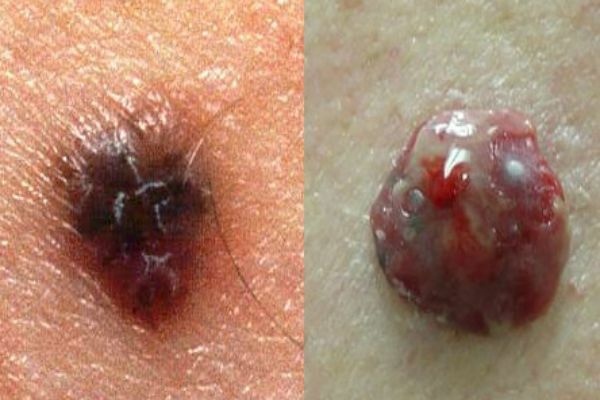
Neoplasm resulting from incorrect removal of a mole( nevus) or its degeneration into a malignant form. Melanoma is a type of skin cancer. The disease is very aggressive, rapidly spreading through the skin. Such a tumor very soon gives metastases throughout the body, to internal organs and even to the brain.
Basalium
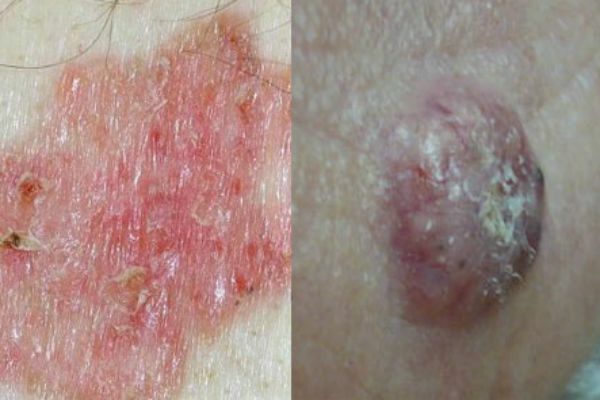
Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, which is formed from the cells of the basal layer of the epidermis, in the form of flat, single purulent wounds. Small nodal wounds-tumors quickly progress and grow into mushroom-shaped ulcers. Most often, wounds appear on the face, cheeks, wings of the nose, area behind ears and ears, lower eyelid are affected. This type of cancer does not give metastasis to internal organs and does not greatly divergence in the skin.
Kaposi's Sarcoma
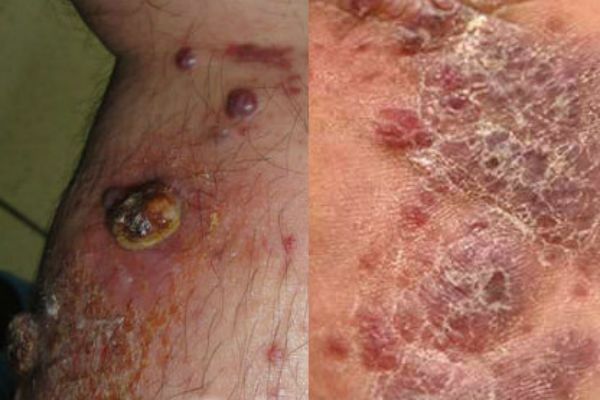
Malignant neoplasm on the skin in the form of extensive dark spots( from the color of clots of boiling blood to black) that merge into large lesions. Diagnosis of the disease in most cases in HIV infected, late disease. Places of sarcoma: hands, legs and feet. This disease is a consequence of serious problems with internal organs, it can not be cured, it is possible to remove only a little medicamentous symptomatology.
Liposarcoma
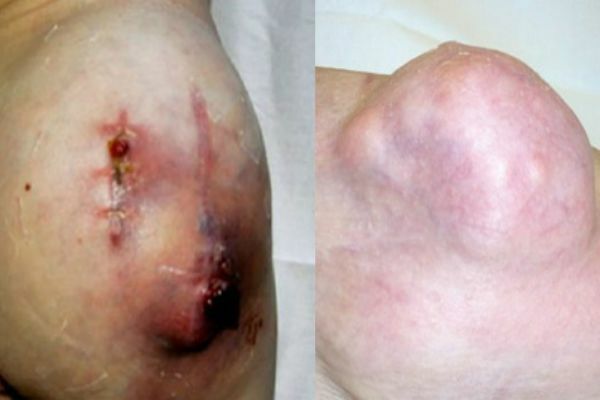
A tumor that occurs as a result of fat tissue damage. This is a large subcutaneous rounded outgrowth( single node), can grow up to 20 centimeters. The outgrowth in itself is uneven, with irregular outlines. When probed, it can be hard and elastic. Such a growth often occurs in people aged 50 years and mostly men. Liposarcoma occurs by the degeneration of lipoma or atheroma into a malignant tumor. The growth is very slow, metastases do not spread to internal organs.
Fibrosarcoma
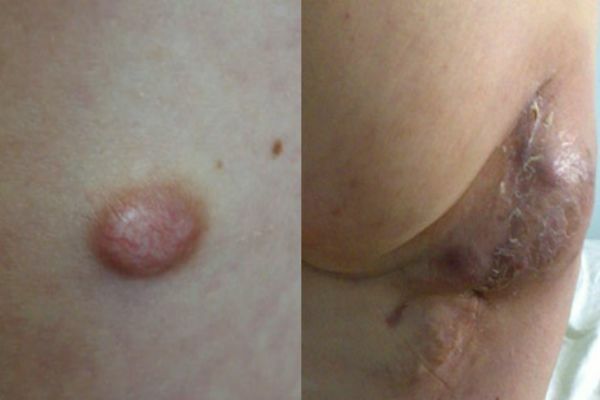
Neoplasm developing in connective soft tissues. Most often, the growth is affected by the skin of the lower limbs.
