 The jaw of modern humans is 10-12 mm smaller than that of the ancient inhabitants of the Earth, since the chewing load on it decreased because of the transition to softer, thermally processed food during evolution.
The jaw of modern humans is 10-12 mm smaller than that of the ancient inhabitants of the Earth, since the chewing load on it decreased because of the transition to softer, thermally processed food during evolution.
Therefore, the wisdom teeth, located last in the dentition, lost their chewing functions and began to be considered rudimentary.
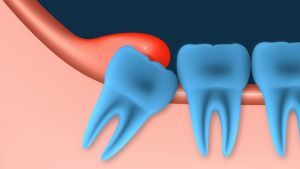
Third molars or "eight", as dentists call wisdom teeth, usually begin to grow at 14-25 years and even later. Although there are two rudiments in each of the upper and lower jaws in each of the upper and lower jaws, not all of them can cut through quite often, having remained retinished, closed bone or gum tissue or cut through only a part of the crown, remaining half-retininated.
G8 grows and forms very long, for years, and for some decades, with alternating periods of development and rest. They do not have dairy precursors, by the time of such late appearance they may not have free space in the dentition, they are difficult to clean because of an uncomfortable extreme position.
All these features can lead to the development of pathologies, complications during and after eruption, after removal, often being 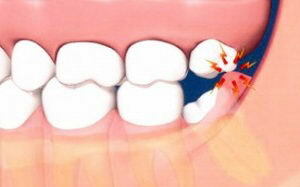 traumatic.
traumatic.
The most common problem is inflammation, swelling and tenderness of the gums near the wisdom tooth.
The causes of inflammation and swelling of the gums may be eruption and complicated sprouting of the wisdom tooth, pericoronaritis, caries, inflammatory and infectious processes in the root and surrounding tissues.
Contents
- Injection and complicated germination
- Development of pericoronaritis
- Caries, infections and inflammatory processes
- Relieve inflammation and pain
- First aid
- Folk remedies
- Professional help
- What if the gum was swollen after tooth extraction
Teething and complicated sprouting
Wisdom teeth can eruptin several stages, in most people this process is accompanied by soreness, swelling and inflammation of the surrounding soft tissues.
This is due to the fact that the eights do not have any milk predecessors, and the large third molars have to break through the thickened bone tissue of the alveolar process, causing a lot of unpleasant sensations.
The lack of space at the end of the dentition causes a complicated germination, a dystopic position, when the eights grow in the wrong direction, on the cheek, under an inclination, are injured by adjacent teeth, and damage the roots of adjacent teeth.
A dystopic tooth has a load on the entire dentition, resulting in bite deformities.
Development of pericoronita
As a result of prolonged or complicated sprouting of the wisdom tooth, the gum may partially move away, forming a gingiva over it.
The remains of food accumulate under the hood, causing the multiplication of pathogenic bacteria, the mucous membrane is injured when biting on the tooth, which leads to the development of a non-infectious inflammatory process in the surrounding tissues and the appearance of pericoronaritis.
In its current this dental disease can be acute, flowing in the catarrhal or purulent form and chronic.
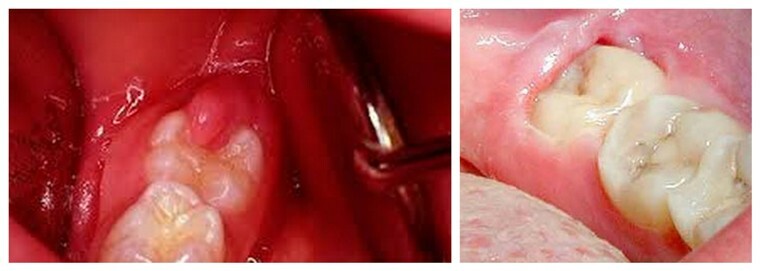
Pericoronaritis looks so
Pericoronoritis is accompanied by:
- gum disease with chewing and palpation;
- with severe pain, giving in the temple and ear;
- swelling of the mucosa;
- with an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- by excretion of pus;
- restriction of mouth opening;
- increased body temperature;
- by enlarging the lymph nodes under the lower jaw.
The chronic form of the disease recurs regularly with the symptom of acute purulent pericoronaritis.
The absence of timely treatment of perecoronite threatens with extremely dangerous complications - the formation of peri-jaw phlegmon, osteomyelitis of the jaw, periostitis, abscess. Therefore, if there are signs of it, you should immediately contact your dentist.
The doctor prescribes treatment depending on the form and stage of the disease, it can be medicated, or surgical, consisting in dissection or complete excision of the inflamed hood.
Caries, infections and inflammatory processes
 Difficulty hampering complete hygiene, complicated, delayed or incomplete eruption, structural features dictate the predisposition of eights to caries, inflammatory and infectious processes in the root and surrounding tissues of the tooth.
