Features of the anatomy of the nails on the fingers and toes. Streonia of nails and care for them. Diseases of the nails.
Contents
- Structure and function of nails
- VIDEO: Anatomy and physiology of nail
- The tank looks like the structure of the nail on the leg:
- schema How the structure of the nail on the arm looks:
- schematic Anatomical structure of the nail and nail plate: photo
- Cuticle on the nail - anatomy
- Nail structureand manicure
- Basics of pedicure and nail structure
- Structure and diseases of nail
- VIDEO: Nail disease
- Can a man live without nails?
- VIDEO: The structure of the nail and the problem after the manicure. Answers to
questions Nails called epidermal derivatives are dense plates at the tips of the fingers and toes of a person( however, they are in all primates).Despite the fact that they are devoid of nerve endings and do not hurt, the marigolds act as indicators of the state of the whole organism.
Firstly, to look beautiful and have a stylish manicure, secondly, in order to understand in time what is wrong with health, it is necessary to be aware of the anatomy and functions of the nail plates on the hands and feet.
Nail structure and functions
Nails are a unique part of the human body. Their anatomy is rather complicated, but studying it, you can learn a few interesting facts. The animal's claws and human nails have a very similar anatomy.
- The nearest "relatives" of the nails on the fingers and toes of a person are his own hair, as well as the hooves of animals.
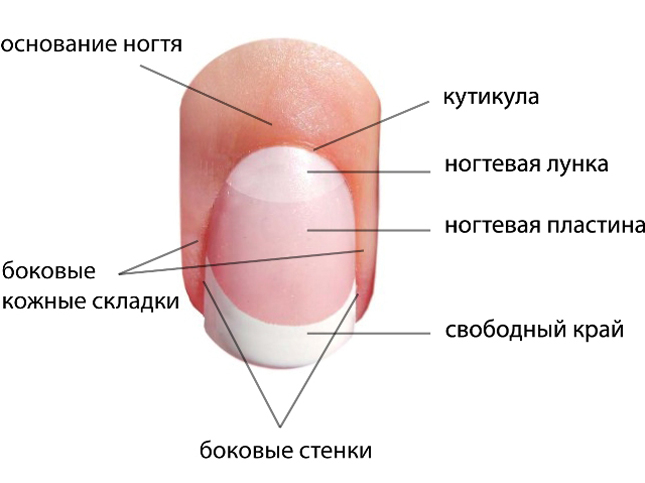
- A horn protection plate consists of three parts: the root( other names are matrix, matrix), the body and the free edge. The root is formed by living epidermal cells, and the body and free edge - dead
- The root of the nail, hidden under the skin, in the nail fissure. We can not see. But its dimensions are not small, they make up a third of the visible part. The white semicircle visible on the plate near the lower roller is a continuation of the matrix. It is called the lunula
- The body of the nail is resting on the nail bed. The average length of this part of the cornified plate on the hands is 1.5 cm, width - 1 cm, thickness - 0.7 mm. On the legs, the extreme phalanges and, correspondingly, the nail plates, on the first and the remaining four fingers differ considerably in size, the thickness of the plate on the thumb is approximately 1 cm.
- The horny plate itself is naturally devoid of blood vessels. But there are a lot of them under it, in the nail bed. It is these vessels that nourish the nail
- A thin layer of living cells lies between the plate and the bed, hyponychia
- The rollers are the folds of the skin located at the bottom and sides of the nail body. With a horny plate, they are fastened with the cuticle
- . Matrix consists of living epithelial cells - onychoblast. They are very intensively feeding on blood, constantly dividing and corroding, forming a protein keratin, from which the dead part of the
- plate consists. Matrix is responsible for how the visible part of the nail looks - its shape, thickness, strength, speed of its growth, smoothness, etc. Injuries to the nail root directly affect the appearance of the
- plate. The growth rate of the nail on the finger is up to 4 mm per month, on the toe - up to 3 mm for the same time. It is interesting that the process of growth occurs more rapidly in women. Also, the nails are cut more often in the summer time
- The nail body, although represented by dead cells, is dense, shiny, elastic, has a pleasant pink tint, if, of course, the person is healthy. This is due to the fact that between the keratin contains sulfur atoms( cysteine), between its parts in the plate there are "gaskets" of fat and water. The pink color of the plate is attached to the blood circulating in the underlying blood vessels
- . The free edge of the nail can grow as much as it is strong and elastic, and also as much as the person wants. For classical manicure, the length is from 2 to 5 mm. Nails - stilettos with an unusual design can be longer. As you grow, the free edge of the nail platinum is twisted and takes the form of a spiral.
