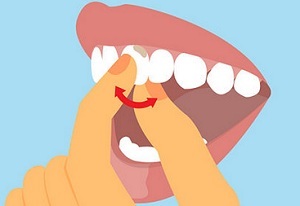
 One of the main symptoms of periodontitis is excessive mobility of teeth. This symptom is manifested in the second and third stages of the disease.
One of the main symptoms of periodontitis is excessive mobility of teeth. This symptom is manifested in the second and third stages of the disease.
In this case, there is not a physiological mobility inherent in any normal dentition, but a pathological one. It is accompanied by inflammation of the autoinfectious origin.
At the same time, the displacement of the dental crown is quite noticeable. The process takes place in the periodontium and contributes to its rapid destruction.
Degrees of mobility
Based on the theory of DA Entin, four degrees of tooth mobility are distinguished:
- in the of the first degree, the tooth mobility in the buccal or oral-vestibular direction, relative to the crown of the adjacent tooth, is no more than 1 mm;
- in the of the second , the mobility develops in the prostane-distal direction, while it exceeds 1 mm;
- in the third degree of the tooth can move in all the above listed directions, and also vertically;
- in the last, fourth degree, the tooth has the ability to rotate around its axis.
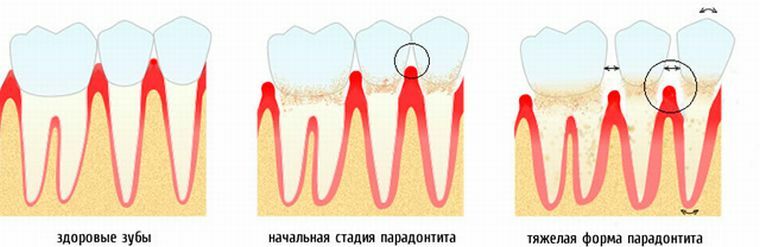
The first and second degrees of mobility are not mineralized. In this case, there is a soft plaque and dental plaque. The remaining two stages are considered demineralized. At these stages dental stones are formed under the gums and above them.
Thus, dental plaques grow into stones. This is due to the mineralization of the formations. The source of minerals is saliva and gingival fluid. Such reincarnation arises because the microorganisms in the plaque release toxins. After that the adjacent tissues become inflamed and the gingival pocket is damaged.
In this case we are talking about gram-negative bacteria. Endotoxin, which they secrete, is resistant to temperature changes and is aggressive towards tissues. Endotoxins contribute to the disruption of normal cellular metabolism. This is accompanied by hyperglycemia, and then hypoglycemia. And as a consequence there is hemorrhagic necrosis.
Causes of the disease
The level of mobility is diagnosed when examined by a dentist, who simultaneously finds out the cause of the disease. Provided that the hole and periodontium are preserved, after eliminating the cause, the mobility of the teeth can be eliminated.
The causes of the development of periodontal diseases can be the following: 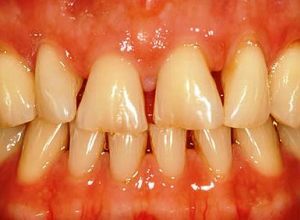
- bactericidal saliva;
- iatrogenic factor;
- periodontal overload;Underdelivery of
- .
Factors that contribute to the development of periodontitis, periodontitis and other diseases:
- avitaminosis;
- atherosclerosis of vessels;
- body reactivity;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pathological processes of the blood;
- psychosomatics.
Methods of treatment
The appearance of excessive mobility of teeth suggests that the treatment was started untimely. If you ignore these symptoms, then the loss of teeth is inevitable. But going to a specialist before the onset of tooth loss can stop the devastating process.
In modern medicine, there are two methods of treating periodontitis in the last stages:
- treatment with the help of special apparatus;
- treatment with surgical intervention.
Hardware treatment can be performed at different stages of the disease. Usually this is, ozonotherapy, laser or ultrasound treatment:
- Ozone has the property of removing inflammation and disinfecting the space. Ozone therapy is preferable to combine with laser or ultrasound treatment.

- The laser helps to safely disinfect pathogenic microorganisms. And in their absence, the tissue regenerates rapidly. The procedure is fast and fairly effective.
- Ultrasonic vibrations of remove plaques, dental calculi, endotoxins, microbial films. With the help of ultrasound, the affected gums can be cured, the depth of the pockets of which reaches 11 mm. The procedure takes no more than two hours. An effective way that prevents the further development of the disease.
Microsurgical method of treatment - curettage, is performed under local anesthesia. During the operation, the affected periodontal pockets are cleaned, after which they introduce substances capable of regenerating tissues. Surgical intervention injures healthy tissues, since healthy and affected areas are nearby.
It is important to remember that timely treatment will help to avoid surgical and hardware interventions, limiting oneself to medication. Therefore, you need to monitor your health, and if necessary, go to the doctor and do not self-medicate, as it can lead to undesirable consequences.
