 Before starting dental treatment, it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis: to determine the state of the enamel, the presence of inflammatory foci in the bone tissue of the tooth, in the gum, in the cheeks.
Before starting dental treatment, it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis: to determine the state of the enamel, the presence of inflammatory foci in the bone tissue of the tooth, in the gum, in the cheeks.
Exterior examination and analysis of patient complaints allow you to make an anamnesis of the disease and determine the methods of therapy. The methods of primary diagnosis in the examination of a dental patient are palpation, sounding and percussion of the tooth crown.
All three methods for primary examination are inextricably linked and always applied in a complex, and also have common features:
- are visual inspection methods;
- examines one tooth at a time;
- is conducted by one specialist.
The whole oral cavity is examined, including not only diseased teeth, but also healthy ones, as well as gums and cheeks. Comprehensive examination allows you to make a primary picture of carious lesions, lesions of nerve endings, periodontal, mucous membranes.
Visual inspection with
probe This method consists of two stages: 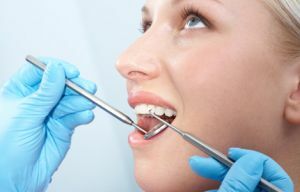
- visual inspection;
- sensing.
The subject of revision is the tooth enamel of the crown. Caries is a pathological process leading to its destruction and penetration of infection into the underlying layers of dentin and root:
- of dentin;
- pulp;
- periosteum.
Visual observation is necessary to establish the degree of carious lesion, as well as the elimination of non-carious diseases( fluorosis and hypoplasia).
The presence of the initial stages of caries( Cretaceous and superficial caries) can be detected only visually and by sounding, it is especially difficult to diagnose pathology on contact surfaces or in interdental spaces.
Attention is drawn to the color of the enamel: shades that differ from the "live" gloss are a signal to clarify the diagnosis:
- gray means the need to remove pulp;
- pink - resorption of channels by resorcinol-formalin method;
- yellow - treatment with depophoresis.
The aim of the probe is to study the condition of periodontal by indirect signs, the definition of secondary caries in the sealed teeth and in grooves on the masticatory surfaces( fissures).
The periodontium consists of a set of:
- soft gingival tissue;
- periosteum( periodontal);
- of the alveolar processes( part of the jaw in which the socket with the root is located);
- tooth cement( bone root shell).
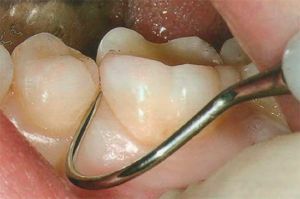 The appointment of periodontium - holding the tooth in the alveolus( a hole in the jawbone).When examining the patient determines the depth of the gap( periodontal pocket) between the neck and gum, at the same time the degree of retraction of the gum( outcropping of the upper part of the dental root) is fixed.
The appointment of periodontium - holding the tooth in the alveolus( a hole in the jawbone).When examining the patient determines the depth of the gap( periodontal pocket) between the neck and gum, at the same time the degree of retraction of the gum( outcropping of the upper part of the dental root) is fixed.
For visual examination and probing, an angular dental probe with a blunt end and incisions at the end is used.
When the instrument is applied to the surface of the enamel, the doctor determines the degree of roughness:
- is smooth if the tooth is healthy;
- rough if affected by tooth decay.
When inserting the probe into the gingival groove from all four sides of the tooth, the depth and width of the instrument's immersion is measured. If the maximum immersion is up to 1 mm, then the dentogingival pocket is normal.
In contrary cases it is a pathology, in some cases, the "failure" can reach a half-size of the dental crown and indicates the atrophy of the periodontium.
Investigation of seals and fissures consists in determining the size of the gap between the tooth and the filling, as well as the degree of softening of the dentin under the chewing surface. These signs are symptoms of a carious process.
With the help of sounding, deposits of tartar under the gum on the neck of the tooth are also fixed in the periodontal pocket. At primary examination of an oral cavity it is not swept up and it is revealed only so. Subgingival stone provokes occurrence of gingivitis and periodontitis.
To recognize the surface caries is possible only with the human eye in combination with the instrumental method. Examination of the gum with the help of a probe makes it possible to identify and classify pathological changes in the tissues holding the tooth.
This is a positive and negative point of this diagnostic method, as it is largely subjective and depends on the qualification of the dentist.
Features of palpation examination
Palpation is a method for determining the stage of destruction of periodontal and the nature of inflammatory processes. To do this, the tooth with the help of tweezers 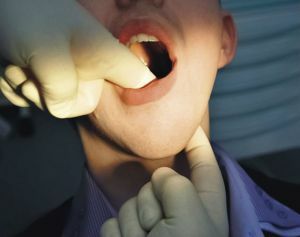 is displaced in different directions, determining its mobility in the alveolus:
is displaced in different directions, determining its mobility in the alveolus:
- in one direction;
- in two;
- in three;
- in five, including the vertical.
Excessive compliance with the applied insignificant force indicates a deviation from the norm, accompanied by inflammation and swelling of the tissues. Such symptoms may correspond to periodontitis, periodontitis, periodontitis, traumatic tooth injury.
Sensing the gums and cheeks gives information about seals, swelling, tenderness, bloody or purulent discharge.
A positive factor in favor of the method of palpation is instantaneous performance when viewed. The disadvantage is that it is impossible to establish an accurate diagnosis with the help of palpatory feeling.
Percussion features
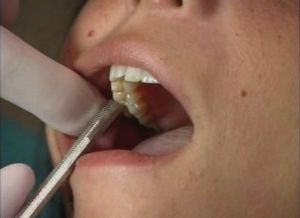 Percussion of the tooth crown with a probe handle or tweezers allows for more precise positioning of the inflammatory site.
Percussion of the tooth crown with a probe handle or tweezers allows for more precise positioning of the inflammatory site.
Examination begins with healthy teeth: rattling chewing and cutting edges on top and side of the crown. The relationship between the direction of impact and the nature of the pain gives an idea of the focus of inflammation:
- vertical - the root nerve;
- horizontal - periodontium.
The advantage of this technique is the ability to quickly establish the place of painful sensations and start treatment in time. But this method is ineffective for studying the pulp condition, which in some cases is necessary, in such cases additional methods of examination are required.
Thus, the listed diagnostic methods allow us to identify:
- early stages of caries;
- character of carious damage to tooth tissues;
- condition of periodontal and mucous membranes;
- concentration of pain.
The set of the revealed symptoms gives an accurate picture of the disease: its cause, severity, possible complications. A timely medical report allows you to prescribe the required treatment.
