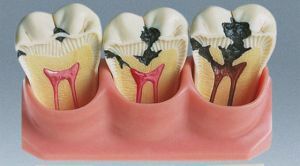
 Acute pulpitis is an inflammation of the internal tissues of the tooth, which includes the nerve, vessels and connective cells. At the first stage of the onset of the disease, the patient notes aching pain gradually increasing with time. Together with this, it is possible to change the color of the enamel, bleeding and swelling of the gums, an increase in body temperature, symptoms of intoxication.
Acute pulpitis is an inflammation of the internal tissues of the tooth, which includes the nerve, vessels and connective cells. At the first stage of the onset of the disease, the patient notes aching pain gradually increasing with time. Together with this, it is possible to change the color of the enamel, bleeding and swelling of the gums, an increase in body temperature, symptoms of intoxication.
After 6-8 hours after the onset of development of acute pulpitis, there is an increase in inflammation, the formation of pus in the area of the pulp. Pains are paroxysmal, exacerbation occurs at night, sometimes with too cold or hot food.
Unpleasant sensations persist for 15-10 minutes after elimination of irritating factors, affect not only the affected tooth, but also the entire jaw, ear or even the temple. The localization of pain is not clear, so the diagnosis of acute pulpitis is almost always difficult. Absence of treatment leads to chronic course, necrosis of tissues.
Contents
- Aggravating factors
- From the point of view of modern classification
- Focal form of the disease
- Diffuse pulpitis in acute form
- How is the diagnosis made?
- Complexity of diagnosis
- Comprehensive medical care
- Conservative method or biological
- Surgical intervention
- Cost of treatment
- This is really very dangerous
- Preventive measures
Provoking factors
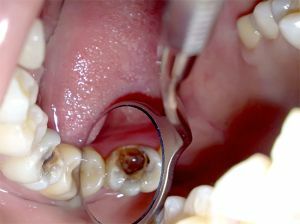
Deep caries provokes acute pulpitis
Development of acute pulpitis can provoke existing diseases of the oral cavity, organ pathologybreathing, trauma and exposure to chemicals. In this regard, all possible causes of inflammation of the pulp are divided into groups:
- Infectious diseases give a push for the spread of microorganisms and enter them into the pulp chamber, which triggers the process of suppuration of soft tissue. This is likely in chronic sinusitis, tonsillitis, general infection, when pathogens are transported to organs with blood.
- Carious lesions, osteomyelitis, periodontitis - poor-quality dental treatment, the entry of microbes into the inflamed cavity and the prigessnevoy pocket leads to the defeat of the neurovascular bundle.
- Mechanical injuries - damage to the integrity of the tooth, fracture of the root or root, denudation or rupture of the neuromuscular bundle increases the risk of acute forms of inflammation and necrosis of cells. An erroneous installation of the filling, pressure on the diseased area, erasure of teeth, drying of the dentin tissue during dental manipulations can also play a negative role.
- Chemical burns and damage to result from the use of concentrated antiseptics, alkaline pads, medications that cause an allergic reaction.
From the point of view of the modern classification of
Acute pulpitis can occur in two forms: focal( serous) and diffuse( purulent).Each of them has its own peculiarities and proceeds in different ways.
Focal form of the disease
Acute focal pulpitis in most cases develops rapidly, literally within two days. The localization of pain and the appearance of pus is observed next to caries. The main symptoms of serous pulpitis include:
- reaction to cold, heat, acidic or sweet foods, unpleasant sensations do not subside for a long time;
- sharp pain, which can go through a few minutes or stay for about an hour;
- undulating course of the disease: periods of remission and exacerbation( pain intensifies at night and disappears for 4-5 hours);
- the ability to indicate the affected tooth( the patient clearly understands exactly where it hurts).
As the inflammation and destruction of tissues increase, discomfort manifests longer and stronger.

Diffuse pulpitis in acute form
The destructive process affects the pulp tissue and the root of the tooth completely. Acute purulent pulpitis lasts from 3 days to 2 weeks, if there is no treatment, the disease takes a latent form.
