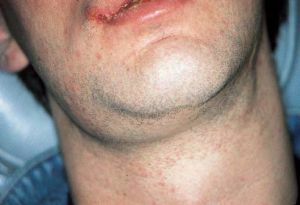
 In medical practice, inflammation of lymph nodes occurs quite often. One of the diseases that provokes the development of the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes is submandibular lymphadenitis( lymphadenopathy).With this disease, inflammation of the submaxillary lymph nodes develops.
In medical practice, inflammation of lymph nodes occurs quite often. One of the diseases that provokes the development of the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes is submandibular lymphadenitis( lymphadenopathy).With this disease, inflammation of the submaxillary lymph nodes develops.
Diseases are equally susceptible to adults and children. The main cause of the development of infringement are infectious lesions.
If the problem is detected in a timely manner, submandibular lymphadenitis is easily treatable, resulting in a favorable prognosis for complete recovery. Otherwise, the consequences can be quite sad.
Contents
- The causes of
- Features of the clinical picture
- Chronic and acute form of lymphadenopathy
- Diagnosis of
- Medical care is not so simple, but possible
- Medical treatment
- Traditional medicine
- Submandibular lymphadenitis in children
- What is the danger?
- Preventive measures
Causes of
The lymph nodes carry an important function of biological filters. They protect the body from the penetration of pathogenic bacteria. The enlargement of the lymphatic system is most often diagnosed in the immediate vicinity of the infectious focus and accompanies the accompanying disease.
Inflammation and enlargement of submandibular lymph nodes can occur against the background of the following diseases:
- inflammation of the tonsils;
- tonsillitis, pharyngitis;
- otitis media;
- gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontitis;
- stomatitis;
- developed caries forms;
- sinusitis;
- purulent sore throat;
- inflammation of tissues under crowns.
Submandibular lymphadenitis can develop as an independent disease, the cause of this pathology is an infection that penetrated into one of the submandibular lymph nodes and caused inflammation. This can occur as a result of the injury.
A major role in the onset of the inflammatory process can be caused by immune system disorders due to the following diseases:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- is lupus erythematosus;
- serum sickness.
To provoke the inflammatory process can the Koch wand( the causative agent of tuberculosis), the bacterium of syphilis, staphylococcus, streptococcus. In childhood, an increase in nodes is often observed with teething.
Features of the clinical picture
In the first stages of submandibular lymphadenitis may not manifest itself in any way, but in the absence of proper treatment the disease begins to progress and soon the following symptoms appear:
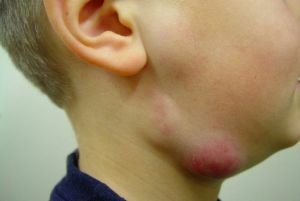
- enlarged, inflamed and painful submandibular lymph nodes;
- on palpation, pain appears and a hard lump is felt;
- appears a slight redness, gradually acquiring a burgundy hue, then cyanosis;
- at the site of inflammation produces severe swelling;
- pain exiting to the ear area;
- when swallowed, there are unpleasant sensations;
- body temperature can rise to 40C;
- asthenic condition;
- in blood elevated white blood cell count.
 From the onset of the disease to the transition to a sharp form can take only three days. The clinical picture changes dramatically and the tumor is already spreading all over the neck.
From the onset of the disease to the transition to a sharp form can take only three days. The clinical picture changes dramatically and the tumor is already spreading all over the neck.
Often in patients at the first stage of the disease development there is a change in mood, irritability appears. Increasing pain does not allow you to sleep and eat well.
The appearance of cyanosis of the skin indicates the accumulation of pus in the area of the lesion.
Chronic and acute form of lymphadenopathy
In acute course, one node or several can inflame. In this case, the disease can occur without accumulation of pus, but most often occurs as a result of an abscess.
Pus is localized in the node and begins to move along it. This can lead to a more extensive spread of infection or a possible breakthrough of purulent inflammation. In the acute form of infectious disease, neighboring tissues adjacent to the node can also be affected, which also leads to swelling and pain. During the movement of the jaw submaxillary lymph node is very sore, and the pain radiates to the neck.
Chronic course can result in improper treatment of acute form. If during the acute stage there is swelling and inflammation of the lymph node and redness around it, then in the chronic course of the disease the nodes become firm to the touch.
The chronic process can also affect adjacent tissues. The symptomatology is manifested in the same way as in the acute form.
When submandibular lymphadenitis is chronic, its treatment can be performed surgically. During the operation, the inflamed node will be deleted.
During an acute stage, pus is removed from the affected node and antibiotic therapy is prescribed.
Diagnosis of
There are several proven methods for diagnosis of the disease. In most cases, even no additional measures are required, since the symptoms of the disease are pronounced, and an accurate diagnosis can be made by visual inspection.

Palpation of lymph nodes is a reliable method for diagnosing
. In addition to the examination, the doctor performs palpation of the inflamed area. It will take a number of mandatory tests, among which the most important is taking blood. It has already been said above that during the development of this disease, an elevated level of leukocytes is observed in the blood.
