- Mechanism of action of free radicals and antioxidants
- Types of antioxidants
- Antioxidants in food
- Antioxidant content in food
- Antioxidant preparations
- Medicinal plants with antioxidant properties
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidative processes. These include the products of the body's vital functions and nutrients that enter it from the outside with food. The action of antioxidants is aimed at protecting and restoring cells from damages caused by free radicals. The older a person becomes, the more the functions of his own antioxidant system decrease and the additional intake of these compounds in the form of drugs, dietary supplements or foodstuffs becomes more urgent. Antioxidants help to prevent or reduce the rate of progression of such life-threatening diseases as cancer and arteriosclerosis of vessels, as well as slow the aging process, protect against the adverse effects of environmental factors.

Mechanism of action of free radicals and antioxidants
Free radicals are particles having one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed in the body as a result of numerous oxidation-reduction reactions aimed at maintaining all vital processes and generating energy. Free radicals are chemically unstable and have a high reactivity. They easily enter into reactions that lead to the loss of their unpaired electron or the acquisition of a pair for it. These particles can reversibly or irreversibly change the structure of biologically active molecules that are close together( proteins, lipids, enzymes, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, etc.).With numerous such damages in the cell, its functions are violated, which leads to its death and provokes the development of various diseases.
Interestingly: For one day, each cell of the body can be attacked by about 10,000 free radicals. Their presence in the body is considered a normal physiological phenomenon.
The following factors can contribute to an increase in the concentration of free radicals in the body:
- smoking;
- alcohol abuse;
- intoxication;
- permanent medication;
- radioactive and ultraviolet radiation;
- improper diet( abuse of fast food, fried and fatty foods);
- is a bad ecology.
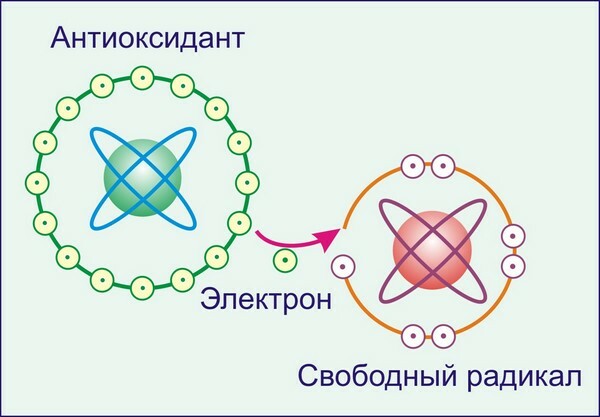
Very often free radical enters the so-called chain reactions. In this case, when interacting with an adjacent molecule, it selects one electron from it, thereby converting it into a particle with an unpaired electron. Then this new free radical does the same with the neighboring molecule. As a result, molecules that have become free radicals lose their charge and ability to perform certain biological functions. This condition is called oxidative stress. Chain reactions can lead to the formation of crosslinks between the two molecules. For example, combine two DNA molecules.
What are antioxidants in simple words? These are compounds that provide the free radical with its electron, and they themselves become low-active radicals, not representing a threat. Thus, they neutralize free radicals, stop the chain reaction or significantly slow it down without harming the body. In medical practice, as part of a comprehensive treatment, antioxidants are used for multiple sclerosis, diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, atherosclerosis, hypertension, coronary heart disease, oncological diseases and other pathologies.
Types of antioxidants
Antioxidants are divided into two main groups: enzyme and non-enzyme. Enzymes are part of the internal antioxidant system of the body, thanks to them, each cell is able to cope with the free radicals attacking it. These include superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidase. Non-enzyme antioxidants refer to the external antioxidant system and come from outside with food, dietary supplements or vitamin preparations. These include vitamins( ascorbic acid, tocopherol, retinol, lipoic acid), carotenoids( β-carotene, lycopene), polyphenols( flavonoids, flavin, tannins, anthocyanins).
Depending on the method of production, antioxidants are natural and synthetic. Natural enter the body with food, and synthetic - from drugs and food additives.
Interesting: Synthetic antioxidants are used in the food industry as preservatives to increase the shelf life of products by reducing the rate of oxidation processes.
Antioxidants in food
The main antioxidants that enter the body with food are carotenoids, vitamins and minerals. They not only neutralize free radicals, but also exhibit many other useful biological properties.
