 The change of teeth in a child usually does not cause any alarm.
The change of teeth in a child usually does not cause any alarm.
This is quite a natural process, when the baby teeth, which began to appear with half a year and lasted their due time, change at a constant age from the age of 6 to 7 years.
Contents
- According to the law of nature
- Think before you delete what should not be left alone
- Sometimes tooth extraction is an unpleasant necessity
- Cases when the operation should be postponed
- What to do if the tooth is unsteady
- Note!
- Preparation for removal: stages of a long path
- Step by step to a full life
- Possible complications
- Home dentistry
By the law of nature
You can find out about the early start of this shift by the spaces between the teeth - they become wider. After all, like the rest of the body and face, the jaws begin to grow rapidly - instead of the twenty teeth of the dairy they must now accommodate 28 to 32 permanent teeth.
First they grow molars, or "six" - teeth, which on the jaws of the child before simply did not exist, then the real work begins.
Permanent teeth appear in the same sequence determined by nature, as dentition teeth appeared: lower incisors change,  then upper teeth, the first pair of premolars changes by ten years, the second pair changes by twelve.
then upper teeth, the first pair of premolars changes by ten years, the second pair changes by twelve.
At the age of 13, permanent fangs grow on the jaws, in 14 - second molars. By the age of 18, third molars( or "wisdom teeth") may grow, but they may not erupt, remaining in the depths of the jaws.
But the fact that the baby teeth are temporary does not mean that they do not need to take care of themselves.
Answer to the question: whether it is necessary to treat( seal, remove) milk teeth?- it sounds like this: yes, it is possible and necessary. After caries( kostode) are exposed and milk teeth, and to transfer it "inherited" to teeth permanent, they are quite capable.
Think before you delete what you should not touch
Do not need to pull out the milk tooth unnecessarily because:
- Occupying a certain space in the gum, , it retains a place in the jaw for the future permanent tooth .On the canal, laid by a milk tooth, the new tooth will pass easily and freely and will occupy the place put to it without any problems by a principle: a post is handed over - a post is accepted. If the milk tooth is removed before the term, a scar is formed on the gums, which will make it difficult to erupt the
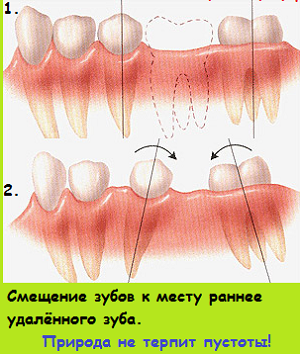 permanent tooth. And then the probability is great that he will not come out on the place he has been assigned, but will grow up at random.
permanent tooth. And then the probability is great that he will not come out on the place he has been assigned, but will grow up at random. - When removing "milk" with unsolved roots, there is a big risk of damage to the permanent tooth inserts , which are located between the roots of the milk tooth.
- In the process of removing , the load on other teeth and on separate parts of the jaw during chewing will be uneven , which will lead to incorrect formation of not only her but also the entire facial skeleton.
- The absence of at least one milk tooth will lead to poor chewing of food and digestion problems of the child .
Therefore, before pulling out the baby's tooth, think three times - at the appropriate time, its roots will gradually dissolve and it will roll itself, swaying.
Sometimes tooth extraction is an unpleasant need for
But there are cases when removal of the milk tooth is necessary. This may be due to the tooth itself, or the question concerns the growth of the permanent tooth under it, or the jaw, or it creates health problems in general.
To pull out the tooth is worth it if:
- it does not fall out in time and interferes with the eruption of the permanent , and that has to grow "bypass," in front of or behind the dairy one;
- it strongly reeling and is ready to drop out, but this does not happen and it creates problems with food and causes pain.
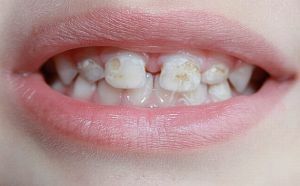 With deep caries or with significant damage, when the milk tooth is not recoverable, it is also removed.
With deep caries or with significant damage, when the milk tooth is not recoverable, it is also removed.
To a similar measure resorted to with problems with the jaw and facial skeleton: with the development of periodontitis, inflammation, phlegmon or the appearance of fistula in the gum or jaw, as well as in sinusitis, which is caused by pathologies in the teeth.
Cases when the operation should be postponed
These cases include both a local acute inflammatory process( categories of stomatitis, gingivitis), and those that have a common significance for the whole organism of the infection( like pneumonia, influenza, whooping cough, sore throat).
In case of a vascular or malignant tumor originating in the area of the milk tooth, the tooth extraction is performed together with neoplasm in a stationary dental clinic equipped with special equipment.
Special care should be taken if necessary in removing the milk tooth in children with pathology of the cardiovascular and central nervous systems, kidneys, and blood diseases.