- The free edge of the nail of the manicure master is given various shapes by the sawing method.
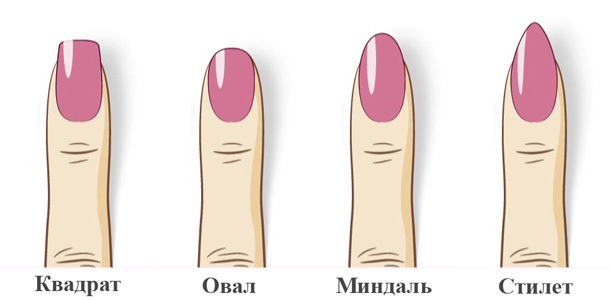 The classic shapes of the free edge of the nail.
The classic shapes of the free edge of the nail. IMPORTANT: There is a separate official science that studies the anatomy and functions of nails, and also deals with the diagnosis of their condition. It is called "onychology"
 Healthy, shiny, elastic, strong nails are needed to protect the fingertips.
Healthy, shiny, elastic, strong nails are needed to protect the fingertips. The main function of nails is to protect the extreme phalanges of the fingers from the negative effects of environmental factors, in particular, mechanical, chemical, vibrational, temperature, etc. Also, marigolds:
- Needed to itch
- Helps a person manipulate with different objects, giving the fingertips the necessary firmness
- Helping a person to tactilely evaluate the object
- Are a means of self-expression
Yes, thanks to the possibilities of modern nail design, the nails for a woman are an ornament comparable toclothing, accessories, jewelry. Ability to care for nails is a valuable quality also for a man.
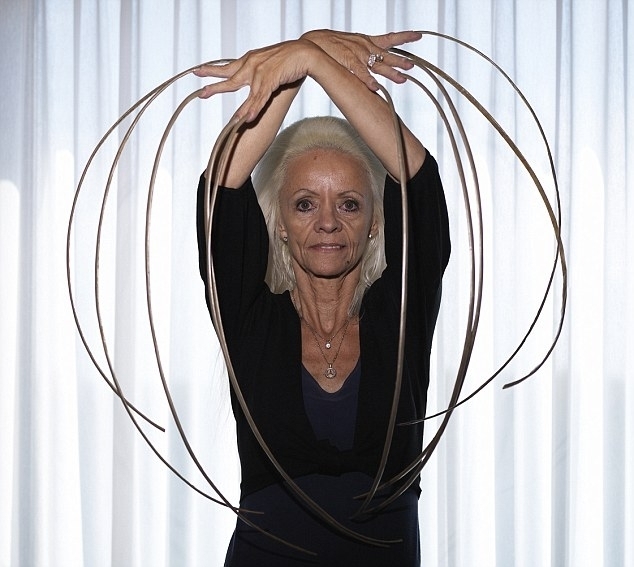 Singer Countess has a record long nails - 91 cm
Singer Countess has a record long nails - 91 cm VIDEO: Anatomy and physiology of the nail
The tank looks like the structure of the nail on the leg: the
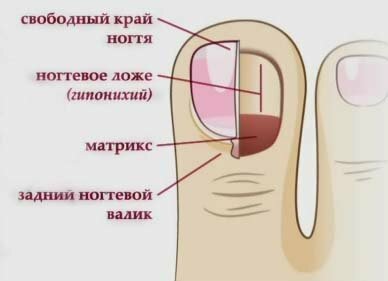 diagram Anatomy of the nail on the leg.