Vitamins
Vitamin antioxidants include ascorbic acid ©, tocopherol( E), retinol( A).They are found in various foods that a person consumes daily. Their daily allowances are:
- vitamin E - 15 mg;
- vitamin C - 75 - 90 mg;
- vitamin A - 1 - 1.5 mg.
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble compound, it is embedded in the lipid bilayer of cell membranes and prevents the process of peroxidation of membrane phospholipids and the destruction of any cells. Tocopherol protects against oxidation formed in the body of vitamin A, limits free radical reactions in cells of the mucous membranes, epithelium and cells of the embryo, which are characterized by rapid division. It improves the skin condition, prevents its aging, increases the body's defenses, promotes better oxygen absorption by cells.

Vitamin C is water-soluble and realizes its antioxidant effect in blood plasma, intercellular fluid and extracellular space. It is also called a "trap" of free radicals and is referred to as immediate antioxidants. It stimulates the immune system, increases the synthesis of interferon, fights against inflammation, reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, and stimulates the work of the brain and protects its cells. In addition, ascorbic acid prevents the oxidation and destruction of vitamins A and E.
Important: For people who smoke, the daily norm of vitamin C can be increased almost 2-fold, as nicotine reduces the absorption of vitamin C and destroys it.
Vitamin A is fat-soluble, is synthesized in the body from beta-carotene and comes with food. It reduces the harmful effect on the body of radioactive and electromagnetic radiation, increases its stress resistance. Retinol strengthens the immune system, has a beneficial effect on the skin and mucous membranes, stimulating their regeneration, lowers cholesterol, increases visual acuity.Minerals
Minerals are an important link in the antioxidant system, they strengthen and supplement the action of vitamins, inhibit the development of cancer, increase immunity. The most important of these are selenium, copper, zinc, manganese, and chromium. Their daily rates are:
- zinc - 8 - 11 mg;
- selenium - 55 mcg;
- copper - 2.5 mg;
- chrome - 100 - 150 mcg;
- manganese - 3 - 4 mg.
The important mineral from the listed minerals has an irreplaceable microelement of selenium. It is part of many hormones and enzymes. In particular, selenium is the active center of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase, which neutralizes the most dangerous and aggressive free radicals. Selenium supports the immune system, liver, heart and lungs. It protects the body from intoxications with heavy metals, tobacco smoke and exhaust gases, protects from the effects of radiation.

| Product Name | Antioxidant capacity per 100g | Product Name | Antioxidant capacity per 100g |
| Fruits | Berries | ||
| Prune | 8059 | Aronia | 16062 |
| Plums | 6100 | Blueberry( wild) | 9621 |
| Garnet | 4479 | Cranberry | 9090 |
| Raisins | 4188 | Blackberry | 5905 |
| Cherry | 3747 | Raspberry | 5065 |
| apricots | 3234 | Blueberries | 4669 |
| Apples | 2589 | Strawberries | 4302 |
| Pears raw | 2201 | Gooseberries | 3332 |
| Orange | 2103 | Nuts | |
| Avocados | 1922 | Walnuts | 13541 |
| Peaches | 1922 | Filbert | 9645 |
| Red grapes | 1837 | FisAshka | 7675 |
| Grapes Black | 1746 | Peanuts | 3166 |
| Tangerines | 1627 | Cashew | 1948 |
| Grapefruit | 1548 | Greens | |
|
| 1346 | Lemon Basil fresh apricots | 4805 |
|
| 1110 | Lettuce Bananas | 1532 |
|
| 795 | Spinach Fresh Vegetables | 1513 |
|
| Spices | ||
| Red beans | 14423 | Rosemary Dried | 165280 |
| Artichoke crude | 6552 | Cinnamon | 131420 |
| Broccoli | 3083 | Vanilla | 122400 |
| Beet | 1776 | Basil Dried | 61063 |
| Radish | 1750 | Curry | 48504 |
| Eggplant | 932 | Black pepper | 34053 |
| Onions | 913 | Mustard | 29257 |
| sweet pepper | 821 | Chile | 23636 |
| Corn | 728 | Paprika | 21932 |
| Tomatoes | 546 | Ginger fresh | 5708 |
| Carrots | 436 |
Copper and manganese act as active centers of the antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase, which catalyzes the conversion of the superoxide radical into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide and thereby protecting from superoxide all cells in contact with oxygen. Manganese increases the degree of assimilation of antioxidant vitamins E and C, vitamins of group B, enhances the ability of cell membranes to resist free radicals.
