- Botanical Description
- Chemical Composition
- Procurement
- Forms
- Therapeutic Properties
- Ginseng Analogs
- Ways of Application
- Precautions
Ginseng is a genus of perennial herbs belonging to the Aral Sea family and includes slightly more than 10 species. In natural conditions, its representatives can be found in North America, Russia( Siberia, Altai, the Urals) and some East Asian countries( China, Korea, Japan, Vietnam).Ginseng ordinary or genuine is one of the most famous medicinal plants. For medical purposes, it is specially cultivated, as natural reserves are limited and unable to meet the demand for it. The root of ginseng has adaptogenic and toning properties, strengthens the body, increases immunity and resistance to various diseases. Eastern folk medicine has been actively using this plant for more than 2000 years and believes that it prolongs life and preserves youth. Due to its valuable medicinal properties and similarity of the shape of the root to the human body, ginseng in the people was given the following names: the root of life, the salt of the earth, the gift of immortality, the divine grass, stosila, etc.
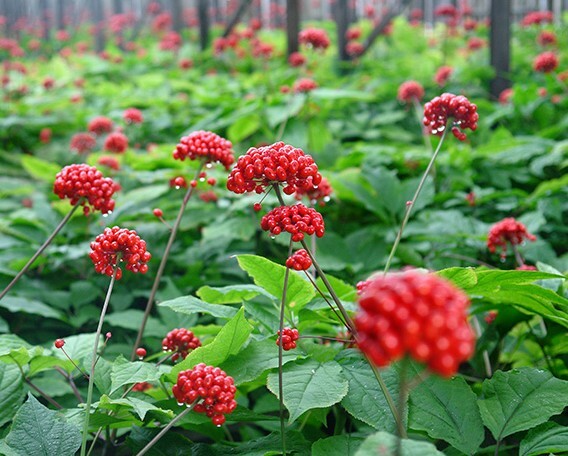

Botanical description of
In places where ginseng grows in natural conditionsshady, coniferous, broad-leaved, cedar, hornbeam and mixed forests. It occurs singly or in small groups. It is well-drained, moderately moist, fertile soils rich in fertilizers. The plant does not tolerate high humidity and direct sunlight. Reproduction is carried out by seeds. Ginseng is a long-liver, its age can reach 100 - 150 years.
Interesting: The plant strongly depletes the soil on which it grows, therefore, when grown in artificial conditions after harvesting, it is recommended not to plant it in the same place no earlier than 10 years later.
Root of ginseng rod( length up to 25 cm, diameter up to 3 cm), fleshy, wrinkled, outside yellowish-white color, spindle-shaped, with large branches( up to 6 pieces).On a fresh break, smooth, white, has a sweetish smell. The root form is cylindrical with pronounced thickenings in the form of rings in the upper part, the number of which is added with age. Rhizome short, narrow, transversely wrinkled, located at the top of the root, has scars from fallen stems. At its top is a wintering bud, from which an aerial shoot develops. By the age of 100 years, the mass of the root of the plant is 300 - 400 g.
The stem is straight, single, thin, 60 to 70 cm long, round in cross section, hollow inside, germinating from the wintering kidney. Every year dies. Leaves palchato-complex, on long petioles( 6 - 8 cm), consist of 5 long elliptical or obovate leaflets with a wedge-shaped base, pointed apex and small-filiform margins. Above, they are covered with sparse hairs. Two lateral lower leaves smaller than the upper( length 2 - 3 cm, width 1 - 1.5 cm), and the middle largest( up to 15 cm in length and up to 4 cm in width).At the top of the stem form a whorl of 2 - 5 pieces.

Flowering occurs in the middle of summer, 8 to 10 years after the germination of the seeds. Flowers are bisexual and staminate, stamens 5 pieces, pistil with a lower ovary and two columns. In size, the flowers are small( up to 2 mm in diameter), white in color, resembling asterisks in shape. They are collected more often 10 - 20 pieces in the inflorescence of a simple umbrella 2-3 cm in diameter at the top of a flower arrow emerging from the center of the leaf whorl. Pollinate independently, have a pleasant aroma.
