 Probably, there is no person who at least once in his life did not encounter acute exhausting unbearable toothache.
Probably, there is no person who at least once in his life did not encounter acute exhausting unbearable toothache.
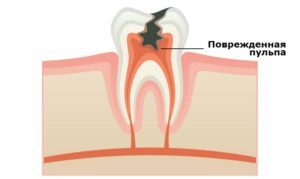
This is the manifestation in combination with a number of other symptoms characteristic of pulpitis.
Contents of
- What is it?
- Causes of development of
- Injury of tooth or gums
- Classification and symptoms of pathology
- Forms of acute pulpitis
- Forms of chronic pulpitis
- Features of retrograde pulpitis
- Approach to diagnosis
- Diagnosis by X-ray image
- Removal of pulp is an integral part of treatment
What is it?
By pulpitis is understood as an inflammatory process, the place of localization of which becomes a vascular-neural bundle of tooth pulp. Often, dentists call the pulp a dental nerve, since nerve fibers intertwined with blood vessels are its main element.
It is the involvement of the nerve fibers in the inflammatory process that provokes strong pain sensations, which can not always be completely removed even by the use of analgesics.
Causes of development of
Pulpitis can develop under the influence of a number of factors:
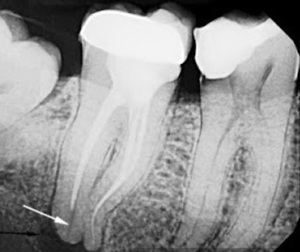
In the picture, incorrectly sealed root canal
- Presence of untreated carious cavities. Initiated tooth decay is considered as the main cause of the development of pulpitis associated with the active propagation of pathogenic microflora in the carious cavity and their penetration with the released toxins directly into the pulp.
- Incorrect dental treatment. It is a question of a poor-quality processing of a carious cavity and the presence of particles of caries-infested tissues under a sealed seal. Also, exacerbation can provoke excessive use of air to dry the cavity( diagnose aseptic inflammation).
- Damage associated with the sharpening of teeth during prosthetics. In such situations, dentists talk about pulpitis under the crown, when the teeth are rotted with the unrepaired pulp, it burns( for teeth replacement, the teeth to be grinded must necessarily be depulled).Usually the symptoms of the disease appear gradually after some time after the installation of the crowns.
- Presence of gum disease. Provoking the development of pulpitis can parodontosis, which is the destruction of bone tissue, exposure of the roots of the teeth, resulting in the formation of dentogingival pockets, allowing pathogens to enter the pulp.
Injury of the tooth or gums
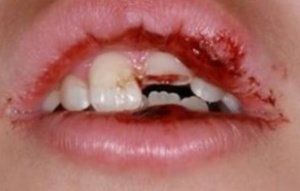
On the photo, a tooth chip with a pulp injury
An example is jaw injury, in which the tooth partially cleaves. As a result, the pulp becomes unprotected from infections.
Most often, infection occurs as a result of penetration of the Streptococcus, Staphylococcus or Lactobacillus into the tooth.
Therefore, in addition to local treatment for pulpitis often carry out complex therapy to prevent the spread of the inflammatory process. It is only the dentist who can correctly select the drugs and the regimen for their administration.
What is pulpitis and the causes of its formation:
Classification and symptoms of pathology
Pulpitis divided into acute and chronic:
- In the acute course of , pain occurs spontaneously, has a paroxysmal character and is intensified during the night.
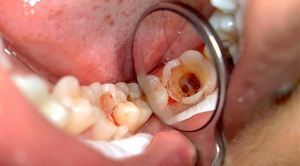
- The difference chronic form is the possibility of both self-development and appearance due to the inflammatory process occurring in the body. Usually occurs on the background of not treated acute inflammation or the presence of an open cavity in the tooth.
In the periods of exacerbations there is a sudden sudden pain. Often the pain is not localized only in the area of the damaged tooth.
There is a painful reaction to the tapping or percussion of the tooth. External changes of the surrounding mucosa are absent.
Forms of acute pulpitis
Acute pulpitis is classified as follows.