The microelement of zinc influences the growth and differentiation of cells, participates in the exchange of proteins, nucleic acids and transcription, promotes the repair of damages in the structure of DNA.It improves the absorption of vitamins A and E, maintains their concentration in the blood, activates the immune system, reduces the negative impact of toxic substances.
Chromium participates in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, increases efficiency, enhances regeneration processes, facilitates the elimination of toxins from the body, assists in the absorption of tocopherol.
Carotenoids
Carotenoids with antioxidant activity include β-carotene, lycopene, etc. β-Carotene is a precursor of vitamin A and has a similar biological effect, but its antioxidant activity is more pronounced. It increases stress resistance, helps to adapt quickly in unfamiliar and difficult conditions, mitigates the negative influence of radiation and chemical pollution, strengthens immunity.
Lycopene is the most powerful antioxidant from the carotenoid group, reduces oxidative stress, slows the development of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases, prevents tumor processes, stops the proliferation of cancer cells.
Antioxidant content in food
Antioxidants are present mainly in green, fruits, berries and vegetables of orange, red, yellow, purple flowers. It is believed that the more intense the color of the product, the more them in it. Products rich in antioxidants include red wine, cocoa powder, green and black tea.
Recommendation: In order to maximize the benefits of fruits, berries and vegetables, they should be used fresh or cooked on a steamed basis, and also based on fresh juices of various composition.
The content of natural antioxidants in food products is expressed in special units of antioxidant capacity - ORAC( Oxygen Radical Absorption Capacity - in Russian translation of "oxygen radical scavenging volume").The recommended daily intake of antioxidants entering the body from food for adults is approximately 5,000 ORAC.The values of antioxidant capacity for some products are listed below. Depending on the place and conditions of their growth, they may differ slightly in the smaller or larger side.
As can be seen from the table, antioxidants in food in large quantities are present in prunes, fresh fruits and berries. From vegetables, the red beans and artichoke are leading by their content. Among the three strongest natural antioxidants, berries are chokeberry, cranberries and wild blueberries. The highest rates of antioxidant activity in spices, but no one uses them in such large quantities to consider them as a source of antioxidants. In addition, spices are contraindicated in a number of diseases of the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, heart and blood vessels.Antioxidant preparations
The lack of antioxidants can be replenished and taking specially developed complexes of vitamins and dietary supplements, which are specially designed with regard to compatibility and synergy of individual components. Especially important is their reception for people with bad habits, suffering from severe chronic illnesses or living in an environmentally unfavorable environment, and also during the winter period when there are no fresh vegetables, berries and fruits.
The list of effective antioxidant preparations includes the following:
- Vitrum Antioxidant complex, contains vitamins A, E and C, trace elements - copper, zinc, manganese and selenium;
- Selenium Forte, the composition includes selenium and vitamin E;
- Synergin, contains vitamins C and E, rutin, lycopene and β-carotene, ubiquinone, lipoic and succinic acids, magnesium oxide;
- Resverilgin, contains polyphenol resveratrol, chitosan, coenzyme Q10, vitamins C and E, β-carotene, selenium, red wine extract and green tea leaves.
In addition to these, a number of drugs with antioxidant activity are also available. For example, Comlivit Selenium, Dihydroquercetin, Mexidol, etc.

Important: The choice of a specific antioxidant drug and its dosage should be performed by the doctor in consideration of the patient's health and individual characteristics.
Medicinal plants with antioxidant properties
Antioxidants are found not only in fruits, berries and vegetables, but also in some medicinal plants used in folk medicine for the treatment of various diseases. These include:
- Ginkgo biloba;
- Chamomile;
- Calendula;
- Ginseng;
- Ginger;
- Eleutherococcus;
- Mokritsa;
- Hawthorn;
- Donnik.
Plant antioxidants contained in these herbs increase the body's resistance, improve physical endurance, strengthen immunity, and normalize metabolism. They facilitate adaptation to new conditions, protect against harmful radiation, reduce the toxic effect on the body of harmful substances.
On the properties of antioxidants:
