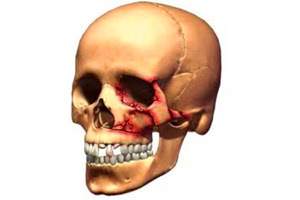
 Unlike fracture of the mandibular fracture of the upper jaw for its occurrence requires a much greater effort.
Unlike fracture of the mandibular fracture of the upper jaw for its occurrence requires a much greater effort.
For example, it could be a kick with a hoof or a brass knuckle.
The cause of the injury can also be:
- transport wreck;
- industrial injury;
- sports injury;
- banal beating with the use of brass knuckles;
- action in a combat situation.
This can be a drop face down from a height, or a drop in gravity on the face.
There is a destruction of the bone with a violation of the integrity of its structure and the onset of quite severe consequences - the disorders of the function of this part of the facial skeleton and the organs located here.
With the onset of a fracture, the jaw can no longer perform the role of a support, it becomes a source of dangerous complications due to rupture of the vascular-neural connections with adjacent bone organs and simultaneous formation of traumatic "scissors" from their cutting edges.
Given that the separation of the maxillary bone with adjacent bone formations is impossible because of the strength of the cranial sutures, the upper jaw breaks out of the bones of the neighboring jaws.
The jaw is usually broken by a block that consists of a jaw with fragments of adjacent bones, with the passage of a line of fracture along sections with a minimum thickness of the skull and where there are cracks, channels and openings between the bones to pass the vessels and nerves.
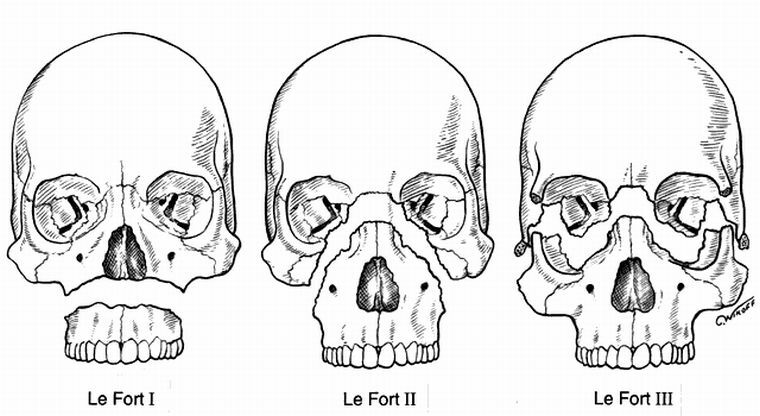
Three classical variants of the passage of lines in fractures of the upper jaw were studied by the French physician LeFor, who described the emerging symptoms, the possible outcomes of trauma, and measures to provide assistance to the victim.
Contents of
- Common symptoms and differences
- Variant Le Fort I - upper
- About Le For II variant - medium
- Variant Le Fore III - lower
- First aid and treatment
- Consequences and complications
General symptoms and differences
Clinic for all three variationsinjury has a number of common symptoms. 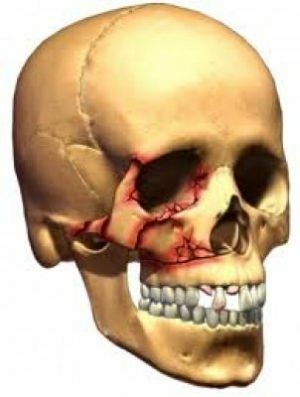
In addition to the inability to close the teeth without increasing pain in the projection of the fracture, complaints arise:
- bleeding from the mouth and nose;
- nausea with urge to vomit - due to the presence of an alien object in the region of initiation of the vomiting reflex and moving to the same area of the soft palate;
- difficulty breathing with the nose.
Sensory and sensory motility disorders are also present due to concussion of the brain, fracture of its base and due to traumas of the orbit structures and the main adjacent cavities of the skull.
Clinic of each version has differences.
The maxillary fracture is capable of shifting either backward or downward, or in both directions, the posterior parts of it are gravitating downward than the anterior ones.
The degree of the height of the fracture line, the maximum mass and volume of the broken out of the skull of the maxillofacial fragment - all this increases the severity of the patient's condition and the probability of the most serious complications.
