
Atrophy of the optic nerve is a disease characterized by a gradual dying out of the optic nerve fibers.
As a result, the information from the retina turns into a distorted form in the brain.
This process is often the result of various ophthalmic diseases.
Atrophy of the optic nerve is most often affected by people in adulthood, and some species develop only in men with hereditary transmission.
In order for a person not to lose sight, it is necessary to diagnose the disease in time and start treatment. And in order to maximize the effectiveness of therapy, it is important to determine which type of atrophy of the optic nerve developed in the patient.
- 1. Description of
- 2. Causes of atrophy
- 3. Symptoms of
- 4. Diagnosis of
- 5. Treatment of
- 6. Prevention of
- 7. Prognosis of
Description of the disease
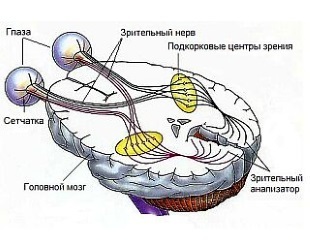
The optic nerve is the channel through which the image, transferring to the retina of the eye as electronic impulses, is transmitted directly to the brain. Already there, all the signals turn into a regular picture.
This optic nerve feeds a large number of vessels. If, due to some disease, its food is disturbed, then the fibers of this optic nerve will also be destroyed in time.
As a result, the nerve tissue is replaced by a connective tissue or glia( ancillary cells of the neural tissue, normally protecting the neurons).The nerve eventually dies and can no longer, as before, transmit signals to the brain from the retina of the eye.
Species
Atrophy of the optic nerve is primary and secondary.
- Primary atrophy of , as a rule, develops as an independent disease. It is passed on a recessive type by inheritance. This disease is linked exclusively to the X chromosome, which is why only men suffer from this pathology. It manifests itself in 15-25 years.
- Secondary atrophy of usually develops after the course of any disease, with the development of stagnation of the optic nerve or a violation of its blood supply. This disease develops in any person and at absolutely any age.

Note - a list of eye drops from allergies. What remedy will help forget about allergies?
In the article( here) all the reviews about eye drops in cataract.
Prices for vitamins for eyes to improve vision!http: //moezrenie.com/lechenie/ vitaminy.html
Causes of atrophy
The causes of atrophy are:
- various infectious diseases( syphilis, meningitis, herpes, encephalitis, influenza);
- circulatory disorders( vasculitis, embolism or thrombosis of the vessels of the eye);
- poisoning;
- craniocerebral or eye trauma;
- is a degenerative disease that affects the nervous system;
- increased intracranial or intraocular pressure;
- compression of the optic nerve( cysts, oncological diseases, abscesses, incorrect fusion after fracture of the skull bones).
Symptoms of

Correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment. Symptoms in different types of atrophy may differ. Its following forms are distinguished:
Primary
Ophthalmoscopy reveals a pale disc of the optic nerve with clearly visible boundaries. Education is flat in appearance, shaped like a saucer.
Vision worsens, the pupil's reaction to light changes, he can jerk frantically, without concentrating on one place.
Color vision is distorted, most often, like colorblind, red and green tones are confused, less often - blue and yellow shades. There are attacks of areas of the field of view, the lower sections or side parts of the view disappear from the view.
Black spots - scotoma - can appear on top of visible objects, and in the later stages tunnel vision develops, that is, a person sees everything as if through a microscope or a narrow tube. Arterial vessels in the retina are often narrowed.
Secondary
With it, as well as with the primary, the pitting of the optic nerve disk is characteristic, but its boundaries are fuzzy, blurred. In the early stages there is an expansion of the vessels in the eye, in the future they can again narrow.
It is easier to identify secondary atrophy in the first stage of the disease, while the symptoms are pronounced, they become less acute with time, but the disease remains, which makes treatment difficult. The patient begins to see worse, the viewing angle becomes significantly narrower, sometimes the individual sectors fall out of sight.
Atrial at compression
This process most often develops due to a tumor or cyst in orbit or inside the skull. Symptoms are similar to normal atrophy - visual impairment, narrowing of the field of vision, full or partial - depending on the affected area.
If the optic nerve is squeezed directly, the pathology develops only on one side, when the entire visual tract is compressed, atrophy is bilateral.
Hereditary atrophy
It is also known as Leber's disease. Suffice from this type of optic nerve atrophy only men at a young age in several generations, but it is transmitted only by the female line. First, with her sharpness falls, sharpness decreases, the field of vision narrows. This occurs for several months, and later develops complete or partial primary atrophy of the optic nerve with blanching of its disc.
Atrophy after severe bleeding
In this case, vision deterioration occurs and its lower field may drop out. Blanching of the visual disc does not have distinct boundaries, as in the case of secondary atrophy. It develops not immediately after the bleeding, but after a while.
With tabes and paralysis
The disease progresses slowly and visual impairments develop over a long period of time. Symptoms can be compared with a simple primary atrophy: this is a deterioration in vision, a change in the field of vision - it narrows considerably, and in many cases, a partial narrowing of the field of vision occurs.
In addition, the disease breaks the color perception, with it in most cases occurs atherosclerosis of the retina.
Atrophy in carotid atherosclerosis
Hypertension suffer from atrophy, which in its manifestations is most similar to secondary atrophy, the field of vision with it can vary in different ways, namely, simply decrease, blur or partially vanish. Scots in this case are extremely rare.
Although different types of atrophy differ significantly in the causes of their development and in the clinical picture, the main and most important manifestations of this disease, which occur in all its species, are two symptoms:
- a significant decrease in visual acuity;
- fallout of the visual field.
Diagnosis

Unlike other diseases, with optic atrophy it is completely unacceptable to engage in self-medication or self-diagnosis.
Quite similar symptoms are inherent in a disease such as peripheral cataracts, when only the lateral vision is disturbed at the initial stage, and only then gradually the central departments.
It is important to remember that atrophy of the optic nerve is not always an independent disease or a consequence of some local pathology of the eye.
In some cases, this is a symptom of a serious illness of the nervous system. Therefore, it is very important to establish its causes as soon as possible.
If you find one of the symptoms, you should immediately contact a professional specialist( neurologist or ophthalmologist).
Diagnosis of this disease usually does not cause any difficulties. The basis of diagnosis is the definition of fields of vision, acuity and the study of color perception. In addition, the ophthalmologist will also necessarily perform an ophthalmoscopy capable of detecting the pallor of the optic nerve disc, as well as narrowing of the vessels and measuring intraocular pressure.
Sometimes, to clarify the diagnosis, it becomes necessary to conduct some examinations:
- X-ray examination,
- magnetic resonance or computerized tomography of the brain,
- electrophysiological or fluorescence-angiographic studies, which can be checked by intravenous contrast( a special substance)patency of all vessels of the retina.
Important information also carries laboratory tests( test for syphilis, general blood test, borreliosis).
Examination of the ophthalmologist should include:
- visual acuity check;
- examination through the pupil( expand with special drops) of the entire fundus;
- spheroperimetry( precise definition of the field of view boundaries);
- laser dopplerography;
- assessment of color perception;
- craniography with a picture of the Turkish saddle;
- computer perimetry( allows to identify which part of the nerve is affected);
- videoophthalmography( allows to reveal the nature of damage to the optic nerve);
- computed tomography, as well as magnetic resonance( determine the cause of the optic nerve disease).
Treatment of