Symptomatic:
- prolonged pain of pulsating or vomiting character, with rare and short remission intervals;
- gradual formation of pus and exacerbation on the background of this pain;
- the patient can not identify which tooth is troubling him;
- pain spreads to the entire jaw, gives to the temple or ear;
- discomfort does not pass even at night;
- soreness persists for a long time after exposure to the stimulus( sour, salty, hot, pressure on the crown), cold foods somewhat alleviate the condition, but this indicates the onset of an abscess.
Combining acute forms of pulpitis, the presence of pain syndrome, which occurs, then disappears. It can appear in response to an irritant or at night.
There are different types of duration, the nature of pain and its location, the index of EOD( electrodontodiagnostics), which is up to 20 μA for the focal shape, 30-45 for diffuse.
How is the diagnosis made?
For the accurate diagnosis, several methods are used at once:
- patient - the doctor is interested in the intensity of pain, its location, the duration of periods of exacerbation and remission;
- examination of the oral cavity - the dentist finds out what damages are on the teeth, the presence of seals, edema of soft tissues, then by feeling and tapping reveal the features and nature of the pain;
- sounding - use of a probe to determine the stage of pathology, the degree of destruction of dentin, the depth of caries, the state of the pulp chamber;
- reaction to temperature - check the response of soft and hard tissues to cold and hot;
- EDI - an estimation of excitability of sensitive nerves at a stimulation by their electric current for revealing integrity of a pulp and a zone of formation of pus;
- radiography - obtaining information about the anatomical structure of the tooth.
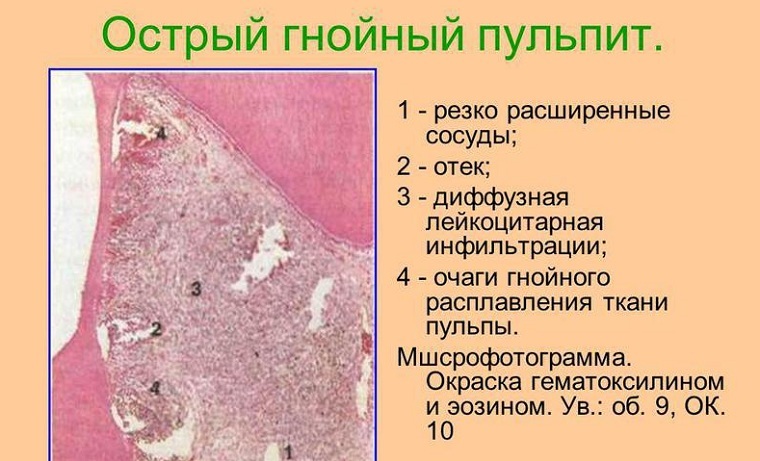
Acute purulent pulpitis on EDI
Difficulties in diagnosing
Often mistakes are possible if a patient has a toothache. This is due to the peculiarities of searching for the damaged area. Often the patient comes to dentistry with a complaint that the entire jaw hurts, unpleasant sensations also exist in the temporal part or near the ear.
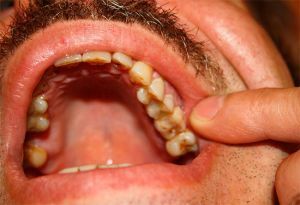 Indeed, with purulent acute pulpitis immediately identify the patient site is difficult. Blame the whole ternary nerve and the structure of the neuromuscular bundle. When detritus and pus appear, the sensitive part of the nerve is squeezed. Immediately in the brain impulses come, which eventually leads to the formation of a pain syndrome of unclear localization.
Indeed, with purulent acute pulpitis immediately identify the patient site is difficult. Blame the whole ternary nerve and the structure of the neuromuscular bundle. When detritus and pus appear, the sensitive part of the nerve is squeezed. Immediately in the brain impulses come, which eventually leads to the formation of a pain syndrome of unclear localization.
The tooth, affected by pulpitis, can be located on the lower jaw, but it will hurt while the upper, and also the head. An inexperienced dentist will begin to treat visible carious patches, repair damaged seals. This ends with procedures on quite healthy teeth, and the pain continues to plague the patient.