Variant LeFOR I - top
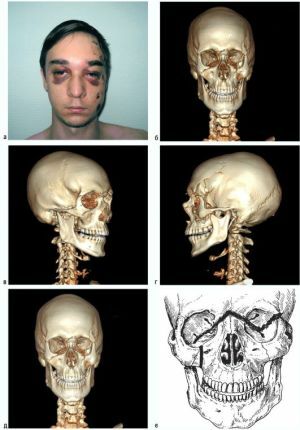
In Variation LeFe I, the puncturing block is the largest, and the fracture gap is the longest, with almost complete puncture of the face from the skull.
The block includes the main arrays of all adjacent bones, and the fracture line runs along the posterior and lateral walls of the orbits, splitting them into the upper and lower half-vanes along the natural orbital fissures. The lateral border of the fracture divides the zygomatic procession of the temporal bone, the larger wing is wedge-shaped, the medial line cleaves the latticed bone and destroys the nasal septum.
In this case, there is always a fracture of the base of the skull, as evidenced by the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ears and nasal passages, the doctor also sees its flowing into the pharynx.
The neuropathologist participating in the examination will confirm the diagnosis by the presence of symptoms indicating the trauma of the cranial nerves. Disorder of the function of the optic nerves leads to the fall of the fields of vision, and its sharpness decreases.
If other pairs of cranial nerves fail, the motor and the sensor of the organ of vision suffer: eyes do not open completely, there are divergent or converging strobism and doubling of the objects of sight, sensitivity in the upper eyelid zone, both corners of the eyes is disturbed.
In addition to sharp soreness, when opening the mouth with the unreality of the full-fledged closing of the victim's affected, the difficulty of swallowing with choking, nausea, urge for vomiting, a sense of presence in the throat of an alien object - due to the displacement of the soft palate.
The external appearance of the victim is a massive swelling of the entire central area of the face with a transition to the temporal zone, a "spectacle symptom" due to hemorrhages in the eyelids of both eyes, periorbital tissues, conjunctiva - until they swell between closed eyelids.
Changing the position of the body due to "swimming" fragments of the jaw changes both the shape of the face and its height.
If the face is flattened in the horizontal position, with the violation of the interposition of the upper and lower teeth, with the phenomenon of enophthalmia, with a low degree of diplopia, then in the vertical position it lengthens with the widening of the eye slits and the shift of the eyeballs downward with increasing diplopia.
Dense closing of the teeth leads to the movement of the eyeballs upward with a decrease in the width of the eye slits and a decrease in the degree of diplopia.
When examining the oral cavity with the maximum possible opening of the mouth, there is a decrease in the distance from the lower to the upper incisors with the formation of an open bite, the dewing of the soft palate downward with the tongue-tongue-tongue root touching the tongue;tapping teeth gives a dull tone.
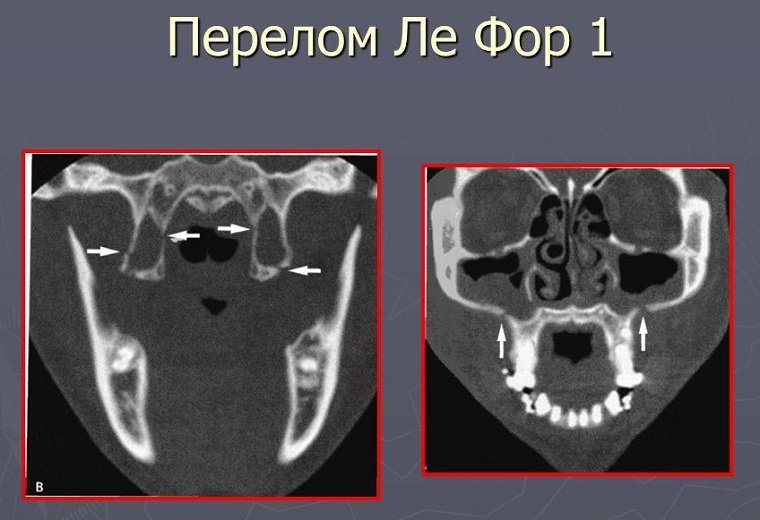
The photo shows the line of fracture of the upper jaw according to Le Fort 1 on the x-ray
. Palpation reveals the presence of bone "steps" on the border of bones:
- frontal and maxilla;Zygomatic and frontal.
The emergence of subcutaneous emphysema causes the appearance of crepitations near the base of the nose.