Fruits, which are juicy bright red two-nest or less often three-nodular globular stems up to 10 mm long, mature at the end of summer - early autumn. Each nest contains one wrinkled cream or white color, 3-6 mm in size, having the shape of an irregular circle or disc.

Chemical composition
Useful properties of ginseng are due to the variety of active chemical compounds in its composition. The main medicinal raw material is the root of the plant, but sometimes also the above-ground parts. It contains:
- alkaloids;
- resins;
- vitamins( ascorbic, nicotinic, pantothenic, folic acid);
- minerals( S, P, Mg, K, Ca, Co, Mn, Fe, Cu, Mo, Cr, Zn, Ti)
- tanning agents;
- mucus;
- triterpene saponins( ginsenosides or panaxosides);
- polyacetylenes( falkarinol, panaxinol, falkarintriol, panaxidol);
- amino acids and oligopeptides;
- polysaccharides( pectins, starch);
- phytosterols;
- fatty acids;
- essential oils( mainly sesquiterpenes).
Important: It is established that the highest content of trace elements in the ginseng root is found near the end of the growing season.
Procurement of raw materials
Wild ginseng is harvested only if there is a special permit in limited quantities( 10-15 g).Accordingly, this pleasure is not available to every herbalist.
Root preparation is performed during the redness of the fruit. The roots are carefully excavated, the above-ground parts are cut off and thoroughly cleaned of foreign impurities. Then, 60 minutes are steamed and dried in a suspended state for one to two months. After drying, the root mass decreases 2 to 4 times and it acquires a light brown color. The product prepared in this way is called the "yellow root".Steam treatment can be avoided, in this case, the roots are washed with cold water, dried in special dryers at a temperature of no more than 60 ° C, and then a "white root" is obtained.
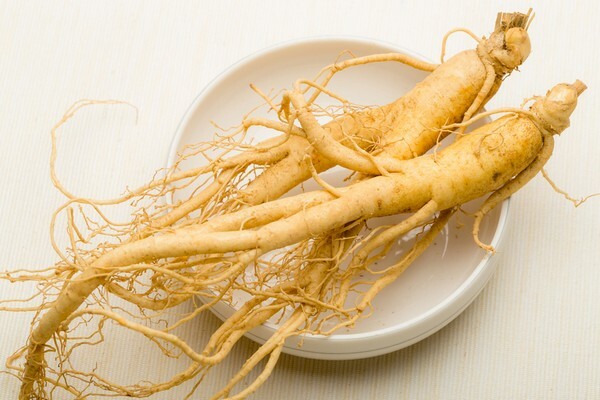

The finished raw materials should be kept in glass jars no more than 3 - 5 years. The root of ginseng in folk medicine is used not only in dried, but also fresh. Fresh roots are stored in wooden boxes, falling asleep with sphagnum moss, which retains moisture well, has an antimicrobial effect and allows them not to dry out for up to 5 years. Without special packaging, they remain valid for 5 days.
Important: Chinese ginseng is listed in the International Red Data Book, the rest of its wild-growing species are strictly protected by regional laws.
For medicinal and cosmetic purposes, mainly cultivated ginseng is used, which is harvested after reaching 5-8 years of age. It is grown on specially equipped plantations or obtained from a cell culture under laboratory conditions. The healing properties of ginseng wild and cultivated are identical, the concentration of active substances( artificially grown below) can only slightly differ. The plant is cultivated in Russia, Australia, America, Japan, Vietnam, China, but the main producer is South Korea.
Forms of release
Cultured ginseng is produced for therapeutic purposes in various forms. After harvesting the roots, the plants are carefully examined by certain parameters and sorted according to the level of quality that four distinguish:
- the celestial root is the most expensive, ideal ginseng root with a mass of 68 grams or more, resembling the body of a person with a strictly defined number of branches,-or holes and damage;
- earth root - has an insufficient number of branches or does not resemble a human body;
- is a good root - all other roots that could not be attributed to the above categories;
- cut root - roots that were damaged during harvesting or cropped.