To identify pus in the node, the patient is assigned ultrasound.
In some cases, a puncture can be taken from an inflamed area to a bacteriological analysis of the fluid. With the help of this method it is possible to establish the kind of bacteria that provoked jaw lymphadenitis, which in the future will help in prescribing the necessary antibiotic so that the treatment is effective.
Medical care is not so simple, but it is possible
In order to prescribe the right treatment, it is necessary to understand the causes that triggered the inflammation and enlargement of submandibular lymph nodes.
All medical measures should be started at the first manifestations of the disease in order to prevent serious consequences. After the necessary examination, the doctor can prescribe the following treatment methods:
- sanitation of an inflamed focus;

- consultation of the dentist with the subsequent opening of the abscess;
- use of the Rinse Booster solution;
- application of lotions;
- therapy with antibiotics;
- reception of vitamins;
- physiotherapy( UHF).
Depending on how many nodes are inflamed, surgical intervention can take place in different ways.
One node:
- over the inflamed knot a thin incision is made on the skin;
- a drainage is inserted under the capsule;
- wound is washed with an antiseptic.
Multiple knots:
- under the jaw reveals the area of inflammation;
- in adipose tissue is introduced drainage for the outflow of pus;
- is prescribed antibacterial therapy.
Medical treatment
Not all antibiotics are effective in submandibular lymphadenitis( and any other as well).Most often the disease is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Therefore, antibiotics of the penicillin group should be prescribed.
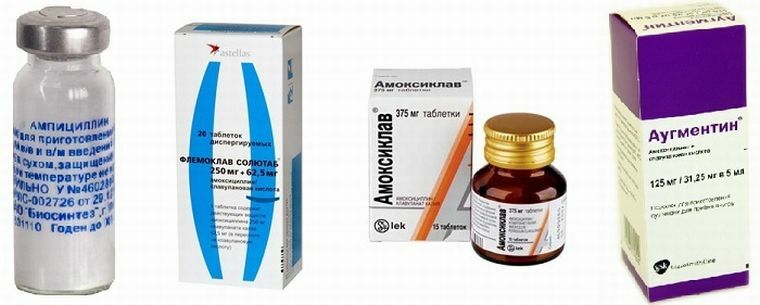
Penicillin antibiotics - drugs of choice for lymphadenopathy
The choice of the drug is based on the degree of damage, the age of the patient and the individual characteristics of the organism. But we must understand that they act to eliminate the cause, not the inflammatory process itself. In most cases, the doctor prescribes injections. Treatment takes at least two weeks.
Ointments of local action may be prescribed as adjuvant therapy.
With the timely start of treatment, it is enough to rinse and apply antibacterial agents. The operation is prescribed only if there is pus in the node.
Traditional medicine
Lymphadenopathy is cured only with the help of traditional medicine is almost impossible. This is especially true for severe, neglected stages. But such methods can be a good addition to the main treatment, greatly easing the patient's condition.
You can apply antiseptic compresses, take drinks that strengthen immunity. The main thing is to consult a specialist before starting such treatment.
Submandibular lymphadenitis in children
The clinical picture is similar to that characteristic of adult patients, with one exception, that in children, lymphadenitis rarely passes with suppuration of inflamed nodes.
Many infectious processes can promote lymph node enlargement. Therefore, doctors direct the main efforts to 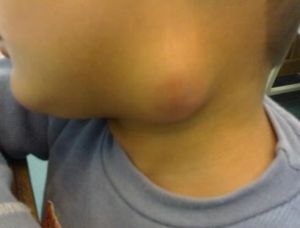 elimination of the main infection, and the treatment of the disease is resorted only in those cases when there is a strong soreness of the inflamed nodes.
elimination of the main infection, and the treatment of the disease is resorted only in those cases when there is a strong soreness of the inflamed nodes.
In childhood, the disease part becomes chronic. If this happens, then doctors need to find out the hidden infection infection and address it. Important measures for treating the disease in children are taking multivitamins and tempering the body. Of course, during an exacerbation period, one should not begin to temper.
In childhood, lymphadenitis, localized under the jaw, is treated in the same way as in adults.
What is the danger?
If the patient is not properly treated, or if the wrong measures are taken, the disease can become chronic. In the worst case, serious complications can arise that threaten the life of the patient.
The inflammatory process can begin to spread to nearby tissues, which can lead to such serious diseases as periadenitis, adenophlegmon or abscess.
With the localization of infection in the respiratory system, a breakthrough of purulent inflammation can lead to the appearance of chronic fistulas in the bronchi or esophagus.
Antibiotic therapy can provoke negative reactions from the body:
- a violation of appetite;
- redness of the skin;
- loose stool;
- dizziness and headaches;
- allergic manifestations;
- feeling uneasy.
Preventive measures
To avoid inflammation of the lymph nodes, several simple recommendations should be followed: 
- treat infectious diseases at their first manifestations;
- monitor oral hygiene;
- visit the dentist's office twice a year;
- treat all injuries and skin lesions immediately with antiseptic agents.
To reduce the possibility of infection can only be in case of careful attitude to your body.
