 Modern dentistry makes it possible to conduct tooth extraction as painlessly as possible and without subsequent complications.
Modern dentistry makes it possible to conduct tooth extraction as painlessly as possible and without subsequent complications.
However, in some cases, soreness can not be avoided. Especially hard is the removal of wisdom teeth due to hard-to-reach and tight fitting of the tooth.
Contents
- The complexity of the procedure
- Why does the gum gum after surgery?
- When should I go to the clinic?
- How to relieve pain?
- If complications arise
- Therapy of the alveolitis
- The appearance of the hematoma
- In cases of neuritis
- Treatment of the cyst
The complexity of the procedure
Despite the use of strong pain medications, acute pain in the operational and postoperative period is possible. This is due to the complexity of the operation and possible provoking factors, among which:
-
 the presence of an inflammatory process;
the presence of an inflammatory process; - long-term use of pain medications before surgery;
- state of alcohol or narcotic intoxication;
- individual features of the body;
- ingrowing of the tooth into the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
In some cases, when a tooth is removed, a gum suture is required. This is due to the wrong formation of a sick tooth.
For example, wisdom teeth can come out at an angle, clinging to neighboring teeth, shaking their root system and causing severe pain due to infringement of nerve endings. In this case, the tooth is subject to cutting and gradual removal. The well and the incisions are sewn to accelerate the healing process and avoid infection.
There are other factors that can complicate the removal operation:
-
 complete destruction of all teeth;
complete destruction of all teeth; - root curvature;
- increased brittleness;
- sprouting into the gum without reaching the surface.
In all these cases, a gum incision is made, which can lead to complications due to infection or poor-quality operation.
Why does the gum hurt after the operation?
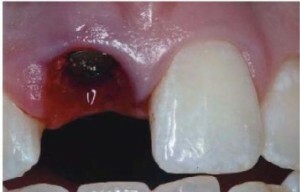 If the gum hurts after the tooth is pulled out, then this may indicate inflammation of the tissues.
If the gum hurts after the tooth is pulled out, then this may indicate inflammation of the tissues.
It is especially important to ensure that after the operation there is no bleeding of the blood clot, which protects the hole from the infection and promotes rapid healing.
The clot prevents the ingestion of food into the damaged area, which can provoke inflammation. To prevent the blood clot from washing out, you should refrain from eating, after which you can eat only soft food.
When should I go to the clinic?
Pain after the tooth is pulled out is normal. With the termination of anesthesia, painful sensations of a nasal character arise. Usually the pain passes during the day, with more difficult removal, pain can be observed for several days.
It is worthwhile to see a doctor if the pain is the following:
- is felt pulsation in the affected area;
-
 appears suppuration of ;
appears suppuration of ; - pain extends to the cheek and nearby tissues;
- observed swelling of ( gingival swelling);
- rises body temperature ;
- appears unpleasant odor .
These symptoms, as a rule, indicate the presence of an infectious complication.
Most often you have to deal with the following consequences when removing a tooth:
- Alveolitis - inflammation of the socket and nearby gum tissue. Occurs when the clot is washed out and the infection gets into the open wound.
- Hematoma - is associated with trauma to the blood vessels of soft tissues, which can cause bruises on the face.
- Neuritis of the trigeminal nerve - is a consequence of damage to one of the branches of the trigeminal nerve located in the lower jaw.
-
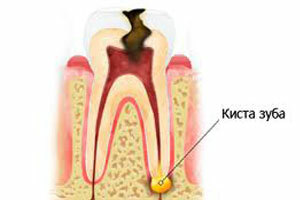 Cyst - occurs when the infection enters the root of the tooth. Usually the cyst is removed along with the affected tooth, but it can remain in the gum and lead to a vast purulent process.
Cyst - occurs when the infection enters the root of the tooth. Usually the cyst is removed along with the affected tooth, but it can remain in the gum and lead to a vast purulent process. - Presence of tooth fragment - after removal, it may be found that not all fragments of the tooth are extracted from the gum. This is more common if the removal operation is accompanied by sawing. Also, the fragments may remain because of the high fragility of the tooth.
How to relieve pain?