The following types of preparations are made from ginseng root:
- vegetable raw materials, is a rectangular or triangular yellowish-white plate up to 10 cm in size, which show pieces of threadlike rootlets;
- tincture;
- capsules, tablets, granules;
- red canned ginseng, sold in sealed cans, wrapped paper or packed in a wooden box;
- extract of red ginseng;
- steamed, ready-to-eat roots;
- ground powder in powder form.
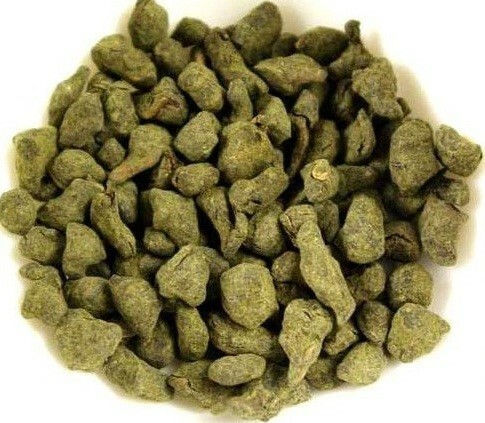
In China, a very popular tonic and refreshing remedy is a special kind of ginseng oolong tea. It is characterized by a pleasant floral spicy taste and aroma. It includes leaves of green tea and medicinal herbs. To make it, tea leaves are rolled into balls, rolled in a special powder, consisting of the crushed root of ginseng, leaves of the wounds, leaves of the holly and other herbs. As a result, it takes the form of balls or lumps, which when brewed with hot water( 80 - 95 ° C) unfold and turn into whole tea leaves. When making oolong tea is not subjected to full fermentation, in contrast to conventional traditional teas. This drink helps to strengthen the nervous system, helps to cope with physical and emotional fatigue.

Some pharmaceutical manufacturers produce various supplements and vitamins with ginseng, which have a general strengthening effect on the body.
The healing properties of
The preparations based on the ginseng root have a fairly wide range of medicinal properties and affect a variety of processes in the body. They:
- have a toning effect;
- increases appetite;
- stops vomiting;
- helps to recover faster after surgery and severe diseases;
- improve performance;
- normalizes blood pressure;
- lowers the concentration of glucose and cholesterol in the blood;
- improves the function of the adrenal glands and other endocrine glands;
- beneficially affect the central nervous system, help with depression, neurosis and neurasthenia;
- increase sexual desire, stimulate sexual functions in women and men.
Tincture of plant leaves can be used to treat diabetes, trophic ulcers and tissue necrosis.
Receiving funds from ginseng contributes to slowing the aging process, improves memory, mental performance, brain activity, metabolic processes in the body, increases its protective abilities.
Ginseng tincture has found application in the complex treatment of diabetes, atherosclerosis, CNS diseases, mental fatigue, neuroses, chronic fatigue syndrome, exhaustion. Ginseng is used to normalize pressure, due to the fact that aqueous extracts of ginseng contribute to lowering blood pressure, and alcohol, on the contrary, increase. It is effective in the treatment of radiation sickness and the effects of radiation exposure.
Interestingly: In eastern countries, the ginseng root is used in cooking. It is added to soups, porridges, boiled, fried. Powder from the root is used as a seasoning.
The plant is effective in diseases of joints and osteochondrosis. It can be used both externally in the form of compresses and lotions, and inside. Ginseng reduces pain, relieves inflammation, which greatly facilitates the overall condition of the patient. External it is still used for toothache, diseases of the throat and oral cavity.
Immunostimulating effect makes effective use of ginseng to prevent the incidence of influenza during seasonal epidemics. In addition, taking drugs on its basis during ARVI helps to reduce the likelihood of complications and ease the course of the disease.
The effectiveness of ginseng for men
The ginseng root for men is effective in such problems as impotence, premature ejaculation. Thanks to the content of saponins, the plant stimulates sexual activity in the stronger sex, increases sexual desire, enhances potency and increases the motility of spermatozoa. The effectiveness of ginseng to increase potency is due to its vasodilating effect, it improves blood supply and nutrition of the penis, which leads to an increase in the duration and persistence of the erection.Ginseng in cosmetology
Ginseng essential oil is used for cosmetic purposes as a component in the means for stimulating skin regeneration and hair growth. It protects the skin from dehydration, strengthens blood microcirculation, cell regeneration, exerts a tonic and bactericidal effect, slows down the wilting of the skin, smooths out fine wrinkles. It is added to masks, creams, balms. Ginseng is effective for hair, it helps with their loss and dandruff. Tincture of the roots and leaves of the plant should be rubbed into hair follicles or used in a diluted form for water rinsing.