Fibrosarcoma may be located externally or subcutaneously. Nudge protrudes above the skin, such a built-up edge has clearly visible boundaries and a dark blue or brown hue.
Subcutaneous fibrosarcoma is located deep under the skin and is barely noticeable. We see only a small venous tubercle.
Precancerous
Despite the terrible name of the category, most of these neoplasms, if detected quickly, can be removed and cured without serious harm to health.
to contents ^Bowen's disease
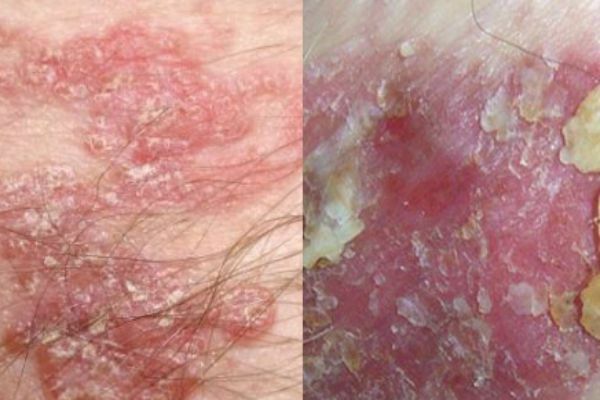
At the initial stages of tumor development, it is located in the upper layers of the epidermis. On the skin appears a well-defined plaque of a brownish hue, with a peeling surface. Under its surface is hidden the purulent purulent layer of the epidermis. Often the disease develops after 40 years, mainly in men. Affects Bowen's disease genitals, skin of the face, hands, mucous membrane of the mouth. If you do not detect the disease at the time and do not start treatment, it starts metastasis and goes to the stage of invasive cancer. Treatment is usually done by local, medicamentous route.
Pigment xeroderma
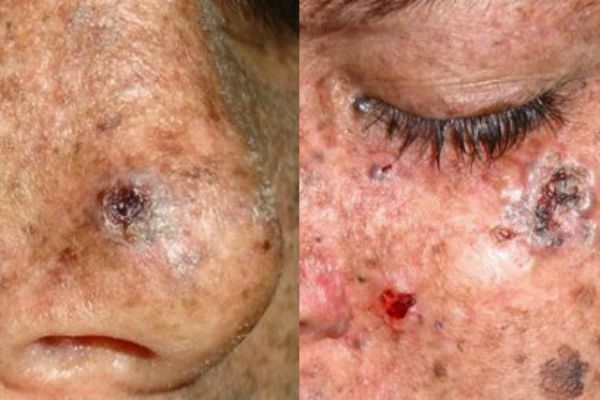
The disease develops by the degeneration of pigmented spots. It occurs in people with increased sensitivity to the negative effects on the skin of solar ultraviolet rays. Such pigmentation is most often manifested on the skin of the hands, face, back and chest. It densely covers the entire skin with dark brown spots. Stains can protrude over the surface of the skin and contain a purulent-bloody suture.
Star keratoma
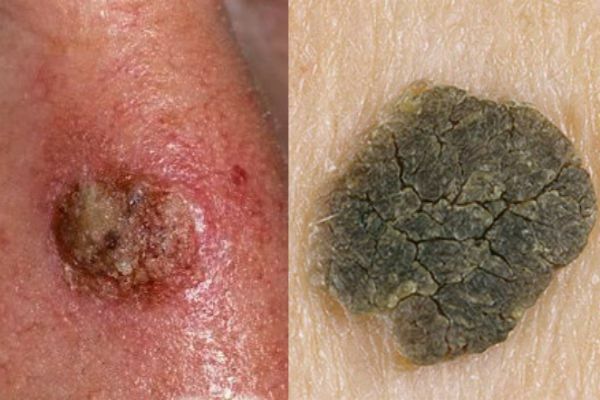
The build is similar to a rash first, after a cluster of small dermal spherical nodes that join together into a common spot. A flat build-up with time acquires a dense, loose crust on its surface. At the initial stage of development the build-up of corporal color, during the progression darkens to brown. Upper flakes of keratomas can exfoliate, the wound begins to bleed.
Cutaneous horn
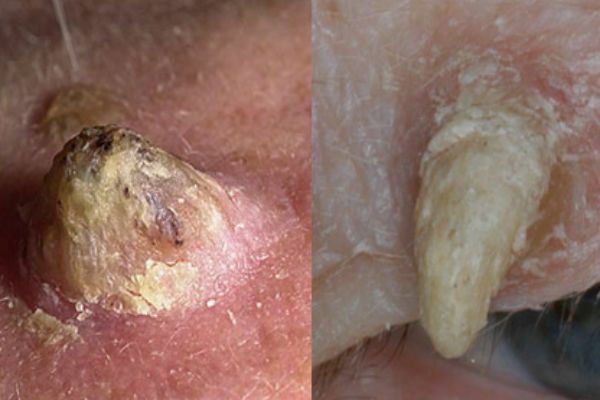
It is formed by the proliferation of epidermal cells of the spiky skin layer. There is a conical rise on the skin, which looks like a small horn. The horn has a multi-layered and scaly structure. Usually a dry outgrowth appears in the elderly behind the ears, on the fingers and toes, feet and coarsened parts of the skin.
