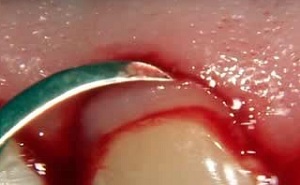
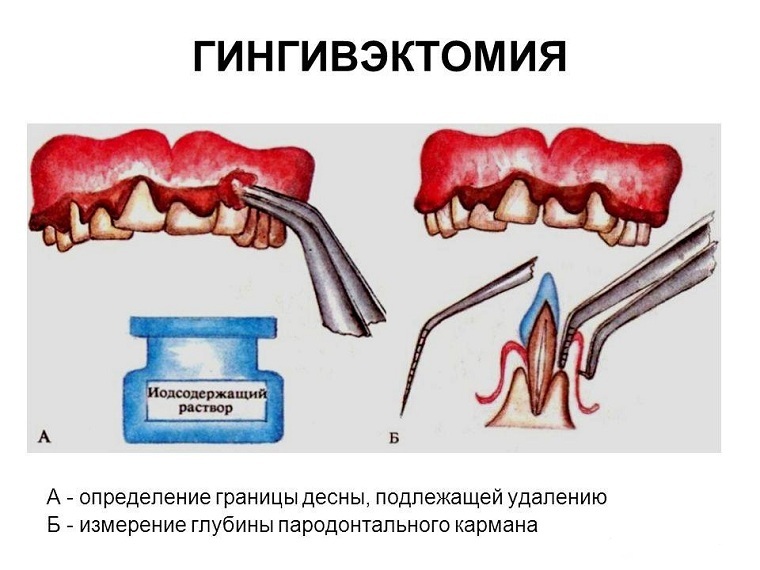
 Gingivectomy is an operation to remove the inflamed edge of periodontium in order to get rid of the gingival pockets.
Gingivectomy is an operation to remove the inflamed edge of periodontium in order to get rid of the gingival pockets.
This kind of surgical procedure, as a rule, is performed by the maxillofacial surgeon or periodontist.
The essence of the operation is to excise inflamed gingival tissue and reduce the depth of the periodontal pocket.
Contents
- Why does parodontium grow?
- When is it necessary to excise the tissues in the gum area?
- Restrictions for surgical resolution of
-
- Possible complications
- Frequently asked questions
Why does parodontium grow?
The periodontal pocket is a small cavity between the gum and the tooth. The gum tissue forms a so-called neck around the tooth.
In the formed cavity, food particles, deleted epithelial cells and microbes remain. The main reason for the formation of an inflamed pocket is poor oral hygiene. In the absence of constant and high-quality tooth cleaning, the scuff gradually becomes  in stone.
in stone.
At the same time the inflammatory process begins to develop on the gum, as a result of which its edge begins to expand. The more the stones accumulate, the more there will be a dentist's pocket.
If in time to not clean the inflamed pocket, then all microorganisms penetrate deep into and damage bone tissue, parodont, cement and root.
To avoid such problems and apply gingivectomy, which is possible even with periodontitis of moderate complexity.
When is it necessary to excise the tissue in the gum area?
In most cases, gingivectomy is prescribed for periodontitis in the case of ineffectiveness of other treatment methods:
- deep scaling of the gingival cavities( curettage);
- drug therapy with the use of antibiotics;
- polishing the roots of the teeth and eliminating pathological tissues.
The following diseases and disorders are also indicative for prompt intervention for the removal of inflamed pockets: 
- epulis;
- gingival fibromatosis;
- defective gingival contour against ulcerative necrotic gingivitis;
- the presence of soft tissue flaps around the crown of the tooth;
- need to correct the edge of the seal( for subgingival location).
Restrictions for surgical resolution of
Contraindications to intervention:
- weak immune system;
- presence of subacute bacterial endocarditis;
- cirrhosis;
- presence of congenital heart disease;
- presence of strands and bridles in the area of the operated site;
- narrow area of the attached gingiva;
- started periodontitis;
- deep bone pockets( more than 5mm).
Preparatory stage
 The preparatory stage for the operation is professional dentistry and anesthesia. Cleaning of the teeth is carried out with the aim of destroying plaque, tartar and food residue, since all these deposits are a breeding ground for the reproduction of bacteria.
The preparatory stage for the operation is professional dentistry and anesthesia. Cleaning of the teeth is carried out with the aim of destroying plaque, tartar and food residue, since all these deposits are a breeding ground for the reproduction of bacteria.
Operative intervention is performed under local anesthesia. After the introduction of painkillers the doctor proceeds directly to the operation itself.