diagram Anatomy of the nail on the leg. How the structure of the nail on the arm looks like: Scheme
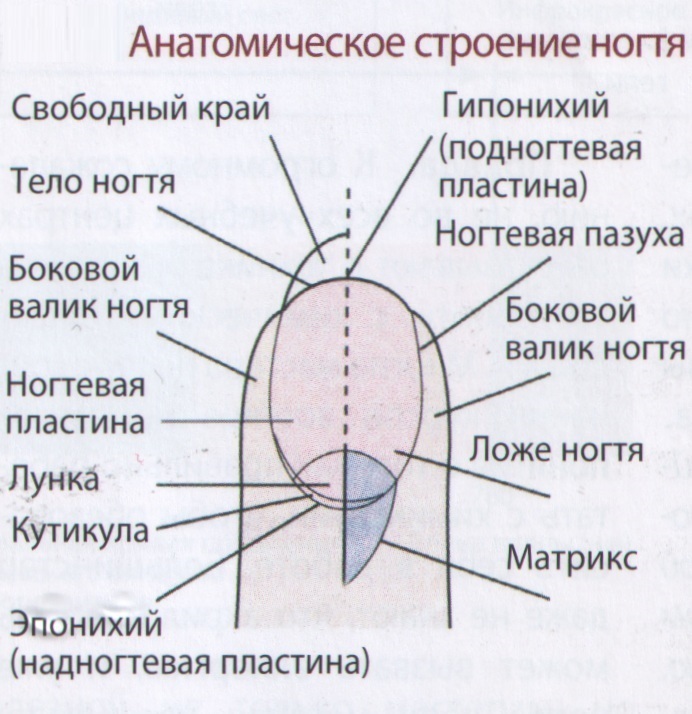 Schematic of the structure of the nail on the arm.
Schematic of the structure of the nail on the arm. 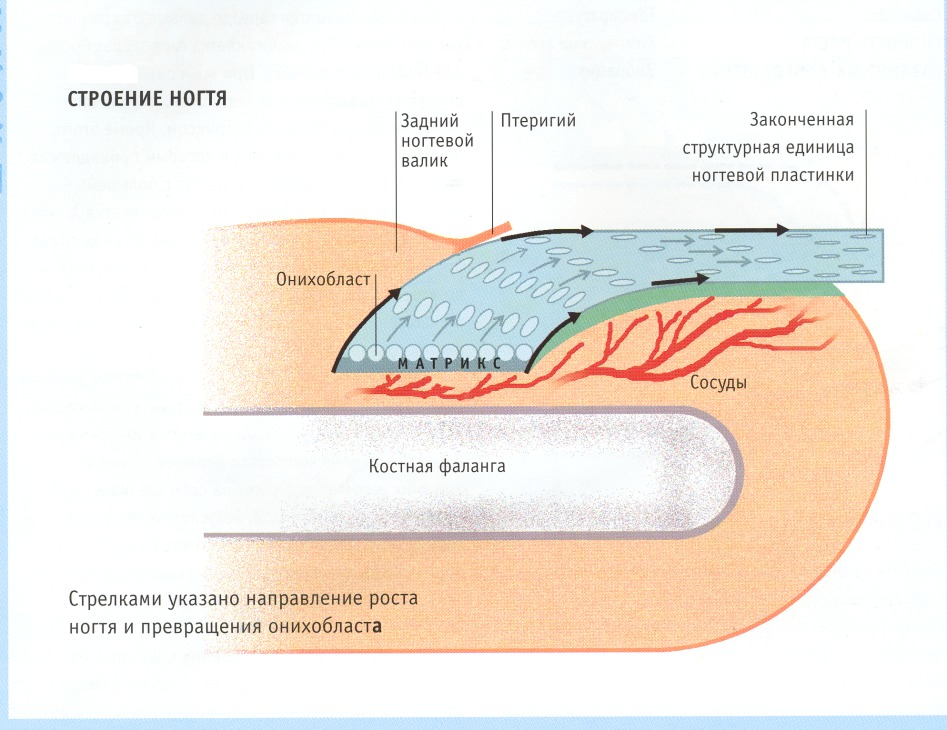 Detailed scheme of the structure of the nail.
Detailed scheme of the structure of the nail. 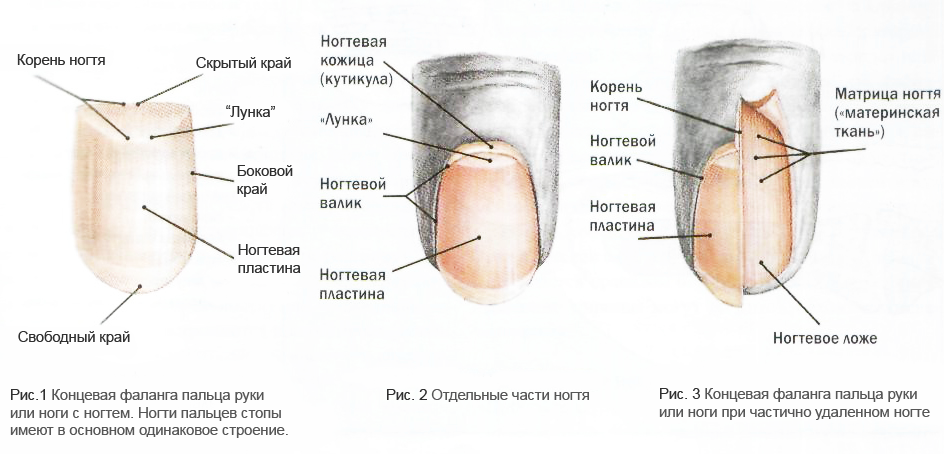 Nail and nail plate.
