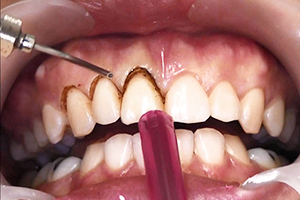
 Periodontitis refers to the diseases that dentists face most often. It is formed due to the development of the inflammatory process on the surface of the gums, which eventually spreads to soft tissues.
Periodontitis refers to the diseases that dentists face most often. It is formed due to the development of the inflammatory process on the surface of the gums, which eventually spreads to soft tissues.
The cause is bacterial plaque, formed due to poor hygiene of the oral cavity. Over time, dental plaque turns into stones that begin to expand deep into the gums, and form dentogingival pockets in which the division and growth of pathogenic microorganisms occurs.
Gingivotomy is used to treat advanced stages of periodontitis.
- Contents General characteristics
- Indications and contraindications for the intervention
- preparatory stage
- surgical stage
- rehabilitation period
- Consequences and complications
- It is interesting
General characteristics
gingivotomy - linear incision periodontal pockets to remove an abscess formed due to periodontitis. During the process,  can be produced in different shapes: vertical, incisions through the interdental papilla, and semilunar sections.
can be produced in different shapes: vertical, incisions through the interdental papilla, and semilunar sections.
When opening the pocket, it is treated with disinfected solutions and antiseptics, curettage is done, and again neutralization is carried out.
Biologically active substances are introduced, the gums are adhered with special dental glue. The last step is to cover the gums with a film or bandage for a few days before the wound is healed. When the abscess is removed, the seams are not applied. Enzymes, inhibitors and other BAS are injected into the oral cavity.
Indications and Contraindications for Intervention
The dissection of the wall of the periodontal pocket is a complex and responsible procedure for both the patient and the doctor, so it should only be done in some cases.
This intervention is recommended for periodontitis of medium or severe form, which develops with severe gum lesions, proliferation of gingival pockets and a lot of purulent discharge, abscesses. Gingivotomy is also necessary in case the dentogingival pockets are too narrow.
The procedure has a fairly large list of contraindications. Therefore, before the operation, it is necessary to make a qualitative and comprehensive diagnosis.
This type of intervention is not recommended in such cases:
- circulatory disorder, leukemia;
- heart problems;
- diseases with endocrine gland;
- problems with the nervous system, accompanied by an unstable psychoemotional state;
- malignant neoplasms in the anamnesis.
Also, the dental surgeon should examine the oral cavity of the patient and make sure that the patient has the right bite, good hygiene of the teeth and the whole oral cavity, there are no disturbances in the bone tissue. Otherwise, the operation is prohibited.
Preparatory stage
 Before the surgery, the patient is taught proper oral hygiene, the dentist cleans all stones and other deposits on the teeth, puts seals, if necessary, and checks the existing ones.
Before the surgery, the patient is taught proper oral hygiene, the dentist cleans all stones and other deposits on the teeth, puts seals, if necessary, and checks the existing ones.
If the seals are in poor condition, you need to replace them. Diagnosis includes radiography of the jaws, a laboratory study using a biochemical analysis of blood and urine.
Surgical stage
During the procedure, the entire differentiated tissue is cut out. This refers to:
- proliferation of the outer layer of the epithelium;
- hardened areas located in the root of the tooth;
- abscesses.
The dentist cuts the dentogingival pocket and cuts the gum line. Curettage is done, treatment with saline is carried out.
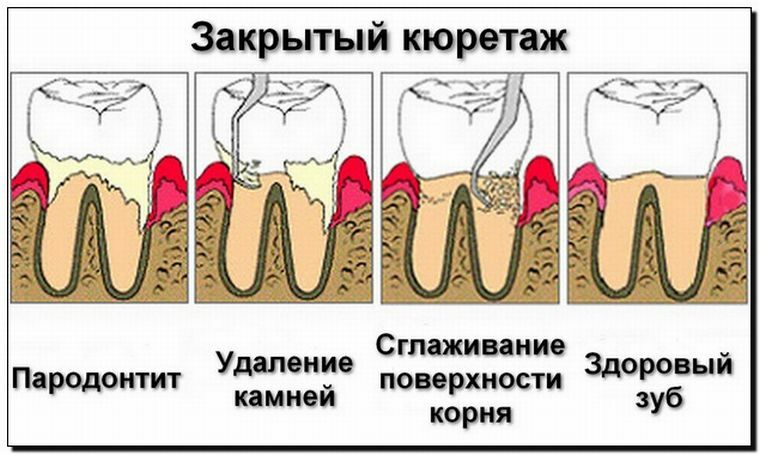
The remaining pocket is closed, a cut and discarded piece of gum is applied, seams and a protective bandage are adjusted for several days until the seams are overgrown.
Standard operation is performed using a scalpel. But now the use of laser gingivotomy( video procedures below) is popular.
The laser procedure has a lot of advantages: 
- during the operation is completely sterile;
- no injury;
- laser does not tolerate heavy bleeding;
- reduces pain;
- heals the wound faster.
This method is safe and does not cause any discomfort to the patient or dentist.
Rehabilitation period
After the operation, the patient should carefully monitor the oral cleanliness. In the place where the procedure was performed, treatment with antiseptic agents using a cotton swab is recommended.
Herbal decoctions will also be useful. They can simply drink or rinse your mouth. It is important not to damage the gum while eating food.
Consequences and complications of
If a wide gingival pocket is formed, then gingivotomy will not help, becauseit is difficult to protect against inflammation. There is a risk that food pieces may remain in it, which adversely affects the effectiveness of treatment.
Large cavities near the gums complicate healing, so in such cases it is better to use gingivectomy. In other cases, the imposition of quality sutures prevents the consequences.
It's interesting
Filed under: asked - answered.
Question: How long does the operation last?
Answer: The operation does not last long - only 30 minutes. Stitching takes place 2-3 days later.
Question: What herbs are recommended to treat the oral cavity after the intervention?
 Answer: processing can be done with chamomile broth. It is very simple to prepare: 1 tbsp.raw pour a glass of boiling water.
Answer: processing can be done with chamomile broth. It is very simple to prepare: 1 tbsp.raw pour a glass of boiling water.
Boil a little and leave to stand overnight. Then drain the broth and rinse mouth cavity several times a day. In the same way can use and thyme. These herbs have antiseptic and wound-healing properties.
To reduce bleeding and disinfection, nettle infusions will be helpful. They are prepared in a similar way.
Question: How is it with anesthesia before and after treatment?
Answer: Before surgery, local anesthesia, and after the procedure, when the action of anesthesia will pass, you can take several painkillers tablets Nospy or Spazmalgona.
Question: How much does an operation cost?
Answer: Such a procedure is not cheap. If you hold gingivotomy within 1 tooth, the price is from 750 rubles, and if you do a laser procedure, then from 960 rubles. Here, the quality of medical material and the biologically active substances used are taken into account.
