 The diagnosis of varicose veins of the esophagus is often exhibited only after the fixation of bleeding, which can occur quite unexpected for the patient.
The diagnosis of varicose veins of the esophagus is often exhibited only after the fixation of bleeding, which can occur quite unexpected for the patient.
More often, the pathological expansion of veins( phlebectasia) in the esophagus occurs as a secondary complication of other diseases, the disease is more typical for people in adulthood, but young people with this pathology also come to light.
Varicose veins are characterized by the pathological expansion of all layers of the vessel, as a result of which its wall protrudes. Thinning and stretching of veins affects their elongation and the formation of nodes.
The modified wall undergoes constant irritation and inflammatory reactions.
predisposes to the appearance of sacciform formations of the outflow from the vena cava due to a number of diseases of the internal organs.
The onset of does not show any symptoms, further increased fragility of veins leads to their rupture and blood flow, the volume of circulating blood can be so high that it threatens the patient's life.
Contents
- Causes of esophagus expansion
-
- risk groups
- risk groups
- disease symptoms and symptoms
- disease degrees Diagnosis
- How the disease is treated
- Disease and complications of the disease
- Prevention
-
Causes of esophageal esophagus
The cause of varicose veins of the esophagus is the multiple increase in pressure in the cavity of the portalvein , in medicine this condition is called portal hypertension.
The following diseases can lead to a high level of pressure:
- structural changes in the tissues and blood vessels of the liver - hepatitis, tuberculosis, cirrhosis, neoplasms, amyloidosis;
- sclerosis of the vein;
- formation of thrombus;
- compression of the vein by a tumor, cyst, gallstones;
- chronic cardiovascular disease.
Risk groups
Varicose veins of the esophagus most often occur in the following categories of patients:
- in men;
- in people older than 50 years;
- in patients with a history of pancreas, stomach, heart, chronic cirrhosis.
The appearance of bleeding is affected not so much by the level of pressure as by its sharp fluctuations. About
The risk of rupture is high also in those patients who suffer from vascular diseases, negatively affecting the structure of the walls of the vessels.
Signs and symptoms of
The pathology of the veins can be sluggish or swift .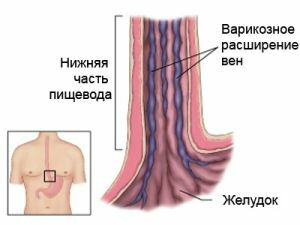
The first symptoms of , characterized by varicose veins of the esophagus of the swift form, most often the outflow of blood from the esophagus, its volume depends on the diameter of the vessel and the size of the rupture, sometimes the amount of blood is insignificant, but appears from time to time.
If a person does not turn in time for help, then he will have jaundice of skin, anemia, weakness, that is, all signs of chronic blood loss.
With , the slowly growing abnormal vessel dilatation, attention is focused on such symptoms:
- heartburn;
- eructations;
- slight discomfort when swallowing solid foods;
- squeezing feeling behind the sternum;
- periodic occurrence of tachycardia.
The listed signs correspond to to esophagitis - inflammation of the esophageal mucosa that arises as a response to irritation from enlarged nodules.
 The complexity of diagnosis and treatment with which uterine varicose veins are known, imposes increased obligations on the patient and the physician for suspected illness.
The complexity of diagnosis and treatment with which uterine varicose veins are known, imposes increased obligations on the patient and the physician for suspected illness.
Doctors and patients recommend the treatment of varicose veins with horse chestnut with insufficient effectiveness of traditional methods of therapy.
With periodic bleeding, melena may occur, that is, the release during the act of defecation of dark feces.
Before a profuse bleeding a patient may develop a strong sense of heaviness behind the sternum and a general weakness within a few days.
Blood is extracted from the oral cavity, its color varies from scarlet to the color of the coffee grounds, while the patient develops dizziness, weakness, sticky sweat, pallor of the skin, a fall in blood pressure.
Degrees of disease
Classification of varicose veins of the esophagus according to clinical and morphological features divides the disease into four degrees:
- The first degree of disease is detected accidentally during endoscopy. An increase in the lumen in one part of the vessel is not more than 3 ml. The patient does not bother, only complaints about primary diseases are possible.
- The second degree of is characterized by the tortuosity of the veins, their unevenness, no narrowing of the lumen. When examining, it is possible to detect protrusion or stretched veins. There are no definite symptoms of the disease, some patients at this stage of the disease complain about discomfort when swallowing.
- With the third degree of , the lumen of the esophagus narrows through the swelling of individual sections of the veins. The mucous layer is changed and more like the folds of the stomach. Patients complain of gastroesophageal reflux - heartburn, eructation, pressure in the upper abdominal cavity.
- The fourth degree of disease is exhibited when numerous nodules of veins are detected in the esophagus that do not subside and have a thinned surface. Numerous erosions are found on the mucous layer. Patients register, in addition to the symptoms of esophagitis, a salty taste in the mouth. The fourth degree most often leads to spontaneous bleeding.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made on the basis of complaints, external examination, detection of primary diseases. Instrumental studies of include:
- laboratory blood test data;
- radiography with contrast agent;
- is an esophagoscopy which must be performed carefully because of the risk of possible bleeding.
Photo of a patient with periastric esophageal varices of the esophagus
Esophageal bleeding even in the presence of phlebectasia can be caused by a plaque of the mucosa, a disintegrating tumor, by the Mallory-Weiss syndrome.
When diagnosing, all possible causes should be taken into account and excluded, only then it will be possible to definitively and accurately determine the root cause of bleeding and changes in the esophagus.
How to treat the disease
Treatment of varicose veins of the esophagus depends on when the disease is detected. If the diagnosis is exhibited during bleeding, then it is necessary to take all measures to stop it.
Only then therapy is assigned to reduce the risk of vessel rupture in the future. Varicose veins are treated complex:
- Initial disease is identified and medications are prescribed by based on its severity.
- The patient is recommended to change the way of life of , that is excludes physical activity, bad habits.
- is assigned a special diet , aimed at treating the underlying disease. Compliance with diet is mandatory, since the load on the liver, stomach, pancreatic leads to portal hypertension. The patient must also avoid overeating.
- In case of bleeding, is prescribed haemostatic drugs in droppers and injections. Select symptomatic therapy, depending on the severity of the shock state.
- Bandage - a surgical intervention aimed at eliminating varicose veins and stopping bleeding. At operation small rubber disks strengthen directly over the thinned wall.
- Sclerotherapy is a procedure consisting in maintaining a special, hemostatic solution in the vein cavity.
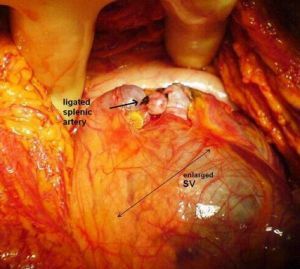
Distal splenorenal shunt
- In case of mild bleeding, is possible to install tamponizing cylinders in a vessel, they squeeze it and stop bleeding.
- Transjugular hepatic shunt .The operation consists in staging a special shunt in the liver, through which the hepatic and portal veins are connected. This technique is aimed at stabilizing the pressure in the vessels.
Danger and complications of
The main danger of esophageal dilatation is profuse bleeding.
In more than half of patients, repeated bleeding occurs in the first two years.
Prevention
Prevention of the development of esophageal veins can be only one way - timely treatment of liver, heart and stomach diseases. The burden on the veins decreases and if a person adheres to a rational diet and is not fond of lifting weights.