Surgical stage
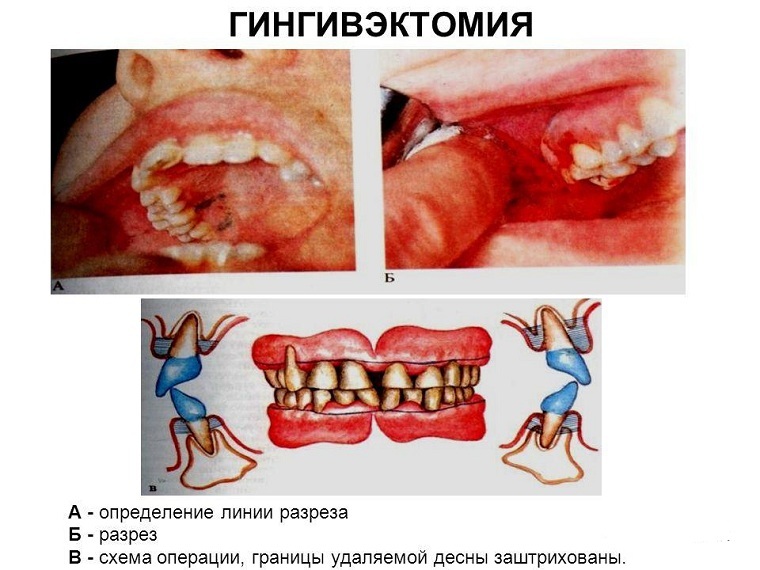
Gingivectomy is performed using three techniques:
- Simple .Initially, a wave-like dissection of the gum and periosteum is carried out in the region of the inflamed periodontium. After this, the same incision must be made from the oral cavity. Vertical dissections are performed at the ends of each of the cuts. The separated gum is eliminated, followed by curettage of the bone cavity and wound surface. At the end of the operation, a gingival bandage is applied to the wound for forty-eight hours.
- Gentle( partial) .It is carried out in general terms as well as simple. In this case, not all the wall of the periodontal pocket is cut, but a small part of it( 2-3 mm).The remaining part of the pocket is curettage.
- Radical .This is a more complicated operation, since during its implementation the bone tissue of the alveolar arch of the jaw is captured. Operative intervention begins with wave-like incisions. Then, together with the edge of the gum, epithelial cords, granulation tissue and affected areas of the bone are removed. Alignment of the alveolar arcs is then performed. At the end of the operation, a special gingival bandage is applied over the wound for its rapid healing.
Laser application
Laser gingivectomy is performed using the technologies of the three above mentioned methods. Instead of a scalpel, a laser is used.
The advantages of this technique include the following:
- the lowest probability of complications;
- short rehabilitation period;
- minimal gum trauma and fast tissue healing;
- slight bleeding and less soreness.
Rehabilitation period
If the surgery has been successful, then the recovery period will not be long. To prevent various complications, the patient must follow all the doctor's recommendations.
During the rehabilitation period, it is desirable to avoid many chewing loads and not to take too cold or hot food.
It is also recommended that you stop taking alcohol and smoking. In addition, doctors recommend that the following prescriptions are adhered to:
- is an exception to the food ration that damages and irritates the gum;
- teeth cleaning should be done only with a soft toothbrush, which will not injure the wounded gum;
- use only warm food.
Possible complications of
One of the most common consequences is the infection of the gum as a result of bacteria entering it during the operation. With weakened immunity, the patient may develop periodontitis or periodontitis.
It is also possible to develop complications in the presence of chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system and contamination tissues. To prevent negative consequences before the operation, the dentist must collect a complete medical history of the patient.
Frequently Asked Questions
From the series: asked - answer.
Question: What kind of food and drinks can not be consumed after the operation?
Answer: First of all, it is not recommended to eat too cold and hot food, as well as drinks, since this will only slow down the  recovery process. In addition, a sharp temperature drop can trigger a secondary inflammation of the gums. Also, you can not take solid food( nuts, seeds, etc.) to not further injure damaged tissue.
recovery process. In addition, a sharp temperature drop can trigger a secondary inflammation of the gums. Also, you can not take solid food( nuts, seeds, etc.) to not further injure damaged tissue.
Question: Is it possible to correct the "gingival" smile with gingivectomy?
Answer: It is possible, because the procedure, in most cases, is carried out with an aesthetic purpose. After the operation, the teeth visually increase in volume. The descreen contour changes and becomes more correct and attractive.
Question: Can wearing braces or crowns be a contraindication for an operative intervention?
Answer: Crowns and braces do not affect the possibility of surgical manipulation. However, in the presence of braces, there can be certain difficulties in the hardware cleaning of teeth.
Question: How long will there be unpleasant feelings after the end of treatment?
Answer: The presence and duration of discomfort after surgery depends primarily on the individual characteristics of the patient's body. It also depends on the technology of performing surgical intervention. When using a laser, the rehabilitation period is as short as possible.
Question: How much will the whole complex of services cost?
The price depends on the type of technique used, - so the average cost of laser gingivectomy is 500-700 rubles( with the intervention in the area of one tooth), and the average with the scalpel is 350-500 rubles( per tooth).