Acute focal is considered as the initial stage of inflammation with the following symptoms:
- pain sensations cause any irritants, after removal of which the pain does not go away, the maximum discomfort occurs when exposed to cold;
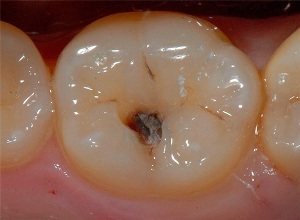
- in the evening and at night there is an increase in pain;
- seizures last no more than 20 minutes, after which for several hours the condition is normalized;
- marked edema of pulpitis surrounding the soft tissue and soreness of the lymph nodes;
- in the tooth is clearly visible deep deep carious cavity with a large amount of softened dentin.
Acute diffuse develops in the absence of treatment of focal pulpitis and is characterized by such symptoms:
- involving the whole coronal and root pulp in the inflammatory process;
- with prolonged pain attacks with short "light" gaps;
- pulsating character of pain, its strengthening in a supine position.
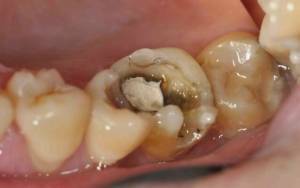
On the photo purulent pulpitis
With festering in the cavity of the tooth, a focus of purulent inflammation, called abscess, is formed. The following characteristic signs appear:
- deterioration of state of health with the appearance of constant pulsating pain without "light" gaps;
- a deep carious lesion of the tooth with a purulent contents detachable at the bottom of the cavity, determined after visual inspection, after removal of which the pain slightly subsides.
Forms of chronic pulpitis
Fibrous is the result of an untreated acute process and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
-
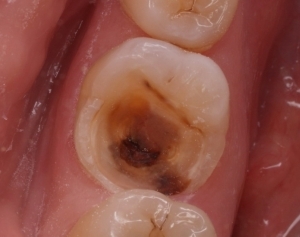
less intense compared with acute form of pain;
- with slight edema of soft tissues;
- with a long course( of the order of a month) with periodic exacerbations, in which intense noisy pain appears;
- by the appearance of pain in mechanical, temperature or chemical effects( particularly annoying cold);
- by the appearance of bad breath;
- strong violation of the integrity of the tooth, the presence of a carious cavity uncovered in one place;
- by a painful pressure reaction and a large amount of affected dentin;
- by changing tooth color.
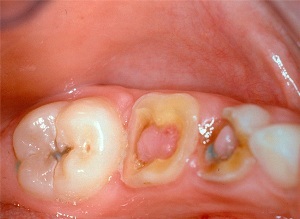 Hypertrophic pulpitis, which in turn distinguish the granulating form and the polyp of the pulp.
Hypertrophic pulpitis, which in turn distinguish the granulating form and the polyp of the pulp.
In the first case, the granulation tissue of the tooth cavity develops and spreads into the carious cavity; in the second case, the overgrown tissue is covered with the oral gingival epithelium.
Also, the following symptoms are present:
- arising when eating food, bleeding;
- pain when exposed to hard food;
- the presence of a build-up in the carious cavity in the form of bright red soft tissue bleeding with slight pressure;
- , when the polyp is formed, the color becomes pale pink, bleeding disappears, pain and reaction to the change of heat and cold decrease.
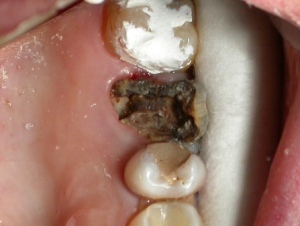
Gangrenous pulpitis is called pulp necrosis, which is characterized by necrosis of the pulp forming cells, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of aching, unreasonable prolonged pain during the exacerbation period;
- increased painful sensations when exposed to hot food and weakened by cold;
- presence in the tooth of a deep carious cavity and a broken crown part.
The cause of necrosis is the prolonged course of the inflammatory process. In some cases, the pain syndrome may be completely absent.
The concremental pulpitis develops as a result of petrification( mineralization) of the contents of the pulp.
This is characterized by paroxysmal pain at night with irradiation along the trigeminal nerve.
