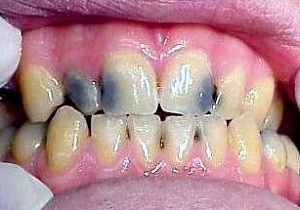
 Often, baby teeth are exposed to various diseases in children, which requires timely dental surgery. A common problem, for example, is an ordinary tooth decay, which in a neglected state leads to the development of periodontitis of temporary teeth.
Often, baby teeth are exposed to various diseases in children, which requires timely dental surgery. A common problem, for example, is an ordinary tooth decay, which in a neglected state leads to the development of periodontitis of temporary teeth.
This ailment can be caused not only by ignoring the presence of caries in the child, but also to be provoked by its poor-quality treatment. According to statistics, approximately 30-40% of cases of untimely caries in children lead to periodontitis of the baby teeth.
Periodontitis is a disease in which the periodontium, located between the cement of the tooth root and the plate of the alveoli, is exposed to harmful microorganisms and infections. They penetrate into tissues from the area contaminated with caries, as well as after the child receives any dental injuries, or in the case of mistakes made by the doctor in the treatment of pulpitis.
Symptoms, the nature of the flow and in many ways the treatment of infant teeth are largely similar to periodontitis of the indigenous.
But, unlike adults, children are much harder to bear the disease, as it is accompanied by severe pain, the appearance of tumors, edema and considerable discomfort. Let us consider in more detail the causes of periodontitis of temporary teeth, the possible forms of this disease, the nature of the course, the symptoms with which it is accompanied, as well as the measures of treatment and prevention.
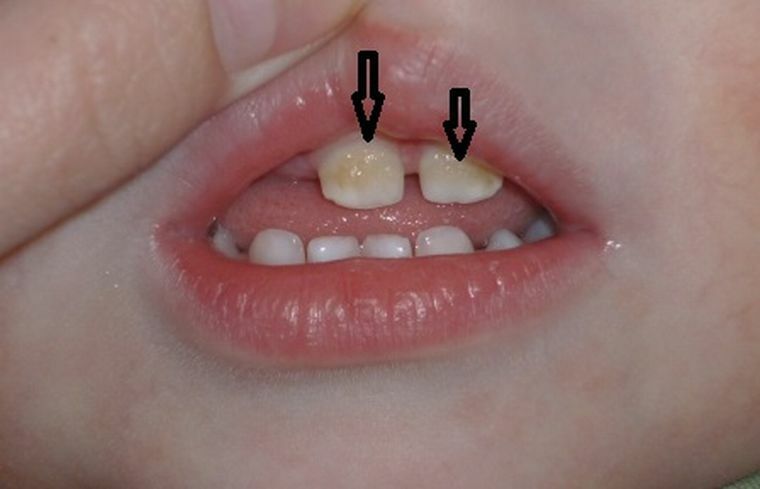
Caries of infant teeth can provoke more serious problems

Contents of
- Causes and risk factors
- Convenient and understandable classification of
- Features of the course of acute and chronic forms of the disease
- Diagnostic features
- Methods and features of treatment
- Prevention measures
Causes and risk factors
Reasons that provokethe development of periodontitis in a child, does not differ much from those in adulthood. In the first place, the provocateur factor is caries, which are very quickly able to destroy the milk tooth, in order to reach the periodontal and root systems.
The periodontium, in turn, has a variety of blood vessels and a loose structure, which leads to a rapid and painful spread of inflammation to nearby tissues. Proceeding from this, we can say that the main risk factor for the development of the disease in childhood is the presence of neglected caries.
Also can cause diseases:
- Injuries of the dentoalysic system ( a traumatic form of the disease develops).Children are very active, they run a lot, play,
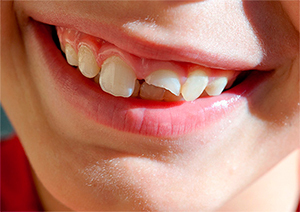 compete among themselves. Often they fall, strike, try to bite hard objects, etc. All this can lead to traumas of the teeth, after which the development of periodontitis is possible.
compete among themselves. Often they fall, strike, try to bite hard objects, etc. All this can lead to traumas of the teeth, after which the development of periodontitis is possible. - Incorrect work of the dentist .Too rough actions or violation of the technology of filling installation can lead to the fact that the periodontium will not be adequately protected and will be exposed to the infection. The use of any strong drugs and chemical elements by the doctor also poses a certain danger.
- The disease can occur as a result of infection in the tooth-like tissues of .Another option is the penetration of dangerous bacteria into the periodontal tissue through the bloodstream.
Convenient and clear classification of
There are many different classifications of periodontitis, we will list the most common types and forms of the disease that are characteristic of children. Depending on the intensity and stage of development of the disease, it can have a chronic or acute form.