At the first suspicion of atrophy, a targeted examination of the ophthalmologist is required. In addition, consultation of a neurologist or a neurosurgeon may also be required.
Until now, there have been no published methods that would quickly and permanently get rid of this disease. The main task of the doctor is to "revitalize" as much as possible of the nerve fibers.
It is for this purpose that direct stimulation of the entire optic nerve is used - by various alternating magnetic fields, a laser and an electric current. How much earlier an accurate diagnosis is made, the results of the treatment will be so much better.
Magnitostimulation is a special treatment by an alternating magnetic field that can activate all metabolic processes and accelerate the healing directly to the optic nerve. And in cases where the disease has not been started, enough 10-15 sessions, for a noticeable improvement in vision.
All these methods combine with the most traditional therapy:
- with tonic and vasodilator drugs,
- with all vitamins of group B,
- with a blood-substitute fluid,
- with blood transfusion.
You can also resort to a surgical procedure. Its main goal is to set up the delivery of medicines to the nervous tissue.

Read more - the reasons for doubling in the eyes. How correctly to appoint or nominate treatment?
In the article( here) the price of clonidine.
Hypermetropia, what is it?http: //moezrenie.com/bolezni/ narusheniya-refraktsii / dalnozorkosti-ili-gipermetropiya.html
Treating folk remedies
For treating such a serious ailment, medicinal herbs offered by traditional medicine are used, but they are only able to help them to some extent and at the initial stage of the disease .
Self-medication is undesirable, and it is possible to use various decoctions and infusions corresponding to folk recipes, as additional medicines only after consulting with an ophthalmologist.
Tincture of forest mallow for the treatment of optic nerve atrophy
The most effective recipe for treating such a serious ailment is a tincture of a forest mallow or a forest mall. Dry powdered roots of these plants in an amount of 3 tablespoons should be mixed with the same amount of mug, and then boil for about half an hour in 1.5 liters of water.
Already in the ready-made broth you need to add a primrose( 2 parts), melissa( 3 parts) and dolnika grass( 4 parts).Allow the broth to cool and drain. The finished product should be taken within a month for 1 tablespoon three times a day.
Treatment of night blindness with cornflower blue

People believe that night blindness helps cure cornflower blue. In order to prepare this infusion, you need 1 teaspoon of dried or fresh flowers, pour boiling water( 250 ml) and leave to stand for 1 hour.
Take ready infusion three times a day for half an hour before meals at 0.50 ml. In the case of blepharitis, this infusion is recommended to wash the eyes twice a day.
Decoction of lemon, pine cones and herbs rue
The full course of treatment according to the folk prescription is somewhere 25-30 days. This broth is prepared from the herb rue( 25 g), cut at its flowering, unripe pine cones( in the amount of 100 pieces), as well as one small lemon, divided into 4 pieces.
This mixture must be filled with water( 2.5 liters), and then add 0.5 cups of sugar and boil for half an hour. Take the drug should be 1 tablespoon before meals three times a day.
Prevention
As a preventive measure one can single out these:
- Warnings of all kinds of intoxication.
- Consultation with the slightest doubt in the patient's visual acuity with a specialist.
- Timely treatment of diseases affecting the development of optic atrophy.
- Blood transfusions in case of profuse bleeding.
Atrophy of the optic nerve is a fairly serious disease. In the case of even the slightest reduction in vision, it is necessary to visit the ophthalmologist to not miss the precious time for the treatment of the disease. There is no treatment, and atrophy will be progressive, vision and may disappear, it can not be restored in this case.
It is very important to identify the reason why atrophy of the optic nerve develops and correct it in a timely manner. The total absence of treatment most often leads not only to loss of vision, but also to death. In addition, when treated with folk remedies, too low efficiency is noted, and in rare cases, danger.
Forecast
Absolutely any disease, with timely treatment begun to become less terrible and much more amenable to therapy. Also with atrophy: when treating the disease at an early stage it is possible to restore the nerve, and also to avoid frightening consequences and to keep one's eyesight.
If the disease is triggered, it is likely to lead to blindness, which is why when the first symptoms change color perception, reduce visual acuity, or narrow the field of vision, you should contact the oculist. A doctor with your help will help to keep your eyesight.
