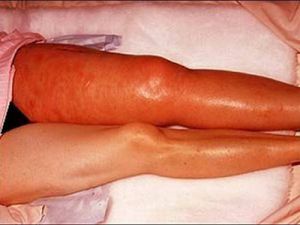
 Thrombophlebitis is a disease manifested in inflammation of the walls of venous vessels and accompanied by the formation of a thrombus in the vein. Possible and the reverse reaction, when a blood clot( thrombus), formed in a vessel, causes its inflammation.
Thrombophlebitis is a disease manifested in inflammation of the walls of venous vessels and accompanied by the formation of a thrombus in the vein. Possible and the reverse reaction, when a blood clot( thrombus), formed in a vessel, causes its inflammation.
Often, occurs as a result of damage to the vessel wall of the , even with an aseptic( non-microbial) trauma, but the ingress of an infection to the vein wall from surrounding tissues or otherwise( lymphogenous, hematogenous) can also initiate an inflammatory process.
The cause of such inflammation may be the presence of a foci of infection in the body - influenza virus, tuberculosis, caries and others.
The most is susceptible to this disease of the lower extremities veins , especially the large subcutaneous vein, but there is also thrombophlebitis of the upper extremities, cervical and thoracic areas.
Thrombophlebitis can affect both deep veins( such a disease is called "phlebothrombosis"), and superficial, located at a depth of 2-3 cm in fatty subcutaneous tissue.
Contents of
- Causes of
- Disease
- Disease classification
- Symptoms that indicate
- Differences from surface vein thrombosis
- Differences from varicose veins
- Diagnostic techniques
- Treatment activities
- Surgical intervention
- What is fraught with the disease
- Preventive measures
Causes of the disease
Basicthe causes of thrombophlebitis are associated with changes in blood composition and disorders of its circulation. But, as a rule, a cluster of factors contributes to the formation of a blood clot in a vein simultaneously.
Among them:
- Damage to the net of veins. The veins located close to the surface are usually thinner, so they are very prone to damage. The vessel can be injured even during treatment, during surgical intervention, catheter placement, injection.
- Disturbance of blood circulation. Slowing the movement of blood can lead to the formation of a blood clot. This can occur as a result of heart failure, when the heart is unable to pump normal blood volume, as well as with prolonged bed rest, gypsum application, the influence of other factors when the surrounding veins are compressed.
- Increased blood clotting. It can be both congenital and acquired, for example, as a result of taking some drugs, the transferred diseases.
The occurrence of these factors of can be affected by:
- diseases, especially infectious;
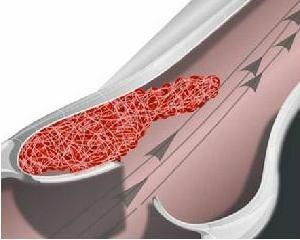
- trauma, which results in damage to blood vessels;
- surgical intervention;
- development of malignant neoplasms;
- injection by intravenous injection;
- allergic reactions;
- reception of contraceptives;
- pregnancy;
- problems with excess weight;
- thrombosis;
- decreased immunity of the body, for example, during vitamin deficiency;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- varicose veins;
- blood transfusion;
- and other causes leading to impaired blood circulation or composition.
Classification of the disease
By species, the disease can be divided into several groups, depending on the characteristics of the symptoms and the course of the disease.
The sharpness of the flow is distinguished by:
- Acute. Usually the duration of acute thrombophlebitis of superficial veins lasts up to a month. The patient feels the general symptoms of inflammation( pain, fever, chills, malaise).At the site of inflammation there is a slight swelling and hyperemia( blood vessel overflow).Depending on the presence of subcutaneous abscesses and suppuration of the affected veins, purulent and non-purulent thrombophlebitis are distinguished. Acute thrombophlebitis can be completely cured if measures are taken in the early days of the disease. Then he goes into subacute.
- Subacute. There is no inflammatory reaction, but there is pain periodically in the affected area. The skin around the affected area may have a brownish-bluish tinge. In the absence of proper treatment, subacute thrombophlebitis becomes chronic.
- Chronic. Can last for several years. On the site of the affected vessel appears a solid or clear-cut strand, touching which causes painful sensations. Also, pain occurs during exercise. Chronic thrombophlebitis can lead to the formation of trophic ulcers on the skin.