Chronic periodontitis in children occurs against the background of a permanent inflammatory process in the tissues, which is caused by a permanent destructive process in them. The chronic phase of the disease can last for a long time, depending on the type of
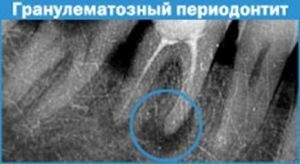 arising destruction, periodontitis can be of three types: granulating, fibrous, and also granulomatous.
arising destruction, periodontitis can be of three types: granulating, fibrous, and also granulomatous. Acute periodontitis is characterized by stronger destructive processes in the tooth and adjacent tissues. In this case, pain symptoms do not just arise from time to time, but are a constant companion of a person, swelling and inflammation can appear in the oral cavity. At the same time, with a chronic course of the disease, there are almost no symptoms, and the child does not complain about anything.
Acute periodontitis, in turn, is divided into two main types: serous and purulent. The second option is the consequence of the first one launched. In many modern classifications, the serous type of the disease is not taken into account, as it very quickly develops into a purulent one.
Depending on the cause of the onset, periodontitis can also occur in three main forms: infectious, medicated and traumatic.
Features of the course of acute and chronic forms of the disease
Chronic and acute forms of the disease have various symptoms. With chronic periodontitis of temporary teeth, the child does not have pronounced painful symptoms, only "signs-hints" are possible:
- periodic weak pain in the area of the affected tooth and the tissues nearest to it;
- , when pressing on the tooth, painful sensations appear;
- there is discomfort and pain with a sharp change in temperature in the oral cavity( taking hot drinks, breathing in frosty air, etc.);
- occasionally there may be a slight inflammation, swelling on the gum;
- if the disease develops long enough, it can cause a general deterioration in health: poor health, increased temperature, weakness.
Acute periodontitis proceeds much more intensively and is characterized by the following negative symptoms:

- in the tooth area, discomfort and constant severe pain are observed, which becomes pulsating with time, differs more sharply;
- the tooth becomes movable;
- with pressure on the gum, even during eating, the pain is further intensified;
- gingiva becomes edematous, there is a strong inflammation;
- the general condition of the child's body also deteriorates significantly, it becomes weak, exhausted, body temperature rises, normal sleep regimes are broken, appetite is lost.
Diagnostics of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease as a whole is not a big problem and includes such methods:
- study of the clinical picture, listening to complaints of a small patient and his parents, probing, percussion( tapping of separate areas of the tooth);
- radiography, - it is the main method of thorough research;
- is also sometimes used such a diagnostic method, like X-ray.
Very important and so-called differential diagnosis, which allows you to determine which type of periodontitis is observed in a small patient, as well as exclude pulpitis and deep caries.
Methods and features of treatment
Treatment of periodontitis of the baby tooth is one of the most complicated procedures for a dentist. The treatment process for both acute and exacerbated chronic periodontitis is as follows:
- doctor cleans root canals;
- further it is necessary to remove the inflammation, for this purpose the channels are treated with special antiseptics and medical solutions;
- when the inflammation subsides is carried out filling of the cleared channels.
 The main feature of the treatment of the disease is that each stage must be performed very qualitatively and do not proceed to the next one until the desired result is obtained on the previous one. For example, it is very important to clean the channels well, completely remove the inflammation, and then to perform the filling.
The main feature of the treatment of the disease is that each stage must be performed very qualitatively and do not proceed to the next one until the desired result is obtained on the previous one. For example, it is very important to clean the channels well, completely remove the inflammation, and then to perform the filling. In case of unsuccessful conservative therapy, the question is raised about the removal of the tooth.
Professionally about the treatment of periodontitis of the baby teeth:
The main thing that affects the prognosis is the timeliness of the treatment. The earlier the problem was identified and the treatment was carried out, the more chances that the tooth could be kept in its normal state. The main conditions for a favorable prognosis are absence of complications and bone tissue safety.
If it is a question of neglected cases, it is possible for tooth loss. In particularly difficult cases, there is a possibility of fistula, granuloma, inflammation and even sepsis.
Prevention measures
To prevent the development of periodontitis, you must first of all train your child to constant oral hygiene -
 it is necessary to regularly brush your teeth and rinse your mouth after each meal.
it is necessary to regularly brush your teeth and rinse your mouth after each meal. It is also very important to monitor the condition of the child's teeth and in case of occurrence of caries on them do not pull with treatment.
These measures will be sufficient to avoid the occurrence of periodontitis of the milk tooth with a high degree of probability.
- Injuries of the dentoalysic system ( a traumatic form of the disease develops).Children are very active, they run a lot, play,