Difficulty hampering complete hygiene, complicated, delayed or incomplete eruption, structural features dictate the predisposition of eights to caries, inflammatory and infectious processes in the root and surrounding tissues of the tooth.
If the gingiva is inflamed, swollen and sore, it could mean that the wisdom tooth is affected by one of the following dental diseases or conditions:
- Caries , including a repaired dystopic tooth. Often, third molars grow with signs of significant destruction of the outer part, it does not protect against destruction and their presence in the gum.
- Pulpitis, periodontitis , a complication of advanced caries, as well as periodontal cyst.
- Fistula, flux, abscess , formed due to the penetration of microbes into the tooth and the development of purulent-inflammatory processes.
Relieve inflammation and pain
It is possible to avoid pain and swelling of the gums near the wisdom tooth with its eruption, even if it grows and develops correctly, without complications.
In this case, analgesics are effective, special dental gels and ointments containing anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antiseptic components, pharmacy solutions for rinsing.
First aid
What can be done to relieve inflammation and pain from the gums at home:
- To drink an anesthetic pill - Tempalgin, Nais, Nimesil, Nimesulid, Analgin, Paracetomol, Ketanov.

- Lubricate the swollen gingiva with gel or ointment - Metrogil-Denta, Solcoseryl, Kholisalom, Kamistad, Kalgel, Dentinox.
- Rinse mouth with pharmacy solutions - Furacilin, Chlorhexidine 0,05%, Miramistin 0,01%.
For the removal of inflammation in pericoronaritis, the pocket under the gingival hood should be rinsed with a solution of antiseptics: Furacilin, Iodoform, and Marganzovka.
Folk remedies
In the initial stages of inflammation, folk remedies can be used as auxiliary ones, in certain situations giving a good result. The most frequently used infusions and herbal medicinal herbs, which have antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, wound-healing and disinfecting properties.
Grasses boil with boiling water in the proportions of 1 teaspoon per glass of water, insist, filter and rinse the mouth 4-6 per day. The most effective decoctions of the following plants:
- sage leaves;

- of chicory roots;
- collection of chamomile, lemon balm and oak bark;St. John's wort;
- calendula.
An analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect has a weak saline solution and a solution of baking soda in the proportion of a teaspoon per glass of water. They can rinse your mouth 3-5 times a day.
Professional help
The most correct thing to do in case of pain, inflammation and swelling of the gum of the wisdom tooth is to consult a doctor.
The dentist will determine the cause by visual inspection or X-ray and will prescribe the appropriate treatment:
- Medical treatment consists in the appointment of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antihistamines,
 anti-inflammatory ointments and gels for gums, trays with antiseptics.
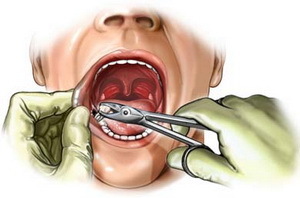
anti-inflammatory ointments and gels for gums, trays with antiseptics. - Surgical intervention is to cut the gums to facilitate the process of eruption, dissection or excision of the gingival hood, and also to remove the problem wisdom tooth, if the situation can not be resolved in other ways.
- In cases of severe pain, severe swelling of the gingiva and reduction of the jaws, is assigned to the novocain blockade .
- The laser therapy has a good anti-inflammatory effect when infrared radiation is applied to the affected area.
What if the gum is swollen after tooth extraction
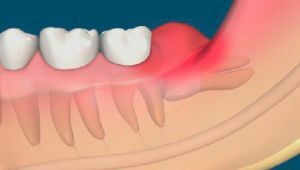 Wisdom tooth removal is often traumatic because of its large size, uncomfortable position, partial retinitis.
Wisdom tooth removal is often traumatic because of its large size, uncomfortable position, partial retinitis.
If the gingiva after swelling is strongly swollen and hurts more than 2-3 days, and the pain increases in intensity, this may be a sign of alveolitis - inflammation of the walls of the hole due to infection in the wound, bone fragments.
The cause of development of the alveolitis can also become too early washing out of the blood clot from the wound from frequent rinsing of the mouth after extraction of the tooth.
Symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- sharp pain in the area of the socket and gums;
- swelling and redness of the mucous gums around the socket;
- no blood clot in the hole before 7 days after tooth extraction;
- purulent discharge from the hole, bad breath;
- increase in body temperature, deterioration of well-being, increase and soreness of submandibular lymph nodes.
Puffy gum in the wisdom tooth may be the first sign of the development of serious dental diseases leading to dangerous consequences. Therefore, do not self-medicate, it is better to seek help from a dental clinic as early as possible.
Determine the cause of inflammation and pain only after a preliminary examination.
