 Recommendations of the dentist regarding the intake of antibiotics must be taken into account, as in some situations without such drugs it is not possible to provide effective tissue healing.
Recommendations of the dentist regarding the intake of antibiotics must be taken into account, as in some situations without such drugs it is not possible to provide effective tissue healing.
When are antibacterial agents needed and how are they taken correctly?
Contents of
- When should I drink antibiotics after removal?
- Strict indications for taking antimicrobial drugs
- What drugs are prescribed?
- Popular variants of systemic antibiotics
- Local antiseptics
- Features of reception
- Painkillers
When it is necessary to drink antibiotics after removal?
The following factors that are prerequisites for prescribing antibiotics can be identified:
-
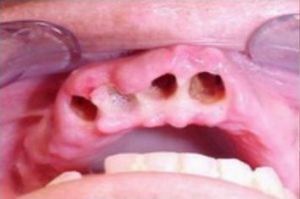
Dry hole
Damage when the tooth is removed from the wall of the socket, resulting in favorable conditions for inflammation of the bone tissue;
- Lack of proper care for the open hole after surgery, irregularity of antiseptic rinses. As a result, the hole is poorly cleaned of pathogenic microorganisms, which is dangerous for the development of the inflammatory process;
- Insufficient local immunity, the reduction of which is associated with the accompanying operation of stress;
- Incorrect thrombus formation with partial closure of the well. The presence of an open space allows bacteria to freely penetrate into the cavity.
In addition, doctors consider the need for taking aniobiotics, if as a result of a control examination of the hole revealed excessive redness of the tissues, their strong puffiness, the presence of necrotic or purulent contents.
Strict indications for taking antimicrobials
Do I need to drink antibiotics after tooth extraction? If it is a question of the development of a secondary inflammation affecting the tissue of the socket, the alveolar crest of the jaw, the trigeminal nerve, the periosteum, then the answer is unambiguous - yes. In such situations, dangerous complications develop in the form of:
-
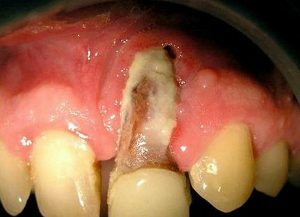
Osteomyelitis
Alveolitis, the symptoms of which include emerging after 2-3 days morbidity in the area of the hole, raising the temperature to 39 degrees;
- Periodontitis, associated with inflammation of the adjacent tissues of the tooth;
- Periostitis, in which the inflammation of the periosteum of the jaw is accompanied by a flux representing a swelling of the facial tissues;
- Osteomyelitis. A dangerous complication is the consequence of the destructive effect of bacterial flora on bone tissue and can be accompanied by the formation of fistula.
Another group for which antibacterial drugs are prescribed without fail are patients suffering from diabetes mellitus, oncological diseases, hematopoietic disorders, since the immunity reduced due to illness is not able to withstand the development of secondary infection.
What drugs are prescribed?
The physician should choose the right antibiotic based on the patient's condition, the presence of allergic reactions and the characteristics of the drugs themselves, which are as follows:
- Effective penetration of medical components not only in gum tissue, but also in bone;
-
 Cumulative effect, implying the creation of optimal concentration of the drug in the field of inflammation and in the blood as a whole for prolonged action;
Cumulative effect, implying the creation of optimal concentration of the drug in the field of inflammation and in the blood as a whole for prolonged action; - Preservation of the required concentration for a minimum of 8 hours for the convenience of taking the drug without disrupting the therapeutic effect;
- Susceptibility to the antibiotic of anaerobic and aerobic flora;
- Minimal toxic effects on the body and minimizing side effects;
- Ability to choose the form of the drug suitable for outpatient treatment.
Antibiotics used in dentistry are divided into systemic and local. Preparations of the first group have a general effect, affecting not only the inflamed part of the oral cavity, but also the whole organism.