The researcher's attempt to change the position of the jaw by clicking on the wedge-shaped hooks, the hard palate, distant molars leads to an increase in pain in the fracture( the positivity of the "loading" symptom).Raising the hard palate shortens the middle third of the face with a decrease in the width of the eye cracks and wrinkles the skin of the root of the nose. The movement of the alveolar process in the frontal direction causes the mobility of the bone structures on the fracture.
The disintegration of the jaw along the sagittal axis, due to a fracture, creates a "step" in addition to the bruise to the sky, or because of the rupture of the mucosa, a narrow wound-slit in the solid sky leading to the nasal cavity.
Roentgenodiagnostics of the Le Fort I variant reveals the fractures of the root of the nose, zygomatic arches, wedge-shaped bones, a scrotal joint, a decrease in the transparency of the maxillary, wedge-shaped cavities;in the picture in the lateral projection, there are turning signs on the bodies of the wedge-shaped bones.
About the Le Fort II variant - the average
The line that delineates the fracture of the upper jaw according to Leo's middle, almost coincides with the natural boundaries of the maxillary bone, but lies either medial or lateral to the seams with contiguous bones.
The synonym of a condition is the term: a suborbital fracture, with it the infraorbital nerves and structures passing through the lower orbital fissures are most often damaged.
Pathology is rarely accompanied by a bruise or severe concussion, a skull base fracture with the phenomenon of liquorrhea.
The patient, in addition to bleeding from the nasal and oral cavity, complains of:
- double-diplopia;
- difficulty swallowing;
- breathing problems with both nose and mouth;
- as well as the nausea caused by the lowering of the palate, the urge to vomit, the presence of an alien body in the pharynx.

But apart from the characteristic for all types of jaw fractures of symptoms, this has differences in the clinic:
- Owing to pinching of olfactory threads, there is a decrease or loss of olfactory function of , deformation of the nasopharynx leads to lacrimation, and its damage to bleeding from lacrimal points.
- In addition to the pain when tightening the teeth, there are extensive complaints about skin sensitivity disorders - stiffness and numbness in various areas of the face: nose, upper lip region, infraorbital, lower eyelid region.
- Complaints on "stiffness" of the front teeth of , alveolar mucosa from the side of the mouth, are typical.
- The face of the victim is distorted by the massive edema of , the development of airy emphysema, the maximum in the nose area, the supraorbital areas, the effusions of the blood in the infraorbital, cheekbone areas, the orbital tissues: eyelids, conjunctiva and sclera, with a minimum in the upper-external sectors of the orbits.
- Massive hematomas and swelling of the eyelids of the can impede the examination of eyeballs, chemosis conjunctiva leads to their bulging even when the eyelid is closed;hemorrhages in the retrobulbar spaces lead to exophthalmos.
- When a patient's posture changes due to the lowering of the fragile posterior to the , the face either flattenes in a horizontal position or lengthens in a vertical .
- When opening a mouth whose volume of movements is limited, soreness increases , due to malocclusion, only molars have contact with each other. Typical are blood outflows on the threshold of the mouth, a zone of molars and partly premolars, the top of the pterygo-mandibular folds, palatine arches, palate, the dewing of the palate with the touch of the glabrous wall of the pharynx or the root of the tongue. Percutary tone from teeth is low.
- Formation of of a peripheral hemorrhage is manifested by the swelling of the pharyngeal walls.
- Palpation of the of the lower orbital margin reveals the presence of a bone ledge, the same gives a palpation of the front of the jaw and its tubercle, as well as the scalo-alveolar scallop - it is difficult to palpate the "step" at the base of the nose due to massive edema.
- Positivity of the "loading symptom" is revealed by pressing the hooks of the pterygoid processes of the sphenoid bone, the upper large molars. The implementation of this action, in addition to wrinkling the skin of the base of the nose, leads simultaneously to a shift to the top of the segments of the frontal processes of the upper jaw, the lower edge of the orbit and the scalo-alveolar comb, palpable.
The X-ray diagram indicates the passage of the line of the jaw fracture near the base of the nose, along the lower edges and the bottom of the orbits, along the scyloalveolar scallop, reveals the hemosyne of the maxillary cavities.
Variant Le For III - lower
A fracture in this variant of the fracture cuts the alveolar process from the jawbone, destroying the nasal septum, breaking off the nasal base with the maxillary cavity, tearing the nerve trunks in the tubules that participate in the formation of the maxillary plexus, or proceeding from it, thatleads to a disorder of sensitivity in the sphere of the structures served by them.