Features of retrograde pulpitis
This form of the disease is provoked by infections that enter the pulp from within the body. Most often the cause is:
-
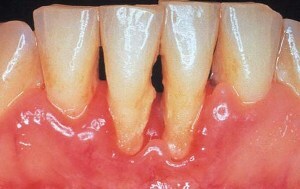 Periodontal diseases .Thus, for middle and heavy periodontitis, the appearance of deep periodontal pockets is characteristic, reaching more than half the length of the root in which pathogenic bacteria accumulate( they enter the pulp through the apertures of the root canals);
Periodontal diseases .Thus, for middle and heavy periodontitis, the appearance of deep periodontal pockets is characteristic, reaching more than half the length of the root in which pathogenic bacteria accumulate( they enter the pulp through the apertures of the root canals); - Infection of the pulp through the bloodstream with influenza, chickenpox, or sepsis.
With such a course of the disease, the pain has a pulsating vomiting character, but can also be accompanied by moderate pain sensations similar to the chronic process.
Diagnostic Approach
For the diagnosis of pulpitis, a dentist necessarily examines the mouth cavity of the patient and assigns an X-ray of the affected tooth, after which a treatment plan is selected.
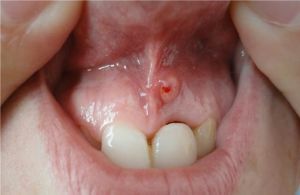 During visual inspection attention is drawn to the following changes:
During visual inspection attention is drawn to the following changes:
- gray enamel color;
- tooth mobility;
- redness of the gums and its bleeding, swelling surrounding the tooth tissues;
- presence of a fistulous course.
Diagnosis by X-ray image
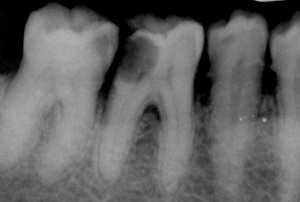
In the picture deep caries and pulpitis
In the development of pulpitis, the dystrophic processes lead to the formation of dencciles, which in the X-ray image are rounded single or multiple shadows in the cavity of the tooth or root canal.
Dencciles can be free( located directly in the pulp) or near-wall( adjacent to the walls of the root canals or cavities of the teeth).
Another obvious sign of pulpitis is the presence of a provoking tooth fracture of the internal granuloma, which in the picture is visualized as a circular enlightenment projected onto the cavity of the tooth with clear contours. In this situation, chronic granulomatous pulpitis is diagnosed. Usually pathology affects the front teeth.
Pulp removal is an integral part of
treatment. Pulpitis is treated in several ways, the main one being a conservative surgical method involving partial or complete removal of pulp.
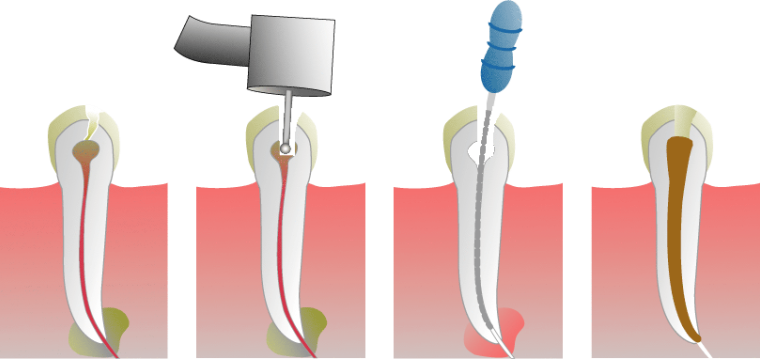
In the photo removal of pulp
There are the following options for the procedure:
- Vital amputation .Using anesthesia, the coronal pulp is removed without first killing the nerve.
- Vital Extraction .Using an anesthetic drug, the pulp is completely removed at one time without killing the nerve before surgery.
- The devital amputation of .The nerve is pre-killed, after which the corona pulp is removed.
- Devital Extraction .The pulp is phased out completely after pre-nerve killing.
Of course, pulpitis is much easier to prevent than treat. But if the inflammatory process does develop, do not delay the visit to the dentist, risking completely losing the tooth. At the initial stage, the treatment passes quickly and effectively, the inflammatory process is easily stopped without causing complications.