Women sometimes use ginseng to lose weight in the form of capsules or tablets, thanks to the normalization of metabolic processes, it helps to get rid of excess weight
Interestingly: Ginseng refers to plants with which various legends are associated. According to one of them, the plant appears in the place where the lightning strikes the source, which subsequently goes underground.
Analogues of ginseng
In folk medicine, the medicinal properties of ginseng are often compared with eleutherococcus, which is popularly called "Siberian ginseng".Both these plants belong to the adaptogens and belong to the same family of the Aral Sea. To the question that it is better to ginseng or eleuterococcus to give an unambiguous answer. Eleutherococcus has a slower and more smooth action, the effect of its use accumulates gradually, but it lasts longer. In contrast to ginseng, the natural reserves of eleutherococcus are richer. It has a more pronounced effect on the normalization of carbohydrate metabolism and to a greater extent lower the level of glucose and cholesterol in the blood. Accidental overdose by means of eleutherococcus will not have such serious consequences for the body.
How to use
In folk medicine from the root of ginseng, ointments, pastes, tinctures, decoctions, teas are prepared and also used as a dry powder.
Warning: Any ginseng should be ingested in the morning, otherwise there may be problems with nighttime sleep due to the stimulating effect of the plant.
Tincture of ginseng on vodka with joint pain
The crushed dry root( 15 g) is poured into 500 ml of vodka and the mixture is kept for 2 weeks. Used for rubbing and compresses for joint pain. Raziraniya spend 1-2 times a day. For a compress, tincture is impregnated with a folded several times gauze and applied to the sore spot for 30 minutes in the morning and in the evening.
Honey extract
The ground ginseng root in an amount of 25 g is placed in 500 g of honey. Put the mixture in a dark place for 2 weeks. Then carefully remove the remains of the roots. Take 1 tsp.a day with headache, fatigue, cold.
Ginseng with grape juice
The crushed fresh root of the plant is mixed with 30 - 40 ml of grape juice. The received remedy is taken orally 30 minutes before meals:
- for arthritis( ½ tsp twice daily);
- for muscular pain( ¼ hl once a day);
- of alopecia( 1.5 tablespoons once a day);
- for strengthening immunity and preventing various diseases( ½ tsp twice a day);
- for hypertension( ½ tsp twice daily).
With acute toothache, this tool is effectively rubbed into the gum, and in case of callosities - in painful patches on the feet.
Ginseng paste
Root( 2 tbsp.) Is ground, poured hot water( 2 tbsp.), Left for 3 hours, then put on a water bath, heated with stirring to 60 - 70 ° C, allowed to cool and usedby appointment. This paste is effective in the form of rubbing for skin diseases and acne, for the treatment of calluses.
Precautions
Despite the large list of useful properties of ginseng, there are also contraindications to its use, so before starting treatment you need to consult a doctor. It is taken by courses, the duration of which should not be more than a month. The root of the plant should not be used for treatment if a person has:
- increased nervous excitability;
- severe form of hypertension;
- disturbances of night sleep;
- bleeding;
- epilepsy, convulsive conditions;
- hyperfunction of endocrine glands;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases in the stage of exacerbation;
- individual plant intolerance;
Ginseng is also contraindicated in children, women during pregnancy and breastfeeding. When he is admitted, the following side effects can occur: allergic reactions, stool disorders, epistaxis, headaches, insomnia, nausea and vomiting, tachycardia, overexcitation of the nervous system. If they appear, stop taking them and see a doctor.
When treating ginseng, it should be considered that it increases the sensitivity of the body to other stimulants, for example caffeine, alcohol.
Important: Taking ginseng remedies for men can be accompanied by episodes of increased blood pressure, increased heart rate, sleep disorders, so uncontrolled use of them is dangerous.