Popular variants of systemic antibiotics
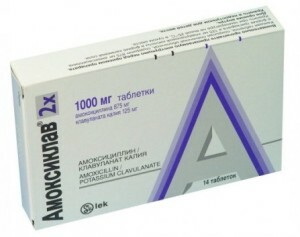 Augmentin( Amoxiclav). Refers to semi-synthetic antibiotics of the penicillin group. The main active substances of the antimicrobial preparation are clavulanic acid and amoxicillin, which facilitates rapid blockage of microbial enzymes.
Augmentin( Amoxiclav). Refers to semi-synthetic antibiotics of the penicillin group. The main active substances of the antimicrobial preparation are clavulanic acid and amoxicillin, which facilitates rapid blockage of microbial enzymes.
Augmentin is available in the form of powder for suspension( usually prescribed to children) or coated tablets. It is taken twice a day for 250 mg( 1 tablet) or three times a day for 20-40 ml when choosing a suspension( for children over 6 years of age, the dosage is reduced to 10 ml).
 Azithromycin( Sumamed). Is an antibiotic of macrolide group, differs by a complex multilevel formula of active substance in the form of azithromycin hydrate. The basic form is gelatin capsules with a white crystalline powder, which are taken, without separating, to ensure the effective absorption of the components of the agent directly in the small intestine. In dentistry, Azithromycin is used in the dosage of 250 mg of , assigning its twice daily to .
Azithromycin( Sumamed). Is an antibiotic of macrolide group, differs by a complex multilevel formula of active substance in the form of azithromycin hydrate. The basic form is gelatin capsules with a white crystalline powder, which are taken, without separating, to ensure the effective absorption of the components of the agent directly in the small intestine. In dentistry, Azithromycin is used in the dosage of 250 mg of , assigning its twice daily to .
 Num. The preparation of the fluoroquinolone group is effective if tooth extraction was performed against a background of other diseases of the oral cavity. The active substance is ciprofloxacin. Among the contraindications - children under 16 years of age, the period of pregnancy and breastfeeding, the presence of serious diseases of internal organs. The drug is prescribed for a single dose after a meal( the duration of treatment is at least 4 days).
Num. The preparation of the fluoroquinolone group is effective if tooth extraction was performed against a background of other diseases of the oral cavity. The active substance is ciprofloxacin. Among the contraindications - children under 16 years of age, the period of pregnancy and breastfeeding, the presence of serious diseases of internal organs. The drug is prescribed for a single dose after a meal( the duration of treatment is at least 4 days).
Local antiseptics
Local antibacterial agents have a direct effect on the affected area and are used as antiseptic solutions for rinses or gels.
Chlorhexidine.  The drug in a concentration of 0.05% is used in its pure form or use special medicinal compounds with the addition of other components. The peculiarity of chlorhexidine lies in the preservation of active properties in the treatment of a well filled with pus or blood and prolonged action, stretching for several hours.
The drug in a concentration of 0.05% is used in its pure form or use special medicinal compounds with the addition of other components. The peculiarity of chlorhexidine lies in the preservation of active properties in the treatment of a well filled with pus or blood and prolonged action, stretching for several hours.
Pre-oral cavity is cleaned of food residues by rinsing with water, after which the procedure is carried out using a tablespoon of the remedy. The duration of the course is a maximum of 12 days. With further use, the microflora of the oral cavity is destroyed.
 Miramistin. The drug at a concentration of 0.01% is an active antiseptic that promotes wound healing( even if the well is filled with purulent contents) and the normalization of local immunity. Can be assigned to children. Among the release forms are aerosols and vials with rinsing solution.
Miramistin. The drug at a concentration of 0.01% is an active antiseptic that promotes wound healing( even if the well is filled with purulent contents) and the normalization of local immunity. Can be assigned to children. Among the release forms are aerosols and vials with rinsing solution.
The interval between antiseptic rinses is from 2 to 4 hours. The procedure is carried out, taking a sip of the drug in the mouth and holding it in the area formed after removal of the socket. Then the solution is spat out. It should be remembered that rinses after tooth extraction are carried out very carefully without vigorous movements to prevent the blood clot from washing away. It is more correct to call such procedures baths.