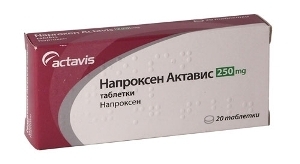
In the absence of complications, cold attachments, anesthetics and anti-inflammatory rinsing solutions are prescribed, which can be applied no earlier than 24 hours after the operation.
To prevent the spread of purulent infection, antibiotics can be prescribed, which are also recommended for complicated operations involving gum cutting.
In case of complications, a special treatment is prescribed, which is determined on the basis of the disease.
What to do if the gum is very painful after the tooth is removed will the dentist tell:
If complications arise
If after removing the tooth something went wrong, then the measure should be taken accordingly.
Therapy of the alveolitis
 The well must be rinsed with an antiseptic solution. Flushing is performed under local anesthesia with the use of such compounds as Furacilin or Chlorexidine. Less commonly, hydrogen peroxide is used, which is usually used for minor damage.
The well must be rinsed with an antiseptic solution. Flushing is performed under local anesthesia with the use of such compounds as Furacilin or Chlorexidine. Less commonly, hydrogen peroxide is used, which is usually used for minor damage.
After extraction of pus and particles of dead tissue, the well is treated and then drained.
In case of severe inflammation, antimicrobial agents are introduced into the well, preventing the spread of infection and stopping inflammation of the gum. Then an antiseptic bandage is applied to the affected area using anesthetics.
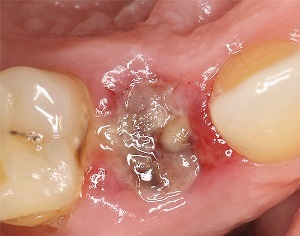 In normal course, the pain passes through two days and the healing takes place.
In normal course, the pain passes through two days and the healing takes place.
If the disease is in a neglected state, physiotherapeutic procedures can be added to these measures, aimed at reducing the inflammatory process and activating the protective forces of orgasm.
The patient is prescribed antibiotics, antiseptic rinses and vitamin complexes.
The emergence of the bruise
 After tooth extraction delivers more aesthetic discomfort than real physical discomfort. Usually a cold is prescribed, which reduces the edema of the gums and promotes rapid resorption of the bruise. On the other hand, a hematoma can indicate infection of the wound.
After tooth extraction delivers more aesthetic discomfort than real physical discomfort. Usually a cold is prescribed, which reduces the edema of the gums and promotes rapid resorption of the bruise. On the other hand, a hematoma can indicate infection of the wound.
Antibiotics and antiseptic trays can be prescribed to avoid unpleasant consequences. To prevent the spread of bruising, a pressure bandage is recommended.
In cases of neuritis
 Pain in neuritis is difficult to confuse with the symptoms of other diseases. This is a sharp "shooting" pain that permeates the entire face. With trigeminal neuritis after removal of the tooth, anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.
Pain in neuritis is difficult to confuse with the symptoms of other diseases. This is a sharp "shooting" pain that permeates the entire face. With trigeminal neuritis after removal of the tooth, anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.
In especially severe cases, a novocaine blockade is recommended, which is performed as many times as needed to eliminate symptoms.
The patient is prescribed antibacterial drugs, B vitamins, as well as physiotherapy procedures.
Treatment of cysts
Treatment of cysts is carried out taking into account the spread of the disease. The patient should take a picture on which it will be possible to determine the location and size of the cyst.
 With a minor lesion, a therapeutic treatment is prescribed, which involves taking antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
With a minor lesion, a therapeutic treatment is prescribed, which involves taking antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs.
It is also recommended to wash the well with subsequent disinfection. In severe lesions, removal of the cyst is performed surgically.
If the cyst has not managed to damage the tops of the roots of neighboring teeth, then its removal is carried out quickly and painlessly.
 When afflicting adjacent teeth, laser dialysis can be recommended, which involves inserting a laser into the canal to stop the growth of the cyst and prevent inflammation.
When afflicting adjacent teeth, laser dialysis can be recommended, which involves inserting a laser into the canal to stop the growth of the cyst and prevent inflammation.
Removal of residual fragments of the tooth is performed surgically. The gum is dissected and the fragment is removed. The patient is then given restorative therapy with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