What to do if the tooth is loose
In this case, the age of the child is of great importance - the process of changing teeth can begin both earlier and later than the usual period.
And undesirable is both the early loss of milk teeth, and the delay of this process.
The first thing to do if a child has one of the baby's teeth loose( or several teeth), it's to consult the dentist, finding out why the tooth has been swaying: whether it's time to fall out, or it's related to health and strength of the gums,or there are problems with the metabolism( diabetes mellitus, developed since childhood).
Please note!
It should be understood that:
- , there is a chance of damage in the operation of the rudiment of a permanent tooth, located directly under the roots of the tooth
 dairy;
dairy; - the possibility of trauma to the growth zone of the jaw, resulting in a disruption of its normal development.
Chewing difficulties associated with the removal of chewing milk teeth, leads to the fact that the maximum load falls on the incisive teeth, resulting in a rapid grinding of the teeth, as well as an uneven load on certain parts of the jaw and the incorrect development of both her and the permanent teeth.
Preparing for removal: the steps of the big way
To avoid fear and hysteria associated with visiting the dental office, you should begin to teach the child to such visits in advance.
It will be useful for the child to attend to the treatment of parents with their own teeth and personally to make sure that the adult in treatment is not painful or scared.
Visit to the dentist every six months to examine the teeth without removing them will not only teach the child to be bound by this procedure, but also to prevent the development of caries and other pathologies.
Finding a loved one near the child during tooth extraction inspires him with calm confidence in the correctness of the actions performed with him. But the adult who is present should be able to control himself, otherwise his excitement will be passed on to the child.
Step by step to the full life of
 Technically pure operation consists of mandatory anesthesia and direct removal, involving several stages.
Technically pure operation consists of mandatory anesthesia and direct removal, involving several stages.
Based on the X-ray images, a decision is taken on the type of anesthesia( anesthesia), which can be applied( gum lubrication with gum) or gum infiltration from two positions.
An important point is a preliminary survey of the parent about the child's tolerability of medicines and the tendency to allergies.
Procedure steps:
- begins the extraction of the tooth from the application of forceps to its protruding portion( crown);
- by moving the forceps along the equator the tooth is separated from the gingival socket of the jaw;
- with forceps fixed to the tooth( without excessive pressure), the tooth is luffed( dislocating it from the jaw as carefully as possible in order to preserve the dental hole);
- the tooth extraction step from the well is called traction;
- after examination of the removed tooth and its socket( the roots should be removed without fractures), a small bleeding stop occurs by squeezing a cotton swab( the child simply closes the teeth).
Possible complications of
Due to the special mobility of the child's psyche, the operation under local anesthesia can be complicated:
- by breaking the root of the tooth leaving it in the jawed hole or breaking the alveolar process of the jaw;
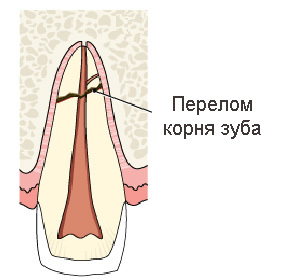
- fracture of the crown part of the tooth to be removed;
- injury of the gums, or mucous membrane of the mouth, or adjacent teeth;
- dislocation of the lower jaw;
- by nerve damage;
- by aspiration( inhalation with inhalation) of the tooth root or blood clot.
Late complications include prolonged non-stop bleeding and an allergic reaction to the injected anesthetic. In such cases, a visit to the doctor is necessary.
Home Dentistry
At home, it is easy to tear out only the milk tooth, which is "on the thread," a tooth for which the time to fall has come and its roots have already resolved. This is a cutter easily accessible for viewing and manipulation with it.
Most often, after applying some of your own efforts, the child easily pulls it out, squeezing it with your fingers. Either the tooth remains inside the chewed viscous candy-toffee.
Either a strong thread is used, pretreated with an antiseptic and securely fixed on the tooth: with a sharp upward movement( not to the side and not forward! ), the tooth breaks away from the area of the gum that is holding it.
The child can only grip the sterile gauze tampon attached to the slightly bleeding hole with his teeth. This child perceives such manipulation with delight, as a game or an adventure.
How to independently pull out a milk tooth without pain and consequences:
 But in everything there should be a measure. Adults should not overestimate their knowledge and abilities in this area - this kind of work should be done by a dentist in specially created conditions. After all, each tooth has its own "character" and its own characteristics, which must be foreseen.
But in everything there should be a measure. Adults should not overestimate their knowledge and abilities in this area - this kind of work should be done by a dentist in specially created conditions. After all, each tooth has its own "character" and its own characteristics, which must be foreseen.
If getting rid of a milk tooth happened on its own, this is normal. In all other cases, which seem difficult, an appeal to a specialist( dentist) is compulsory.
