 Chronic periodontitis is mostly a consequence of an acute inflammatory process or develops independently if a person has a weak immune system.
Chronic periodontitis is mostly a consequence of an acute inflammatory process or develops independently if a person has a weak immune system.
Periodontitis is characterized by unimportant or complete absence of symptoms, for example, when biting, a person may experience mild pain. The development of inflammation from time to time can worsen against a background of worsening of the immune system.
During an exacerbation the symptoms of chronic periodontitis always look like the signs of an acute form of the disease. Such a reaction of the body can provoke hypothermia or worsening of the immune system after SARS.
Contents of
- What forms of violation are distinguished?
- The stage of exacerbation - what is its peculiarity?
- Causes and risk factors
- The acute form of the disorder is short
- Approach to diagnosis
- The main thing is the goals and therapies
- Forecast and complications
- Beat the whole body
- Local impact
- Preventive measures
What forms of violation are different?
There are only three forms of such a disease, as chronic periodontitis, each of them has its own symptoms and features:
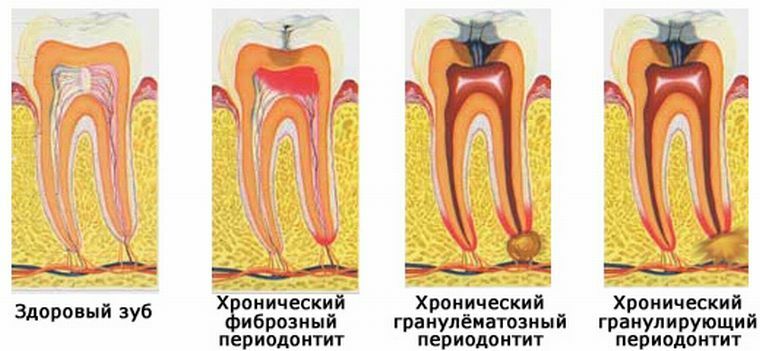
- Fibrous .For this form of the disease is characterized by a gradual replacement of the fibers of the ligament of the tooth, connecting it with the bone( periodontal) by the fibrous tissue. The disease is characterized by a minimal manifestation of symptoms, as well as a complete absence of pain. Sometimes the dentist can diagnose fibrous periodontitis only after examining the X-ray. The normal condition of periodontium is determined visually, as a narrow strip between the roots of the teeth and bone. With the same disease characterized by a marked expansion of the periodontal gap.
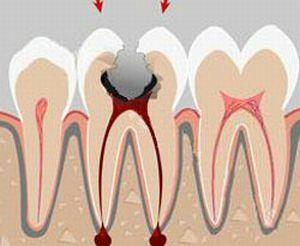
- Granulomatous .The abscess, characteristic of the chronic form of granulomatous periodontitis, is a kind of pouch consisting of a mucous membrane densely filled with pus. If we consider the possible size of such purulent sacs, we can distinguish three main varieties of this form of the disease: a granuloma, the size of which is up to 0.5 cm in diameter;Cystogranuloma, the size of which is from 0.5 to 1 cm;cyst, the size of which is more than 1 cm at the top of the root. As the granuloma develops, it grows into a cystogranulum, and then to a basal cyst, which in turn can grow to 4-5 cm and more, which as a result often causes a fracture of the lower jaw. Such a cyst inside is also filled with pus.
- Chronic form of granulating periodontitis. This is the most active form of all the existing manifestations of chronic periodontitis. It is characterized by the formation of a granulation shell in the region of the apex of the roots, which resembles a loose granular bard fabric. This disorder is characterized by accelerated growth, which promotes active deformation of bone tissues and replacement by fragments thereof. On the X-ray images, dentists fix significant changes. At the tops of the roots, you can see small blackouts, the outline of which visually resembles flames. Similar darkening indicates that in this area, bone tissue is destroyed, and in its place now there are granulation formations.
The stage of exacerbation - what is its peculiarity?
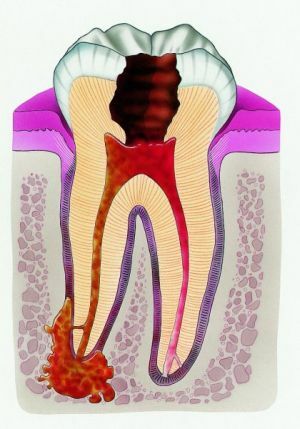 Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis in the clinical sense is similar to acute purulent inflammation. Mostly, before the stage of inflammation, there are minor symptoms, which are characteristic of an independent disappearance. In most such cases, patients do not seek qualified help from the dentist.