 Metrogil Denta. This antiseptic is available in the form of a gel that is applied directly to the affected area with a clean finger, gently distributing the gel along the tissue adjacent to the well. Before applying the gel, antiseptic rinses are carried out using the methods described above. The treatment is done twice a day, maintaining after the application of the gel a two-hour interval before drinking and eating.
Metrogil Denta. This antiseptic is available in the form of a gel that is applied directly to the affected area with a clean finger, gently distributing the gel along the tissue adjacent to the well. Before applying the gel, antiseptic rinses are carried out using the methods described above. The treatment is done twice a day, maintaining after the application of the gel a two-hour interval before drinking and eating.
Features of
As already noted, only a doctor prescribes antibiotics, specifying the duration of treatment. Typically, the duration of the course is up to seven days. In the period of taking antibacterial drugs it is important to observe the following recommendations:
- Drugs are taken one hour before meals or two hours after meals, otherwise absorption of the drug will be difficult;
-
 For drinking use boiled water. Juices in this case are not applicable due to the destruction of the structure of the antibiotic ascorbic and fruit acids;
For drinking use boiled water. Juices in this case are not applicable due to the destruction of the structure of the antibiotic ascorbic and fruit acids; - If necessary, taking other drugs take into account their compatibility with the antibiotic. General recommendations imply a refusal to jointly take antibacterial drugs and antacids;
- It is advisable to exclude alcohol;
- Antifungal agents in the form of fluconazole, diflucan and others in combination with probiotics( bifiform, linex ) are additionally taken to minimize the negative effect of antibacterial drugs on flora of the mouth and intestines.
If after 2-3 days there is no positive effect of the prescribed drug, you need to revise the treatment scheme by choosing another remedy.
Analgesics
Removal of the tooth is often accompanied by strong painful sensations that occur after the end of the anesthesia. Pain can be observed for 3-7 days after surgery, so dentists prescribe special painkillers.
 Nimesil( Nyz). Provides rapid analgesia and has an anti-inflammatory effect. Available in the form of powder for the preparation of solution. In a day you can take the drug twice, not combining with the reception of food. To prepare an anesthetic composition, the contents of the sachet are poured into a glass of boiled warm water and mix well until complete dissolution.
Nimesil( Nyz). Provides rapid analgesia and has an anti-inflammatory effect. Available in the form of powder for the preparation of solution. In a day you can take the drug twice, not combining with the reception of food. To prepare an anesthetic composition, the contents of the sachet are poured into a glass of boiled warm water and mix well until complete dissolution.
 Ketanov. This drug belongs to the category of prescription drugs, so it is indicated for unbearable severe pain. Take Ketanov with caution because of the large number of adverse reactions. As a rule, dentists prescribe taking 1 tablet twice a day. The maximum daily dose is limited to 4 tablets.
Ketanov. This drug belongs to the category of prescription drugs, so it is indicated for unbearable severe pain. Take Ketanov with caution because of the large number of adverse reactions. As a rule, dentists prescribe taking 1 tablet twice a day. The maximum daily dose is limited to 4 tablets.
Dexalgin. Effective for relieving toothache and normalizing the general condition. In addition to anesthesia reduces inflammation, contributes to a decrease in temperature.  Contraindications include children's age, pregnancy and lactation, the presence of stomach ulcers, cardiac, kidney and liver disorders. The effect of the drug begins half an hour after its administration and is maintained for 5-6 hours. The dosage is determined by the doctor.
Contraindications include children's age, pregnancy and lactation, the presence of stomach ulcers, cardiac, kidney and liver disorders. The effect of the drug begins half an hour after its administration and is maintained for 5-6 hours. The dosage is determined by the doctor.
What else to take after removal, the dentist will tell:
The use of antibiotics and analgesics should not be uncontrolled. It is important to understand that non-compliance with recommendations can result in the development of serious complications that are difficult to cure. Of course, antibacterial drugs are not the most "harmless" drugs, but in most cases they are prescribed in minimal doses, so the harm to the body is minimized, and the benefits become unquestionable.
The main thing - to strictly follow the prescribed recommendations and assess your own feelings, reacting to the slightest negative changes
