 Quite often, patients turn to dentists with a problem such as a tooth dislocation. What is this form of injury?
Quite often, patients turn to dentists with a problem such as a tooth dislocation. What is this form of injury?
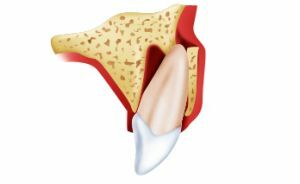
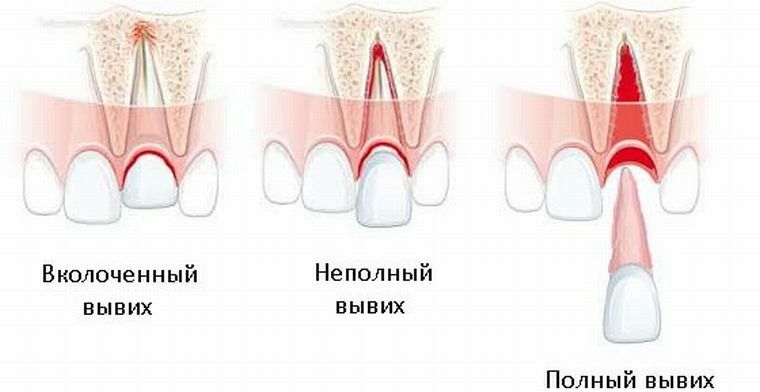
When the dislocation occurs, the position of the tooth is changed and its displacement from the alveolar cavity, in addition, the connective tissue is damaged. In medicine, there are several types of dislocations of the tooth: nailed, incomplete and full.
Contents of
Causes of trauma
Causes of injury
Trauma can occur due to several factors:
- falling , in which the whole blow takes the tooth, blow and stuff;
- can be caused by ingestion of solids , which should not be there, also excessive rigidity and hardness of the products;
- negligent attitude of , that is, opening bottles with teeth and other prohibited manipulations;
- unprofessional or incorrect removal of teeth , as a result of which a dislocation of a nearby cutter occurs.
Features of the clinical picture
Symptoms with a dislocation of the tooth will differ, depending on the shape of the injury, in fact this plays a huge role in the diagnosis.
Each form of the injury has its own clinic and signs:
- If the tooth remains in place and the connective tissue is not completely ruptured, the incomplete is diagnosed. There are cases when during a trauma the vascular-neural bundle is not ruptured, this occurs when the tooth turned around its axis. With this form of injury, biting and chewing causes discomfort, painful sensations appear, and strong tooth mobility is noted. Also, when examined in the mouth, there may be abrasions and wounds, on the lips and mucous cheeks due to injury
 there are hematomas. In addition, with respect to adjacent teeth, the crown of the damaged tooth will have an incorrect position.
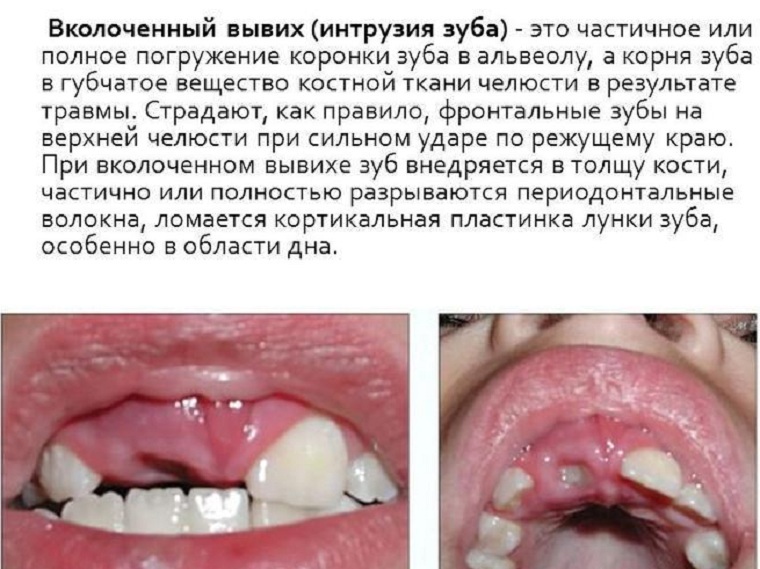
there are hematomas. In addition, with respect to adjacent teeth, the crown of the damaged tooth will have an incorrect position. - Twisting of the tooth into the bone is observed with the nested form dislocation( so-called intrusion).This form is quite dangerous, as when injuring the tooth of the upper jaw, it can screw into the maxillary sinus or nasal cavity. If a dislocated dislocation of the tooth is noted, the patient feels pain when eating the food, and around the damaged tooth, the gum bleeds. But, at the same time, the tooth remains motionless, although it changes its position and is in relation to the rest of the teeth incorrectly, inclined or rotated along the axis. If you tap on the tooth, then there is no pain, as in the case of other forms. There is also swelling in the affected area, inflammation, hypermobility, if you press on the gum, you may experience pain.
