 Sometimes in the dentistry requires the implementation of minor medical manipulations, causing the patient unpleasant sensations, which in turn attract various kinds of reflex movements that interfere with the quality of medical care.
Sometimes in the dentistry requires the implementation of minor medical manipulations, causing the patient unpleasant sensations, which in turn attract various kinds of reflex movements that interfere with the quality of medical care.
In such cases, the use of general anesthesia is not advisable, and most often local anesthesia is used.
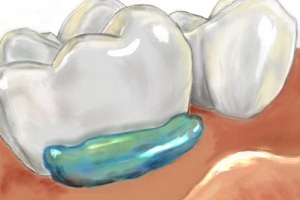
This is a kind of local anesthetic, the use of which leads to the penetration of anesthetic agent in the tissue to a depth of 2 to 3 mm, thereby blocking the nerve receptors and causing a disruption in their functions, which causes the patient to lose sensitivity in the required place. In Latin, the application means application.
Application anesthesia is also called:
- superficial;
- terminal;
- of the topical.
The peculiarity of this type of anesthesia is that it does not cause any unpleasant sensations, as it is done without injections or the use of other equipment.
The effect of the use of anesthetic begins in 2 - 3 minutes and lasts 10 - 20 minutes, if this is not done repeatedly the process.
Contents
- Scope and limitations
- Types of anesthetics used
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Procedure and technique for conducting
Scope and limitations
Apply topical anesthesia to: 
- of urology ;
- of gynecology - during childbirth, so as not to injure the mother in childbirth with pain from the insertion of the needle-catheter into the lumbar region with epidural anesthesia;
- of dentistry - is used most often, before the syringe is inserted into the mucosa, by fitting the crowns or bridges, when removing the stones;
- of pulmonology ;
- of otolaryngology ;
- ophthalmology and other fields of medicine.
Surface anesthetics are used:
- for small-time and time-based surgical interventions in inpatient or outpatient settings;
- in patients who have contraindications to general anesthesia;
- during surgical operations in the absence of an anesthesiologist;
- in military field conditions.
Applicative agents are contraindicated:
- for individual intolerance to components;
- for mental illness;
- in early childhood;
- during psychomotor agitation;
- if breathing is impaired, as artificial ventilation may be necessary;
- if the patient refuses;
- during the course of operations using muscle relaxants.
Types of used anesthetics
For the application of drugs on the surface of the mucosa or skin, many substances are used, most often the crucial role in the selection of the component is played by the type of tissue being treated and the nature of the necessary analgesia.
There are a number of widely used local anesthetics for surface anesthesia:
- Chloretil - cold pain anesthesia, most often used to relieve pain.
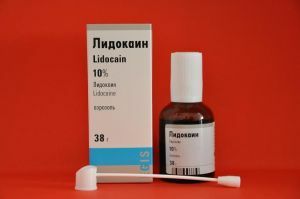
- Lidocaine - does not carry any special complications, however, in pregnancy and cardiovascular diseases the drug is contraindicated. It is available in the form of a spray and is effective when applied to mucous membranes.
- EMLA - a cream used for application anesthesia, is very popular during cosmetic procedures, for example, epilation. It is based on lidocaine and less toxic Prilocaine. To achieve the optimal result, the product is covered with a bandage.
- Perilene-ultra - the basis of the formulation - Tetracaine, a vasodilator widely used in ophthalmology. Produced in the form of an aerosol or solution. The desired result is achieved in a few seconds after instillation of the substance in the eye, just as effectively helps to perform simple dental manipulations.
- Anestol is a broad-spectrum preparation for a long time, up to 2 hours. It is based on lidocaine, benzocaine and tetracaine.
Some medicines contain antibiotics for decontamination.
Each tool has its own release form, in which it will be used optimally. Anesthetics are available in the form of:
- cream;

- gel;
- aerosol;
- ointment;
- spray;
- powder;
- alcohol or aqueous solution;
- lozenges;
- records.
Advantages and disadvantages of
Naturally, the greatest advantage of application anesthesia is the speed of action, but apart from this this kind of anesthesia has several advantages:
- safety - the agent is applied exclusively to the surface of the tissue without penetrating too deeply and without interacting with the otherspreparations;
- controlled exposure duration - which, depending on the concentration, can last from a few minutes to a couple of hours;
- the minimum number of adverse reactions , because of what means it is possible to apply to children.
Despite all the positive qualities, the use of anesthetics has its drawbacks:
- no dosage of - especially for aerosols that penetrate into the bloodstream at a high concentration and have a mental effect;
- lack of deep penetration of - which is why the range of application is narrowing;
- expressed vasodilator effect of .
Technique and technique of carrying out
 In order for the device to function as efficiently as possible, its application must be properly carried out in compliance with the appropriate technologies.
In order for the device to function as efficiently as possible, its application must be properly carried out in compliance with the appropriate technologies.
Depending on the type of release, the procedure will be slightly different.
Scheme of anesthetic application is as follows:
- before application of the main substance, the surface of the mucosa or skin is disinfected;
- then this place is dried;
- spray is applied from a distance of 2 to 3 cm;
- liquid substances are applied to a cotton swab and applied to the required place;
- cream or ointments are rubbed into the skin;
- for imposing maximum effect impose a bandage.
With the correct application, the effect of anesthesia begins in a couple of minutes at a depth of 3 mm.
Application anesthesia is of great importance for people with contraindications to general anesthesia, it allows performing small manipulations, relieving the patient of shock experiences and unpleasant sensations.
