 The dental stone causes a lot of inconvenience. In addition to the fact that it spoils the appearance of the teeth, it also has a devastating effect on them. The stone itself is formed from a soft plaque in which bacteria accumulate. The mineralization of the tissue in the periodontal pockets is not always noticeable with the armed eye.
The dental stone causes a lot of inconvenience. In addition to the fact that it spoils the appearance of the teeth, it also has a devastating effect on them. The stone itself is formed from a soft plaque in which bacteria accumulate. The mineralization of the tissue in the periodontal pockets is not always noticeable with the armed eye.
Clear hard-to-reach places with an ordinary toothbrush is also not always possible. The upper and lower molars are the most affected, although in some cases tartar can form in the interdental space on the front teeth.
In fact, it is calcium deposits - the concentration of calcium salts in the tartar can reach up to 90%.The organic components of hard plaque include:
-
 proteins;
proteins; - epithelial cells;
- polysaccharides;
- microorganisms.
The color of the stone can vary from pale yellow to brown. There is a gray and black coating, which is more often observed in smokers.
Contents
- Education process
- Dental deposits - what are they?
- What causes the formation of stones
- Possible consequences
- Methods of therapy and prevention
The formation process
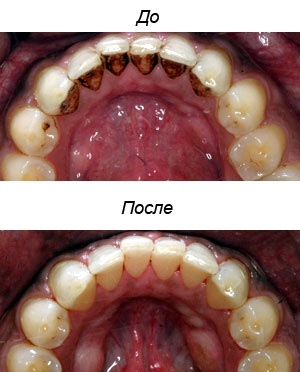
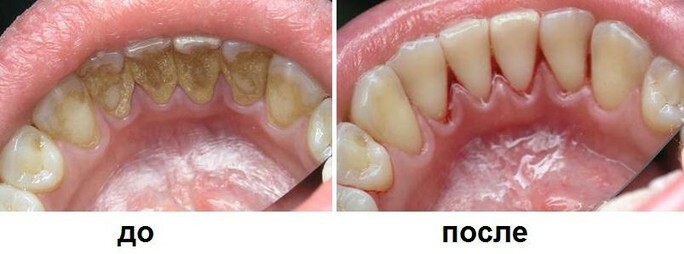
The photo shows what the tartar
looks like The appearance of tartar is preceded by a soft plaque. Crystallization of plaque occurs on day 10 of the in the absence of proper hygiene. Fully tartar is formed within six months. The density of the stone is high, which is why it is almost impossible to remove it by yourself. Without the use of special dental tools can remove the plaque in the initial stage of mineralization.
Single formations are usually rare. Plaque is formed either from the inside of the lower dentition, or in paired parodontal pockets. Accelerates the formation of plaque consumption of caffeine, alcohol, tobacco.
Even with good oral hygiene, plaque remains. As a rule, it is formed in that part of the tooth, which is difficult to clean yourself even by using elixirs and dental floss.
Mineralized plaque makes dental treatment and filling difficult. According to statistics, more than 60% of the adult population has a stone on teeth.
In the process of mineralization of the deposit, the microorganisms in its composition penetrate into the surface of the enamel. This explains the tight adherence of the stone to the tooth and the impossibility of its self-removal.
Scaling of the tartar leads to a displacement of the gum tissue, which leads to their inflammation. Plaque is formed not only on the teeth themselves, but also on the crowns. Penetrating the crown, the bacteria continue to destroy the tooth.
It is known that tartar can develop not only on the surface of the gum, but also in the depth, reaching up to the root of the tooth.
Dental deposits - what are they?
Dental stones come in the following forms:
-
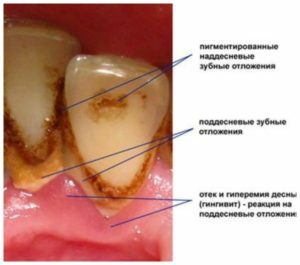 Supragingival - easily detectable on examination. Most often located next to the ducts of salivary glands( the inner side of the front lower teeth, the outer surface of large molars).They have increased fragility, which allows the painless removal of calcium deposits with the help of special tools. Can be formed on dentures and in the absence of an antagonist tooth.
Supragingival - easily detectable on examination. Most often located next to the ducts of salivary glands( the inner side of the front lower teeth, the outer surface of large molars).They have increased fragility, which allows the painless removal of calcium deposits with the help of special tools. Can be formed on dentures and in the absence of an antagonist tooth. - Subgingival - formed in periodontal pockets, have a dark color. Have increased hardness due to the ingestion of blood serum components from the vessels of the gum. Sometimes subgingival dental deposits are called serum. The localization of tartar in this case is not associated with the saliva release - this kind of deposits can be formed on any tooth or teeth.
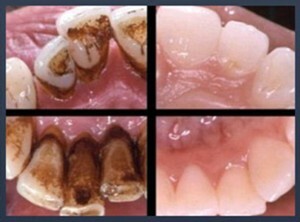
Before and after tooth cleaning
Supragingival deposits are easier to treat and do not require preliminary preparation. To remove subgingival formations modern dental methods are used - ultrasonic cleaning and laser therapy.
To soften calcium deposits, special chemical formulations based on acid are used.