- Migratory. Some experts consider it a kind of acute thrombophlebitis. This species is characterized by the appearance of inflammation in several places at once. It can often be a symptom of a malignant neoplasm. Therefore, in addition to treatment is recommended to conduct additional research to exclude the possibility of tumor development.
Due to the development of , the following are distinguished:
- Infectious. This type of disease can occur as a result of surgical intervention, after childbirth, in the presence of purulent processes in the body, after the transfer of typhus.
- Aseptic .It occurs as a result of varicose veins, injuries, in which the vessels, pathologies of the cardiovascular system were damaged.
 You have suspicions of thrombophlebitis, but do you doubt not thrombosis of the lower extremities? Learn how to distinguish these diseases will help our material.
You have suspicions of thrombophlebitis, but do you doubt not thrombosis of the lower extremities? Learn how to distinguish these diseases will help our material.
With trophic ulcers, ointments are of particular importance. We will help you figure out how to choose wound healing ointments with trophic ulcers.
Symptoms that indicate
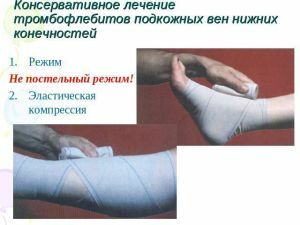
disease Among the main symptoms of superficial thrombophlebitis: the appearance of thrombophlebitis on the skin surface is the appearance of so-called nodules at the site of passage of vessels, the vein contour is clearly visible around the affected area, the skin can blush and the swelling of surrounding tissues is also possible; For example, reddening with thrombophlebitis is localized only around the affected vessel and does not increase with time, unlike redness caused by diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Venous thrombosis is a disease manifested in clotting of a vessel with a blood clot( thrombus).Thrombophlebitis is also accompanied by the formation of a thrombus, but, unlike thrombosis, is not limited to this, but leads to inflammation of the vessel wall. The difference between acute venous thrombophlebitis and varicose veins is that is accompanied by inflammatory reactions of , and varicose veins are not characterized by such symptoms. In addition, with thrombophlebitis there are reddening and swelling on the affected area, which is not observed with varicose veins. Chronic thrombophlebitis no longer has such pronounced external manifestations, but it can still be distinguished from varicose during palpation( a seal will be felt on the site of the affected vein). Currently, the diagnosis of superficial thrombophlebitis of both upper limbs and lower limbs is not a difficult task. The diagnostic aims is to detect thrombus in the vein of , determine its size and evaluate the risks. To solve these problems is applied such methods: Thrombophlebitis of superficial veins is allowed outpatient treatment and even treatment at home. The objectives of treating surface vein thrombophlebitis are, above all, preventing the formation of thrombi in the deep veins of , arresting inflammation, preventing recurrence of the disease. The peculiarity of the treatment is in maintaining the active mode of the patient in order to prevent the slowing of blood flow in the affected area. Most often with the thrombophlebitis of superficial veins conservative methods of treatment are used. Their goal is to stop the formation and spread of thrombi, neutralize inflammatory processes and pain sensations. Conservative methods for treating surface thrombophlebitis include: The photo shows schematically how venous thrombophlebitis is treated with phlebectomy If conservative treatment of superficial thrombophlebitis does not yield positive results, administration of treatment by surgery is possible. Also indications for surgical intervention are acute ascending thrombophlebitis and acute purulent thrombophlebitis. As a rule, surgery is used only for thrombophlebitis of superficial veins of the lower limbs, resulting from varicose veins. The operation quickly relieves the disease, prevents deep vein thrombosis and prevents relapse. Types of operative intervention: Consequences of thrombophlebitis of superficial veins: Prevention of thrombophlebitis of the surface veins: Differences from thrombosis of superficial veins
Differences from varicose veins
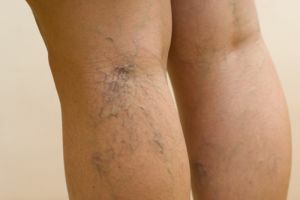 Thrombophlebitis is often a consequence of varicose veins. However, varicosity consists only in loss of elasticity of the vein walls, whereas thrombophlebitis is accompanied by the formation of a thrombus.
Thrombophlebitis is often a consequence of varicose veins. However, varicosity consists only in loss of elasticity of the vein walls, whereas thrombophlebitis is accompanied by the formation of a thrombus. Diagnostic techniques
Treatment measures
Surgical intervention

Than the disease
Preventative measures