Nail and nail plate. Anatomical structure of the nail and nail plate: photo
 Nail design with photo.
Nail design with photo. Cuticle on the nail - anatomy
From the rollers around the body of the nail on the horny plate as it grows a thin protective film called the cuticle.
IMPORTANT: Cuticle consists of two kinds of cells - living and dead. Living cells are located closer to the skin folds, the dead ones - to the keratin plate. The dead part of the cuticle is easily damaged, barked, which often leads to inflammation of the living areas of the skin around the nail.
 Cuticle performs a protective function.
Cuticle performs a protective function. The main function of the cuticle is protective. The film is needed so that bacteria, dust, and other foreign bodies do not enter the gap between the nail and the skin.
Onihologists and manicure masters are still arguing whether it is necessary to remove the cuticle.
Earlier it was believed that a beautiful manicure with this film is simply impossible, and it was mercilessly cut off with scissors or bitten with tweezers. Today, most people are inclined to believe that the living part of the cuticle is needed. The dead, after softening by special means, is removed with the aid of a nozzle of a router or carefully moved away with a stick.
Also, the cuticle is offered to look after with:
- baths
- massage
- special oils and creams
Nail structure and manicure
To work in the nail industry, you need to complete the courses and get a certificate in addition to having the desire and abilities.
 The manicure master is obliged to know the anatomy of the nail.
The manicure master is obliged to know the anatomy of the nail. Manicure and pedicure courses are huge in any city. Regardless of their cost and duration, the first thing that future nail designers are to meet is the anatomy of the nail, its injuries and diseases. This knowledge block is necessary for them to:
- understand exactly what they will have to work with
- to protect customers from injuries and damages while manipulating the nails, and themselves - from the troubles following these injuries and damages
- answer numerous questions arising fromclients
IMPORTANT: By the way, the knowledge of the structure of the marigold should be for every person who makes himself a manicure. After all, ignorance becomes a lasting injury to the plate, matrix, skin, infection during unskilled caring procedures. Often such troubles occur in children who are being treated by their parents
Here are some questions that the manicure masters hear most often:
- Why do I have such short nails? This parameter is laid genetically. Matrix is responsible for the shape of the plate. But the length of the nail plates is influenced by external factors. For example, the marigolds are "disfigured" by the parents, when in the infancy they damage the hyponychia, cutting them too short. Short nails are also often found in those who have a habit of gnawing them
- My nails seem tight. But, why do they often break down? The fact is that the nail plates are very hygroscopic. Having nourished water, they thicken, but lose elasticity, and, accordingly, break. It is recommended to wear special gloves
- with frequent contact with water. My nails grow too slowly. Why? On the speed of nail growth, again, heredity answers. Also, it depends on the hormones. For example, pregnant women quickly acquire long nails. To increase the growth rate, it is necessary: to eat properly and adequately;to be in the sun;take vitamins;do massage of the fingers( this promotes more active feeding of the matrix with blood);To be examined for the presence of cardiovascular and endocrine diseases, if necessary, treat them
- Nails are dead. Why it hurts me to cut or file it? The nails do not hurt, because they do not have nerves. Soreness occurs when a well-innervated hyponychia is injured. This occurs when the nail plates are cut too short. Or, on the contrary, the marigolds have been too long for too long, and the hyponychia has overgrown them. To eliminate discomfort, it is recommended to oil the inner surface of the nail plate and gently move the skin over it with the help of the orange stick
- . I bruised the nail and it blackened. What will happen now? About the bruises of the nail can be read in detail in the article: link
Basics of pedicure and the structure of the nail
The toes are subject to extreme stress in connection with the walking and wearing of shoes. Doing a pedicure, you need to think not only about aesthetics, but also about the health of the feet.
