 Pulp depilation is the removal of its nerve, a loose fibrous tissue filling its cavity and consisting of a large number of blood vessels, neural bundles.
Pulp depilation is the removal of its nerve, a loose fibrous tissue filling its cavity and consisting of a large number of blood vessels, neural bundles.
Timely operation stops the pathological processes of the soft tissues of the mouth and prevents the extraction of units of dental rows.
The main purpose of depulpation is the preservation of hard tissues of the oral cavity, the restoration of functionality and a significant extension of their life. Inflammation of the pulp is accompanied by unbearable acute pains.
Contents
- Indications for ablation of the nerve of the nerve
- Methods for depopulation
- Preparation for the operation
- Standard scheme for the vital pulposotomy
- Stages of the devital extirpation
- Possible complications
- Causes of pain in the depulled teeth
- How to avoid pulpotomy
Indications for the removal of the nerve
Nerve removaltooth is appointed in certain cases.
Among them note:
- pulpitis , causing acute inflammation of the dental nerve;
- periodontitis , a dental disease caused by acute or chronic lesions of the root membrane of dentition units and connective tissues surrounding their roots;
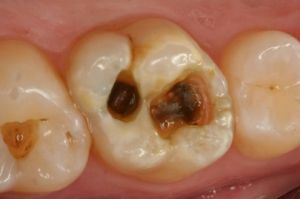
- diagnosing of deep caries of , affecting the tooth pulp;
- mechanical injuring of the oral cavity ;
- need for prosthetics and restoration of teeth ;
- Detection of a stripped bundle of vascular and nerve fibers in the dental cavity of , which appeared as a result of unsuccessful dental treatment or cleavage of the tooth;
- abnormal arrangement of dentition units of congenital;
- large size of the pulp chamber .
Methods of depopulation
Nowadays, the traditional method of removal of the nerve with arsenic has been replaced by modern methods, among which there are two methods of depopulation:
- vital pulpotomy , based on the amputation of the inflamed nerve under anesthesia and allowing treatment for one visit to the dentist;
- is a devital amputation of the pulp , which involves the application of special pastes to an open pulp chamber and the procedure is carried out a few days after the death of the nerve.
Preparing for operation
The preparatory stage for the depopulation of the dental nerve is the appointment of a radiography of the problem area and the conduct of  anesthesia.
anesthesia.
According to the X-ray, the dentist determines the depth, width of the channels, volume and complexity of the operation. The dentist, after choosing an anesthetic, directs the patient to an allergy test.
A negative result indicates the possibility of its use during the operation. After the introduction of anesthesia and waiting for a certain period of time, sufficient for the beginning of the drug, the dentist begins to depulpate the problem tooth.
Standard Scheme for Vital Pulpotomy
Removal of the inflamed nerve and cleaning of the dental canals is performed using a dental drill and sterile burs.
After preparation of the patient for the operation and the onset of the action, the anesthetic begins the surgical procedure of vital extirpation of the pulp of the problem teeth.
It consists of the following steps:
- removal of the destroyed tooth enamel together with dentine;
- antiseptic treatment of the tooth cavity after preparation of carious tissues;
- cutting a part of the dental cavity with the capture of the coronal site of the inflamed pulp;
- removal of tissue from nerve, vascular bundles from canals and pulp chamber;
- stop bleeding, mechanical and drug treatment of dental canals;
- preparation of root canals for sealing using endodontic tools: measurement, expansion, partial alignment, purification of pulp residues;
- filling of cavities of root canals with composite material;
- X-ray examination to check the tightness of sealed channel cavities with microtubules;
- installation of temporary seal;
- closure of the tooth cavity with a permanent composite material taking into account the natural shade of the crown surface;
- polishing, polishing permanent seal;
- carrying out fluoridation of surfaces of units of dentition rows for strengthening strength of enamel.
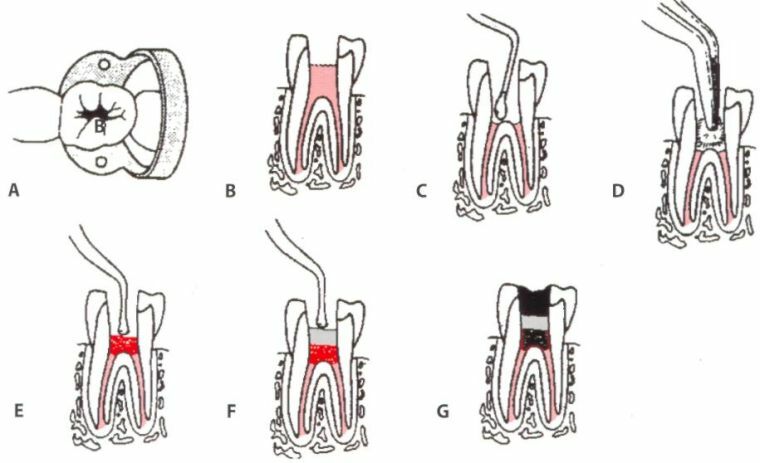
Vital pulpotomy step by step
Stages of devital extirpation
Surgical procedure of devital depopulation of an inflamed dental nerve is also performed under local anesthesia. The scheme of carrying out devital pulpotomy includes certain stages of removal of loose tissue from the nervous, vascular bundles from the canals and the pulp chamber of the tooth, performed by the method of vital extirpation.