Exacerbation of chronic periodontitis in the clinical sense is similar to acute purulent inflammation. Mostly, before the stage of inflammation, there are minor symptoms, which are characteristic of an independent disappearance. In most such cases, patients do not seek qualified help from the dentist.
For the stage of exacerbation of the inflammatory process, which is of a chronic nature, an increase in the granulation fragments in periodontal tissues is characteristic.
Similar manifestations are often accompanied by painful sensations during meals, sensations that the tooth is slightly enlarged, swelling of the gums, and also of the face. The signs of such exacerbations also include: fistula, deep caries cavity, hyperemic mucosa.
Chronic periodontitis in some cases resembles a sharp form of sinusitis, jaw osteomyelitis or other diseases. For accurate diagnosis in modern dentistry, precise techniques have been developed and a sufficient number of technical aids have been used.
Causes and risk factors
Periodontitis is divided into infectious and non-infectious. In some cases, the disease develops due to the penetration of infection into the tissues surrounding the upper part of the roots of the teeth, from separate root canals.
A non-infectious type of disorder may well be due to a common trauma.
Causes of infectious periodontitis:
- Pulpitis was not treated at the right time. In some cases, the infection can get from the carious cavity directly to the pulp of the tooth, and then, passing through the canal openings on the upper parts of the roots of the teeth, adheres to the periodontium, where an abscess occurs and a purulent sac forms. Having made the roentgenogram, the dentist can notice the carious cavity, as well as the periodontal abscess at the top of the root in the form of a blackout.
- The root canals were not sealed .If the root canals were not completely filled during pulpitis treatment, an infection can develop in the remaining cavities. After some time, the inflammation spreads beyond the tooth itself, causing the formation of a periodontal abscess near the top of the root. On x-ray images, the development of such a process is determined visually, as intense darkening around the apex of the root of the tooth.
- Marginal periodontitis. With the development of an average and severe degree of disease between the bone and the tooth root, depressions are formed, from which the infection can spread further along the periodontium, falling into the region of the apices of the roots. Due to the peculiarities of education, this form of violation is usually called marginal.
Acute traumatic periodontitis is related to diseases of non-infectious origin and can result from a one-stage sport, domestic trauma. Disease can occur as a result of regular physical effects.
In such situations, a chronic form of traumatic periodontitis is implied.
In some cases, patients may develop a pharmacological appearance of the disorder. Most often, this effect is due to unskilled pulpitis treatment at the stages of filling or the use of various medications.
Acute form of disorder
The acute form of the disorder can have such clinical manifestations: 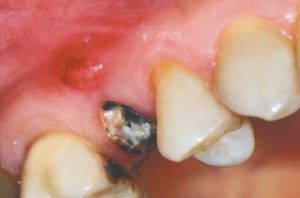
- fracture of the root;
- when the neurovascular bundle is torn, the tooth crown can be colored in a characteristic pink color;
- dislocation of the tooth is always accompanied by its mobility and painful sensations when nibbling.
The development of this form of the disease is associated with overloading, resulting from mistakes made in the process of medical procedures and prosthetics.
In some situations, dentists with a low level of training do not observe the correct height of the filling.
This causes uneven clamping, which is characterized by premature nicking on the tooth. When a person chews food, constant pressure often becomes the cause of traumatic periodontitis.
In some cases, patients may experience an allergic reaction to the components of the filling mixture.
Approach to the diagnosis of
It is very difficult to diagnose a dysphagia due to the sluggishness of the disease and almost no visible symptoms.
All doctors use the same conventional oral examination algorithm. Qualified specialists evaluate the results of all procedures, carefully examine the oral cavity, conduct an anamnesis.
The most effective technique for determining chronic periodontitis is the study of X-rays and an additional visual inspection.
X-ray can be performed several times, for example, at the first visit, after the completion of therapeutic procedures, during the endodontic treatment to determine the dynamics and effectiveness of the actions performed.
Clinical examination implies such procedures:
- close examination of the oral cavity;
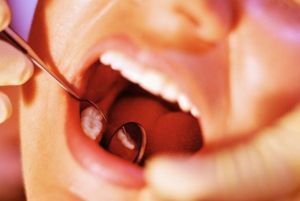
- percussion of a diseased tooth;
- palpation of the oral cavity, as well as individual fragments of periapical tissues;
- determines the degree of pain in the dental canal when passing a special probe;
- temperature testing, which yields the best results during diagnosis of the disease in adult patients;
- determination of the level of mobility of a diseased tooth by means of a root indentation, as well as translational movements;
- it is possible to use radiovisiographic, electro-odontodiagnostic equipment for qualitative assessment of pulp vitality.