Comprehensive medical care
Treatment of acute pulpitis is possible in two ways: biological and surgical. The choice depends on the form and extent of the disease.
Conservative method or biological
The aim is to select treatment methods with preservation of pulp and restoration of its functions.
Treatment is performed using a whole set of procedures:
- special paste is laid on the bottom of the treated and disinfected cavity for drawing of pus or stopping of inflammation;
- proteolytic enzymes are used to relieve edema, inflammation, reduce the repair time of
 tissues;
tissues; - preparations with calcium hydroxide are laid in the treated cavity next to the neuromuscular bundle, help regenerate faster the hard tissues of the tooth, prevent the spread of microorganisms in the damaged area;
- physiotherapeutic procedures help to eliminate inflammation - use UHF, laser treatment, depophoresis;
- temporary or permanent fillings of are put - the first ones are necessary for revealing the tooth reaction, put for 5 days;the latter are intended for complete and long-term restoration of the organ.
Surgical intervention
The following methods are common:
- vital amputation - partial extraction in the crown zone with a healthy enough root( shown to children and adults up to 40 years old);
- devital amputation ( extirpation) - complete removal of the neuromuscular bundle and closure of the cavity with a filling( it is possible to save the tooth, although it is deprived of nutrition);
- combined method - a combination of the two methods.
When acute focal pulpitis is eliminated, conservative treatment with preservation of root tissues is appropriate, but most often doctors choose surgical canal removal and sealing. It is much more practical and reduces the risk of re-occurrence of inflammation.
Acute purulent pulpitis requires complete or partial removal of pulp to avoid further infection and get rid of pain.
The cost of treatment
The cost of treatment depends on the degree of neglect of the disease, the number of necessary visits to the dentist, the quality of the materials used by  , the method chosen by the physician, the complexity of the procedure, and the prestige of the medical facility and the region where the clinic is located.
, the method chosen by the physician, the complexity of the procedure, and the prestige of the medical facility and the region where the clinic is located.
So, in Moscow the treatment of acute pulpitis of single-root tooth will cost 7,000 rubles or more, 2-root - from 9,000, 3-root - from 11,000. On the periphery, prices for dental services are somewhat more modest, but still perceptible to an ordinary citizen.
The cost, as a rule, includes the work of a doctor, anesthesia, seal materials, radiography. Also, in addition to complete treatment, the patient may be offered to relieve acute pain by laying various drugs( eg, Depulpin), which is two times lower than the standard treatment procedure.
It's really very dangerous
Feeling pain, the patient first of all hopes that everything will go by itself and does not hurry with a visit to the doctor. With the intensification of symptoms, many resort to the use of folk remedies or analgesics. Both of them only mask discomfort, but do not provide full treatment. At this time the pathogenic microflora continues its development, and the soft tissues rot.
In the absence of treatment, possible development of such complications and consequences:
- pulpitis in chronic form;
- acute periodontitis( decay of tissues fringing the tooth);
- nerve wilt;
- purulent sinusitis;
- brain abscess;
- meningitis.
Preventative measures
A significant role in prevention is played by hygiene of the oral cavity, operative treatment of carious teeth and other dental diseases.
It is important not to forget about the removal of food residues from the surface of the enamel, especially in hard-to-reach places such as fissures. It is necessary
Dental examination never hinders, even twice a year
regularly use dental floss, and if you have pain or other unpleasant symptoms, you should consult a doctor as early as possible.
The recommended interval between visits to the dental office is 6 months. On reception at the doctor professional cleaning, removal of a touch and remineralization is spent. The procedures are completed by strengthening the enamel with fluoride varnish.
Acute pulpitis is a dangerous condition for the health of teeth, and in some cases even for human life. Microorganisms, in a large number of multiplying in rotting tissues, with the flow of blood are carried to other organs, which is already fraught with an odontogenic infection that can lead to death.
To prevent this, it is necessary to visit the dentist at the first suspicion of pulpitis, to treat caries and other diseases of the oral cavity in time.