Dentists do not recommend using such remedies at home. High acid solutions can adversely affect the enamel and lead to tooth decay.
In rare cases, mechanical removal of tartar is used. It is used to remove single plaques located on an exposed surface. This method is characterized by high soreness and is potentially dangerous for healthy dental tissues, as a result of which dentists refuse to perform mechanical cleaning in favor of modern hardware therapy.
The removal of subgingival deposits is preceded by sounding, which is used to determine the localization and size of dental deposits.
What causes the formation of stones
The main reasons for the formation of tartar include:
- Insufficient hygiene - untimely removal of soft deposits, food debris and pathogenic microflora leads to mineralization of the plaque. Impossibility of high-quality hygiene in hard-to-reach areas leads to the formation of calcium-like formations, which can not always be detected by simple examination.
-
 Incorrect food - the use of soft and viscous food provokes plaque formation. The natural removal of dental plaque occurs during chewing coarse and fairly stiff food.
Incorrect food - the use of soft and viscous food provokes plaque formation. The natural removal of dental plaque occurs during chewing coarse and fairly stiff food. - Change in saliva properties - increasing the viscosity of salivary fluid and changing its chemical composition, due to malnutrition or in the presence of various diseases, can provoke the formation of dental deposits.
- Curvature of teeth - with various defects of the dentition, the possibilities of qualitative cleaning of the oral cavity are significantly reduced. On curved and improperly formed teeth, the mineralization of deposits occurs more quickly.
- Cervical caries - plaque lingers on affected areas and quickly hardens.
Hereditary predisposition also plays a role in the formation of dental deposits. This is due to the peculiarities of the water-salt balance and the specific composition of the salivary fluid.
To secondary causes of calculus formation:
- immune diseases;
- presence of chronic foci of infection;
- inflammation of the gums.
Possible consequences of
Why is it important to remove tartar in a timely manner? Solid deposits are a favorable environment for the reproduction of bacteria. Subgingival formations lead to periodontal inflammation and the development of periodontitis. Among other complications:
- Soreness in the gums of the - is strengthened during meals and with pressure on the gum.
- Odor from the mouth - appears more often if there is a subgingival tartar. The impossibility of self-cleaning and the rapid development of the inflammatory process leads to a constant unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- Caries - tartar is often accompanied by caries, boosting its development. On the one hand, cervical caries is one of the provoking factors for the formation of mineralized deposits. On the other hand, dental deposits intensify carious manifestations and prevent the treatment of caries.
- Pathology of the gingival pocket - the tartar pushes out the gum, contributing to the denudation of the tooth. In the absence of timely treatment, a pathological cavity is formed in the prigessine region, unable to recover even after removal of the stones.
- Soft tissue abscess - inflammation of the tissues of the mouth occurs when there is a bacterial infection.
- The phlegmon of the cheek is a serious complication, which is characterized by hyperemia of the tissues and a strong edema.
- Submandibular lymphadenitis - occurs in the presence of concomitant diseases against a background of low immunity.
What causes tartar and what it is dangerous to tell a dentist:
Methods of therapy and prevention
Treatment is the process of removing deposits and cleaning the surface of the tooth. To achieve the most stable result, the surface of the tooth, cleansed mechanically or mechanically, is ground and covered with fluorine-containing compounds.
After the procedure, it is necessary to refrain from using products that contain dyes, as well as from smoking and alcohol.
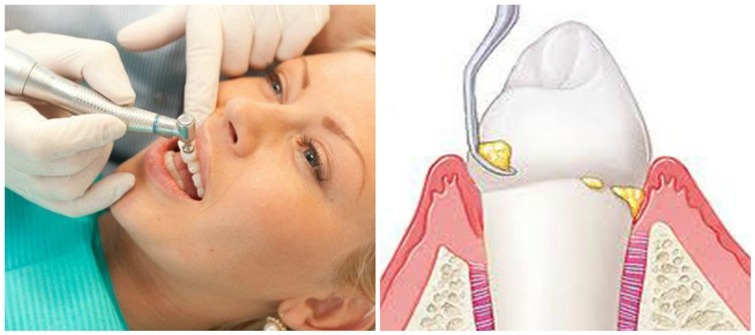
For how the sediment removal process goes, see this video:
Preventative measures:
- High-quality hygiene - if you can not clean the oral cavity with a toothbrush, use a floss and special rinses, the components of which dissolve and remove soft dental deposits. For the prevention of plaque, it is recommended to use abrasive toothpastes that remove soft deposits and weakly mineralized plaques well.
-
 Proper nutrition - a natural form of oral cleansing is the use of foods such as apples and carrots.
Proper nutrition - a natural form of oral cleansing is the use of foods such as apples and carrots. - Professional cleaning of - people at risk will require professional dental care. Ultrasound will be an excellent prevention of deposits on the teeth.
- Preventative examination - subgingival formations are not visible to the eye, and therefore often diagnosed too late. Timely detection of mineralized tissues at the very beginning of their formation will avoid unpleasant consequences and complications of tartar.
- Prevention of inflammatory diseases - the formation of calculus is accelerated in the presence of inflammatory diseases of the gums. Antiseptic rinses will reduce the likelihood of tartar and calm the inflamed gums.