- On , a complete dislocation indicates a rupture of the neurovascular bundle and connective tissue. As for the tooth, in this case, it completely leaves first the site, in some cases it can be held there only by the gum tissue and symptoms of incomplete form appear. If the tooth falls out, a blood clot forms in the hole, if it remains in place, then there is a strong mobility.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnostic methods are selected individually for each case, thus incomplete dislocation can be established based on examination of the injured area. With this form of trauma, the mobility of the entire root will be felt during manipulations conducted by a specialist.
Also, when viewed, there is an increase in the interdental spaces on both sides of the damaged tooth. In addition, there is pain syndrome with percussion, enlarges the dentogingival fissure along the entire circumference, from the side into which the tooth is displaced a bit more.
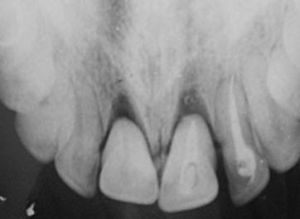 In some cases specialists use X-ray diagnostics to exclude root fracture. On how much the tooth was shifted, the widening of the periodontal gap depends. If there is a strong displacement, the tip of the root leaves the bottom of the alveoli. If a dislocation of the canines and incisors of the lower jaw has occurred, the absence or narrowing of the periodontal gap will be seen on the x-ray, this is due to the structure of the roots of these teeth.
In some cases specialists use X-ray diagnostics to exclude root fracture. On how much the tooth was shifted, the widening of the periodontal gap depends. If there is a strong displacement, the tip of the root leaves the bottom of the alveoli. If a dislocation of the canines and incisors of the lower jaw has occurred, the absence or narrowing of the periodontal gap will be seen on the x-ray, this is due to the structure of the roots of these teeth.
To obtain more accurate information, a three-dimensional computerized tomography is performed. This study allows you to study the structure of the tooth at any angle.
Electroodontodiagnosis is also performed in order to determine the state of the pulp, bone tissue of the alveoli and periodontal tissue. In some cases, these areas may not remain viable, and therefore additional diagnostic methods are needed.
At the same time, the degree of reaction of the nerves of the tooth to electric current is determined in the course of the study. If the procedure is performed for a short time after the injury, then the sensitivity can be significantly reduced, so these manipulations can be carried out more than once a few weeks after injury.
Methods of treatment
To begin with, you should determine whether it is worth starting to work on restoring and preserving such a tooth or it will be more expedient to remove it. This can be determined by the state in which the bone tissue is located in the affected area. If more than half is left in order, then such a tooth is best preserved.
In general, tooth dislocation treatment, regardless of shape, implies a whole complex of manipulations that are carried out with the purpose of restoring the former functionality to  .
.
If incomplete dislocation is observed, then the tooth will retain its former position and the wire ligatures help fix it. This happens by tying them to the crowns of the teeth that are located next to the injured one.
In this case, tires made of plastic, metal or a filling version are used, which should be worn for approximately 10 days. The way in which the fixation takes place depends on the severity of the damage. If as a result of the injury the crown was damaged, then an artificial analogue is used.
With a complete dislocation, the tooth is also fixed in the well, special constructions are used for this. But before installing it, the well is thoroughly cleaned of blood and other foreign substances, and antimicrobial and pain medications are placed.
Intervention of specialists should occur no more than 12 hours after injury, otherwise the pulp will die and further its elimination will be required.
If a dislocated dislocation is diagnosed, repositioning and subsequently splinting is performed. If the pulp is damaged, it must be removed and sealed. To restore the functionality of the tooth, specialists conduct engraftment activities. If the implantation is not possible, prosthesis is performed.
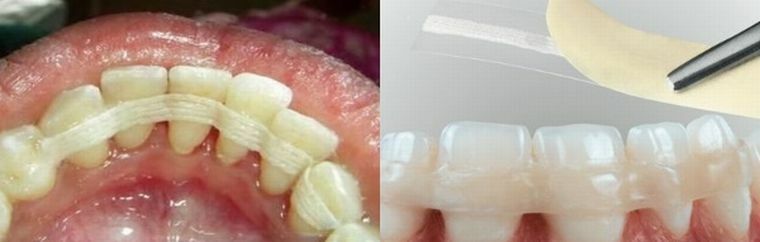
Splinting with aramid filament
Possible consequences of
In some cases, after a tooth dislocation, a number of complications arise, often it is just an untimely treatment. Thus, if you do not contact the specialists at the time, or the methods of therapy are chosen incorrectly, the following complications are possible:
- traumatic pulpitis , accompanied by sensitization and pain syndrome;

- traumatic periodontitis , accompanied by increasing pain, can lead to tooth loss;
- chronic periodontitis , which can be asymptomatic or persistent pain;
- also dislocation of the tooth can be accompanied by periostitis , in which the temperature rises, the gum swells up, a purulent abscess forms, and pains appear in the jaw;
- in the background of traumatic periodontitis may further develop posttraumatic radicular cyst ;
- purulent inflammatory process of , which in the future can cause not only tooth loss, but also infection of blood.