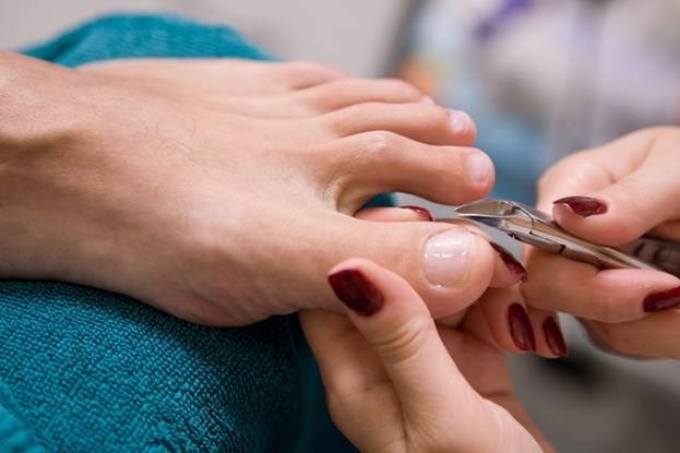 It is correct to make a pedicure only if you know the structure of the nail.
It is correct to make a pedicure only if you know the structure of the nail. Here are some rules:
- Cuticles on toes are better to be moved away rather than cut
- Nails on four small fingers can be cut short, "under the root".On the large, the length of the free edge should be about 1 mm.
- . Shorten the nail on the thumb and it is thick, you need to be very careful not to break it. If the nail has grown too much, it is cut off, if moderately - filed. Shorten the free edge from the corners, and not from the middle.
- Nail corners on the toes do not round out, otherwise they can grow into the skin.
IMPORTANT: If any injury to the nail or skin around it occurs during the pedicure procedure, use an antiseptic. The risk of developing the infectious process is great.
Nail structure and diseases
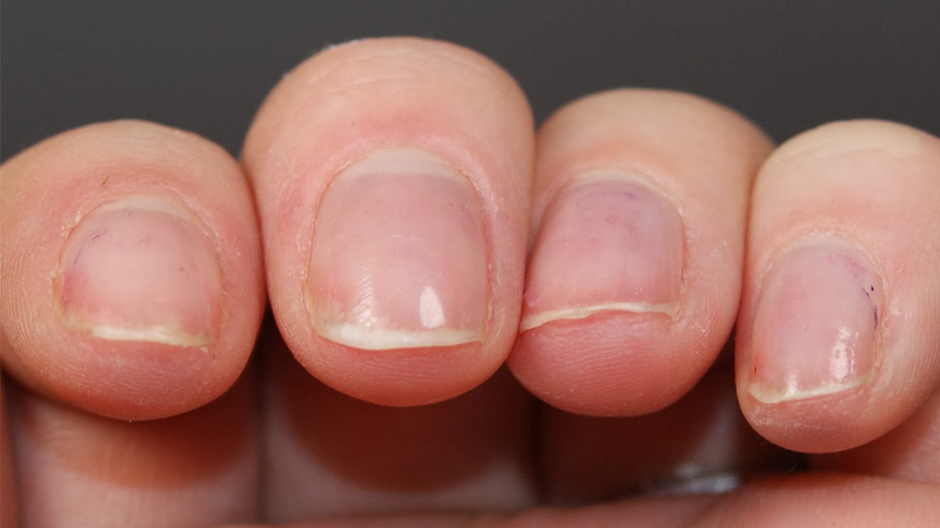
Healthy nails are strong, elastic, smooth, translucent, pleasant in color. Broken, yellow, dull, furrows and irregularities speak about this or that disease.
Nail breaks are caused by:
- lack of nutrition( deficiency of proteins and vitamins)
- by the destructive effect of water, household chemicals, other external factors
- by prolonged exposure to sun
- by typing, playing musical instruments
- by habit of ripping
- nail polish
- ( fungal nail disease)
 Brokennails.
Brokennails. Nail plate becomes dull and yellow due to:
- of
- smoking of cardiovascular, endocrine diseases
- of elderly
- aging
fungi
Unevennesses and furrows on the nail plate appear if:
- injured nail root
- human nutrition unbalanced
- in humans iron deficiency anemia
 Furrows on the nails.