Complaints of the patient with the third variant of the upper jaw fracture in lefor:
- pain in the jaw, especially when tightening the teeth and chew the food, with the unreality of biting off the front teeth;
- loss of sensitivity by all teeth and mucous gums or mucous membranes;
- malocclusion;
- shortness of breath with both nose and mouth;
- sensation of the presence of an alien object inside the pharynx with popperhivaniem and urge for vomiting.
Inspection reveals:
- The change in the face shape of with the smoothness of nasolabial folds due to the limited third lower edema, the presence of hematomas in the perioral tissue and the presence of airy emphysema. The facial skin can be damaged.
- Lowering of bone fragments leads to lengthening of the lower third of the face of the patient in a vertical posture, the closing of the teeth results in a shift of the osseous part of the nasal septum to the top.
- The examination reveals blood outflows to the top of the mouth of the with the involvement of the entire dentition, frequent hemorrhages to the top of the winglessly single-jaw fold.
- There are violations of the bite of the , either open or straight, its nature is affected by the significance and type of displacement of the fragments. If the fragment is not displaced, the type of bite remains unchanged.
- When rattling, the teeth give a low tone of .Noticeably drooping of the palate, uvula reaches out to the root of the tongue.
- Sensing reveals the presence of a bone ledge within the boundaries of the hematoma on the frontal and transverse surfaces of the jaw .In the variant with a slight displacement of the fragments and the absence of rupture of the periosteum along the fracture line by palpation, the bone ledge is not detected.
- The load symptom is positive. If pressing the wedge hooks, distant molars, hard palate initiates pain in the
 fracture zone, then the symptom is also positive, even when palpation does not reveal ledges in typical zones.
fracture zone, then the symptom is also positive, even when palpation does not reveal ledges in typical zones. - The amplitude of fragility is estimated by carefully moving the alveolar process in the direction of the back-forward - unnatural mobility is felt in the areas of the fracture and palpable in the area of the scapulo-alveolar scallops of the bone ledge.
- When assessing the sensitivity of , there is either no pain, or a reduction in the pain threshold for the entire upper dental order, due to damage to all the lymphatic branches of the infraorbital nerves.
X-ray reveals a regular for this case fracture line with bilateral deformation of pear-shaped apertures, damage to the scalo-alveolar scallops, a decrease in the transparency of the maxillary cavities due to the presence of hemorrhages in them.
First aid and treatment for
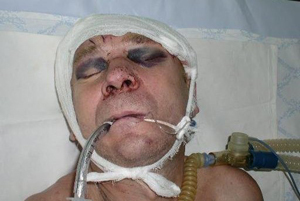
If you suspect a fracture of the upper jaw, first aid at the scene is to give the body the most gentle position in order to reduce pain and take anti-shock measures( analgesics are mandatory in any but preferably injectable form).
Prevention of asphyxiation involves laying the patient down face-to-face with a turn of the head toward the wound.
The application of an aseptic dressing to the wound area allows to stop bleeding and serves as a measure of protection against infection. If the wound is accompanied by chemical burns of the face, the rests of acid or alkali are washed off with water.
 Immediate call of an emergency ambulance or ambulance crew, performed in parallel with first aid, is all that a street person or participant in the incident can help a victim.
Immediate call of an emergency ambulance or ambulance crew, performed in parallel with first aid, is all that a street person or participant in the incident can help a victim.
Provision of full-fledged first aid is the use of anti-shock drugs, taking measures to stop bleeding and prevent asphyxia, providing transport immobilization.
In the future, with fractures of the upper jaw, surgical methods of treatment or specialized emergency care are used in the department of maxillofacial surgery of a regional or regional hospital and includes surgical intervention to fix bone fragments for their subsequent consolidation.
Consequences and complications of
The consequences of a jaw fracture include complications as an early general in the form of mental and neurological disorders, and the development of a life-threatening pathology of the circulatory, respiratory and other systems. Preventing their occurrence is the prerogative of the maxillofacial surgeon, who works in partnership with other specialist doctors.
Of complications of a local nature, concerning the oral cavity, there are:
- sluggish consolidation of fragments;
- development of dysfunction of temporomandibular joints and traumatic osteomyelitis;
- formation of suppurative hematoma, the appearance of lymphadenitis, abscess, phlegmon.
To no less serious consequences is the development of sinusitis and the formation of other sources of chronic infection of the body.