To the main thing - the goals and methods of therapy
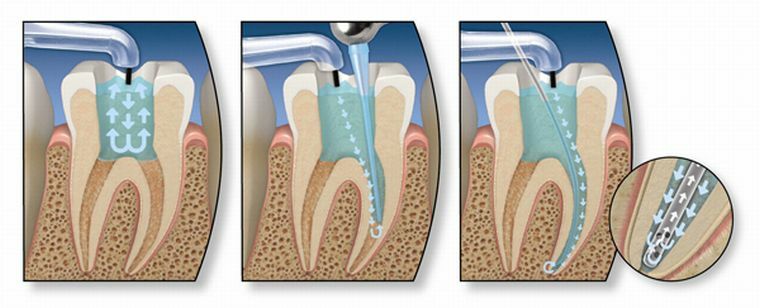
Treatment of any form of periodontitis is aimed at the destruction of the primary focus, the elimination of harmful microflora throughout the area of inflammation. Therapeutic treatment usually begins with access to the root canals.
To do this, the dentist must accurately dispense the cavity cavity, and then get rid of the obsolete seal in the patient. After this, the doctor must organize the outflow of exudate and thorough washing periodontal with a prepared antiseptic solution.
In this case, not only the channel is washed, but also the apical space.
The period of full restoration of damaged areas lasts up to 12 months, therefore treatment of some forms of the disease can be quite long and complex. Regeneration of tissues should always be carefully monitored by a specialist, by examining X-rays.
In addition, patients can be given physiotherapy and mouth rinsing with antiseptic agents.
The way to treat chronic periodontitis is always due to the degree of inflammation, and the dentist chooses an adequate and most sparing method of stopping the pathological process.
Prognosis and complications of
The prognosis of the disease is always due to the time of going to the doctor for qualified medical care and, of course, the quality of the medical procedures performed.
Measures to prevent such a disease involve frequent visits to the dentist and an attentive attitude to the condition of your own teeth.
Of great importance is the correct implementation of all dental procedures, as well as the rational use of affordable medicines.
In medical practice, general and local complications of the disease are known.
Beat the whole body of
Common arise as a result of an organism's intoxication caused by the spread of harmful microflora, which can cause a negative reaction of the whole human body when it enters the blood.
Local impact
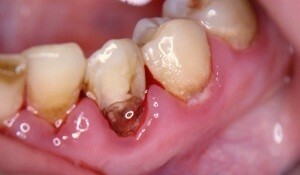
Fistula on the gum - complication of periodontitis
Local are fistulas or cysts of the teeth. Fistulous passages often form, as in the oral cavity, and on the place of the top of the root of the affected tooth.
Similar formations can occur even on the skin, contributing over time to the formation of external facial defects. When periodontitis develops, purulent mass is excreted through the fistulas.
Such formations can be independently closed and opened during an exacerbation of the disease. A similar process is accompanied by scarring and the formation of a peculiar funnel after drawing the tissues into the fistula.
In some cases, such fistulas can appear on the chin, in the cheek area, on the upper jaw, near the inner side of the eye. When the granulating focus extends to the periosteum or areas of soft tissue, odontogenic granulomas are formed, which, when developed, put pressure on the bone tissue, which as a result may lead to the destruction of their alveoli.
The cyst can be formed from the tissues affected by granulation in the region of the apex of the root of the tooth.
The cyst, formed as a result of the development of periodontitis, belongs to the most complex chronic diseases in dentistry. Inside such an education, inflammatory processes are continuously occurring.
For this reason, the cyst can spread to healthy teeth as it grows. For the most part, such formations arise at the places of non-professional dental interventions.
If oral hygiene is not respected, the harmful microflora can penetrate into unprotected dental canals and contribute to infection. When the cyst develops, the patients in parallel develop a flux, acute pain in the affected area, and the body temperature rises.
Such an education grows slowly and until a certain time they are difficult to detect by visual inspection of the oral cavity of patients.
Preventative measures
The actions taken to prevent the development of a chronic form of periodontitis basically involve the prevention of pulpitis and caries.
For this it is necessary:
- to carefully and constantly care for the oral cavity;
- to think over your diet and use sweets in proportion;
- regular visits to the dentist from an early age, according to the results of statistical data, it can be determined that the number of caries diseases is reduced by 65-70% in case of medical examination;
- when there are troubling symptoms, it is necessary to contact the dentist;
- you need to follow every recommendation of the doctor in the treatment of the disease.
 In addition to paying attention to one's own health, enlightening activity on the part of qualified specialists is also important.
In addition to paying attention to one's own health, enlightening activity on the part of qualified specialists is also important.
Modern dentistry has long ceased to be as traumatic as it used to be, so a visit to the dentist should not cause patients such fears as they did a few years ago.
Regular examinations at the doctor are considered the main method of disease prevention.