Furrows on the nails. Nail foliation is explained:
- using household chemicals without gloves
- lack of vitamins
- a habit to nail or rip off nail polish
- allergy
- internal diseases
- nail fungus
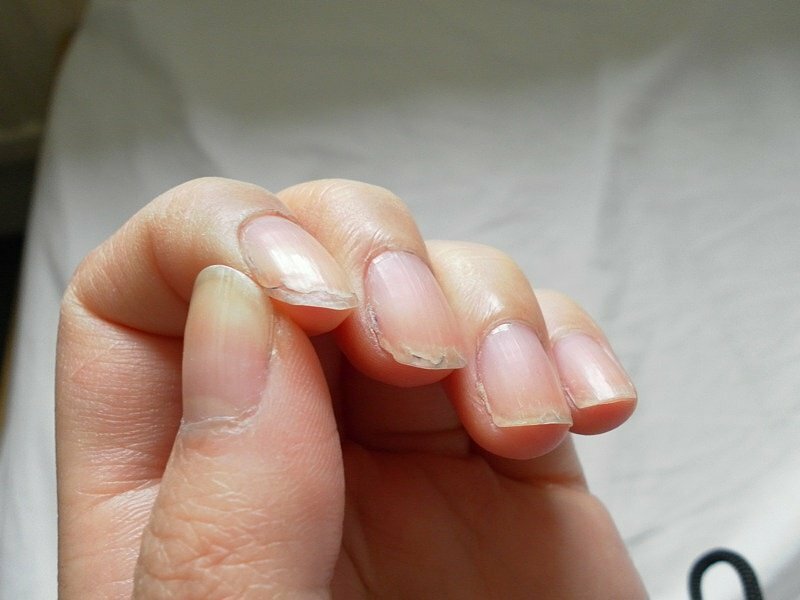 Layering nails.
Layering nails. About the nail fungus and the ways of its treatment is written here: link
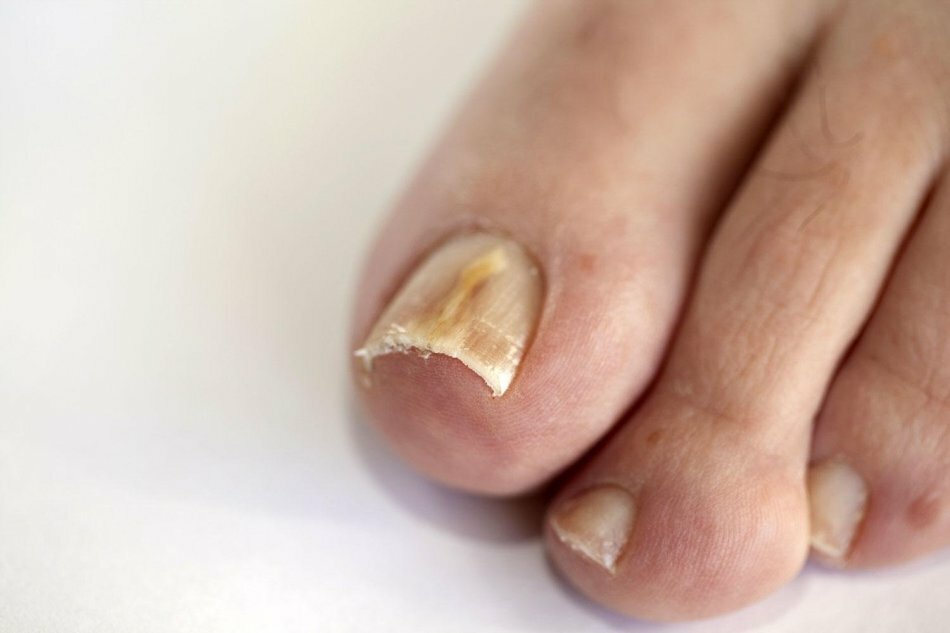 Nail fungus on the legs.
Nail fungus on the legs. VIDEO: Nail disease
Can a man live without nails?
It happens that a person has to live without nails. The reason for this can be:
- Heredity. Congenital complete or partial absence of nails is transmitted from generation to generation. The complex congenital pathology is considered to be arthro-osteo-onychosplasia, in which the person lacks not only the nails but also the patella, the pelvic bones and the radial bones
- are incorrectly formed. The nails depart partially or completely due to diseases. Such ailments are psoriasis, lichen, bullous epidermyolysis, other
- Injuries of the nail plate, in which its nutrition is disturbed, and it departs. In this case, on hands new nails grow for 4 months, on the big toe - for half a year.
- The nail can also be removed surgically due to a fungal disease or infection.