It provides:
- removal of damaged enamel and dentin using a drill;
- washing with antiseptic means of the tooth cavity and its subsequent drying;
- placing a special paste in a diseased tooth for dying off the pulp;
- drug closure temporary seal;
- carrying out the depopulation of the inflamed nerve a few days after placement in the diseased tooth substance for killing channel nerve fibers;
- qualitative cleaning of root canals from pulp residues and their careful treatment with disinfectant antiseptics;
- setting a temporary seal and replacing it with a permanent composite material after a certain period of time determined by the attending physician.
The quality of the filling of the dental canals, the completeness of their filling with the composite is controlled by X-rays.
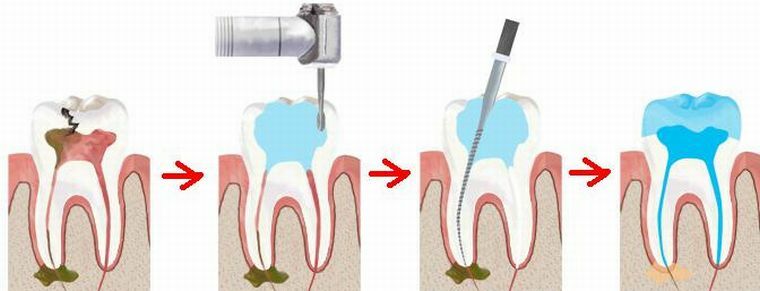
Extirpation of the dental nerve
Possible complications
Surgical procedure for depulpation of the problematic dentition units, regardless of the method of its conducting, can have complications.
Dentists note such problems: 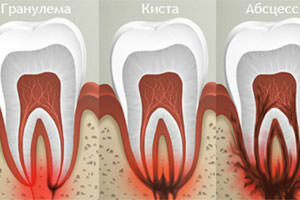
- formation of granuloma , which is an inflammatory formation of small size with clear contours;
- development of flux , which is considered a serious dental disease and is a purulent periostitis of the periosteum;
- diagnosis fistula , a peculiar channel for removing pus from the lesion with localization of the inflammatory process in the upper part of the root;
- appearance of cysts , which is a pathological formation at the apex of the root and creates a risk of tooth loss.
Causes of pain in depulled teeth
Complaints of patients for the appearance of pain in the teeth after the removal of inflamed pulp belong to fairly frequent phenomena.
Among the reasons for the unpleasant situation, it is necessary to note the following factors:
- individual reaction of the human body to the procedure of extirpation of the dental nerve;
- poor-quality treatment in the form of not completely cleared channels, insufficient tightness of their filling with filling composite material and disinfection with antiseptic;
- use of materials not suitable for treatment;
- soreness of neighboring teeth, giving off to the depulled tooth;
- trauma of soft tissues, which causes their inflammation;
- performing a surgical procedure for pulpotomy with contraindications, including ARVI, stomatitis, infectious hepatitis, leukemia, cardiovascular diseases, mental disorders.
 Pain in the depulled teeth serves as a signal for immediate treatment for the help of a dentist who will identify the cause of their appearance and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Pain in the depulled teeth serves as a signal for immediate treatment for the help of a dentist who will identify the cause of their appearance and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Medication-based anti-inflammatory therapy will accelerate the healing process with the individual reaction of the body to the surgical procedure of dental nerve extirpation.
If the appearance of pain has resulted in poor-quality canal filling, then the treatment involves the re-holding of all stages of the standard scheme of depul- dation of teeth.
How to avoid pulpotomy
Removing the pulp of the problem tooth leads to a decrease in the resistance of the enamel to mechanical action. Its color becomes darker.
A depulled tooth is considered to be a physiologically inferior organ, which loses its biological protection function.
To avoid surgical procedure for dental nerve extirpation, it is recommended:
- to visit the dentist on a regular basis and timely to remove carious foci of solid oral tissue, preventing the formation of
 deep, wide cavities;
deep, wide cavities; - to avoid soft tissue pathology;
- observe daily oral hygiene with the use of high-quality toothpastes and brushes corresponding to the state of soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity;
- choose high-quality composite material in the treatment of caries and do not save on the payment of seals.
By following such simple advice and recommendations, it is always possible to minimize the risk of removing the pulp of the problem tooth.
