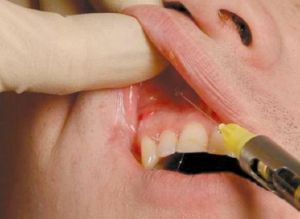
 Infraorbital( infraorbital) anesthesia is a kind of local conductive anesthesia used in dentistry and maxillofacial surgery.
Infraorbital( infraorbital) anesthesia is a kind of local conductive anesthesia used in dentistry and maxillofacial surgery.
The purpose of this method of anesthesia is to create an anesthetic depot in the place of exit from the infraorbital canal of the nerve, which conducts pain sensitivity to the middle third of the face.
Contents
- Related methods of anesthesia
- Anesthetic area
- Indications and contraindications
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Techniques used
- Possible complications
Related methods of anesthesia
The main types of local anesthesia that are used in dentistry are infiltration and wiring. Infiltration is carried out directly in the area of dental intervention and its action lasts no more than one and a half to two hours. The needle is inserted, as a rule, in the projection of the apex of the root of the tooth to be treated.
In the conductive method of anesthesia, the solution is administered at a certain distance from the tissues to be operated - to the place where the nerve lies, which transmits pain impulses to the surgical intervention zone.
Anesthetic injected perineurally, that is, it is released from the needle around the nerve trunk. Endo-neural injection, directly into the nerve thickness, is possible only on special indications and can cause serious complications.
The infraorbital nerve, leaving the infraorbital foramen, divides into several branches called the "small crow's foot".These branches conduct pain sensitivity to the areas of the middle third of the face from the corresponding side.

Anesthetic area
Infraorbital anesthesia blocks pain sensitivity in the following areas:
- angle of the eye and lower eyelid;
- cheek and infraorbital area;
- sidewall of the nose along the entire length, including the nose wing;
- bone and mucosa of the maxillary sinus;
- upper lip;
- the vestibular part of the gingiva of the upper jaw;
- lateral incisor, canine, premolars and molars of the upper jaw.
With this type of anesthesia, it is often not possible to achieve effective anesthesia of the central incisor and the second premolar, because pain sensitivities also occur in the nerves of the opposite side of the face, the so-called anastomoses.
In this case, it is also necessary to apply the infiltration method of anesthesia-the introduction of an anesthetic directly into the tooth region.
Indications and contraindications
Indications for use of infraorbital analgesia.
For prolonged and traumatic operations in the area of two or more teeth: 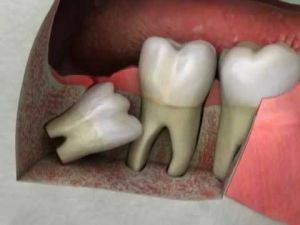
- a complex removal of atypically located( retinirovanny and dystopic) teeth;
- implantation;
- cystectomy( surgery to remove cysts);
- removal of neoplasms on the upper jaw.
For inflammatory lesions in the upper jaw area:
- periostitis;
- osteomyelitis;
- drainage of purulent foci.
In the treatment of 2-3 or more teeth simultaneously:
- multiple simultaneous removal or treatment of teeth;
- preparation of teeth for orthopedic constructions.
In modern dentistry, indications for conductive anesthesia are not so many, compared with the past, when this method of anesthesia was used in 75-80% of cases of all dental manipulations. This is due to the fact that now use drugs of a new generation with a much more powerful analgesic effect than before.
Contraindications:
- allergic intolerance or hypersensitivity to anesthetic solutions;
- trauma of maxillofacial area, at which the anatomical position of tissues is changed, which makes it impossible to perform anesthesia;
- traumatic operations lasting more than 2-3 hours;
- violation of the patient's psyche or its instability;
- series of cardiovascular diseases, recently suffered heart attack;
- pregnancy.
Advantages and disadvantages of
Advantages of infraorbital analgesia: 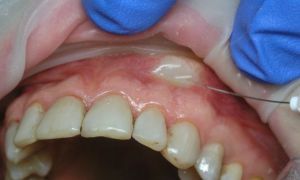
- allows blocking pain impulses in a large area of the maxillofacial area;
- long-term action of this type of anesthesia - up to 2-3 hours;
- powerful anesthetic effect is achieved by a small amount of anesthetic solution;
- the possibility of anesthesia in the presence of purulent foci in the tissues.
The disadvantages include the complexity of implementation and the high risk of complications.
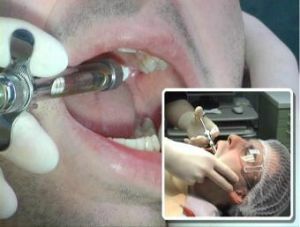
Techniques used
Extraoral( external) method:
- in the projection of the infraorbital opening with the left index finger, it is necessary to press soft tissues to the bone to prevent their displacement and trauma of the eyeball;
- deviate from this point down the center by 5 mm, insert the needle, directing it up, back and out until contact with the periosteum, release 0.5-1.0 ml of the drug, then with caution seek the mouth of the canal with a needle;
- entering the canal, which is confirmed by a sense of failure, the needle is injected by 7-10 mm and, after an aspiration test, 0.5-1.0 ml of the drug is withdrawn, the anesthetic effect is manifested after 3-5 minutes.
Intraoral method: 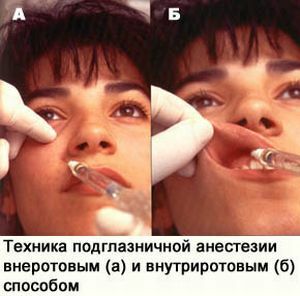
- in the projection of the infraorbital opening with the left index finger it is necessary to press soft tissues to the bone, with the thumb to pull the lip upward, to the index finger;
- the needle is punctured between the canine and the first premolar by 5 mm above the transitional fold, moving outward, upward and posteriorly to the infraorbital canal;
- , the same actions are repeated as for the external method.
Possible complications of
If the rules and proper technique are not observed, the following complications may occur:
- bleeding;
- hematoma;
- post-traumatic neuritis;
- eye needle damage;
- muscle blockade of the eye;
- diplopia( double vision);
- edema of the lower eyelid;
- ischemia( decreased blood supply) of an isolated area below the orbit.
 To avoid complications, it is necessary to strictly follow the technique of anesthesia, adhere to anatomical landmarks, mandatory to perform an aspirate test.
To avoid complications, it is necessary to strictly follow the technique of anesthesia, adhere to anatomical landmarks, mandatory to perform an aspirate test.
An aspiration sample is performed to ensure that the needle does not enter the blood vessel and that the anesthetic solution will be released into the tissues surrounding the nerve. For this, before introducing the solution, the syringe piston is pulled back on itself. The appearance in the blood syringe indicates that the needle is in the vessel.
The infra-orbital technique of anesthesia is an effective method of anesthesia, which has many advantages. However, it should be remembered that only an expert with relevant knowledge and experience should conduct it.
