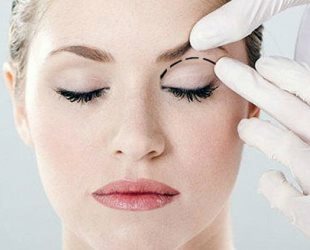
Have you ever observed a lack of symmetry in the position of the eyelids of friends or yourself? If one eyelid is omitted too much, or both, this may indicate the presence of the next disease.
Ptosis( from the Greek word - fall) of the upper eyelid means its omission. Normally, in a healthy person, the upper eyelid, about 1.5 mm, inflames on the iris.
In ptosis, the upper eyelid is lowered by more than 2 mm. If ptosis is unilateral, the difference between eyes and eyelids is very noticeable.
Ptosis can occur in any person, regardless of sex and age.
- 1. Types of the disease
- 2. Causes of the disease
- 3. Symptoms of the disease
- 4. Diagnosis of the disease
- 5. Treatment of the disease
- 6. Conclusion
Types of the disease
Of the varieties of ptosis isolated:
- one-sided( appears onone eye) and bilateral( in both eyes);
- complete( the upper eyelid completely covers the eye) or incomplete( only partially covers);
- is congenital and acquired( from the cause of occurrence).
By how much the eyelid is lowered, the severity of ptosis is determined:
- 1 degree is determined when the upper eyelid covers the pupil from the top by 1/3,
- 2 degree - when the upper eyelid is dropped on the pupil by 2/3,
- 3 degree - when the upperthe eyelid almost completely hides the pupil.
The severity of ptosis depends on the degree of visual impairment: from a slight decrease in vision to complete loss of vision.
What can be confused?
For ptosis, you can mistakenly take such pathologies of the eyes:
- dermatochalasis, which causes the excess skin of the upper eyelids to represent the cause of pseudoptosis or ptosis;
- ipsilateral hypotrophy, which is expressed in the descent of the upper eyelid following the eyeball. If a person fixes his eyes with a hypotrophic eye, while covering a healthy eye, the pseudoptosis will disappear;
- eyelids are poorly maintained by the eyeball due to a decrease in the volume of the orbit content, which is typical for patients with an eye-patch, microphthalmos, eyeball phthisis and enophthalmos;
- contralateral retraction of the eyelid, which can be determined by comparing the levels of the upper eyelids. It should be borne in mind that the covering of the cornea by the upper eyelid by two millimeters is the norm;
- ptosis of the eyebrow, caused by the abundance of skin in the above-eye area, which can occur when the facial nerve paralysis. To determine this pathology, you can raise your eyebrow with your fingers.
Causes of the disease
Let's analyze in detail, for what reasons there is ptosis.
Congenital
Congenital ptosis occurs in children due to underdevelopment or even a lack of muscle, which should be responsible for raising the age. Congenital ptosis sometimes occurs with strabismus.
When a long time does not pay attention to the treatment of ptosis, the child may have amblyopia( lazy eye syndrome).Congenital ptosis is most often unilateral.
One of the most common eye diseases is the pterygium. Read more about its proper diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
We continue the analysis of eyelid diseases! In the news, all the main causes of barley on the eye.
Acquired
Acquired ptosis develops for several reasons and is divided into:
- aponeurotic ptosis , which is associated with the fact that muscle aponeurosis is weakened or stretched, which should lift the upper eyelid. This type includes senile ptosis, which is one of the processes in the natural aging of the body, ptosis, which appeared after operations on the eyes.
- is a neurogenic ptosis , associated with the damage of the nervous system after diseases( stroke, multiple sclerosis, etc.) and injuries. Ptosis can appear with paralysis of the sympathetic cervical nerve, since it is the innervation of the muscle that lifts the eyelid. Along with ptosis, the pupil is narrowed( or miosis) and the eyelid( or enophthalmos) is occluded. The syndrome that combines these symptoms is called Horner's syndrome.
- at mechanical ptosis the reason of occurrence are mechanical damages of a century by foreign bodies. In the risk zone, athletes fall in which eye injuries are quite common.
- false ptosis ( apparent ptosis), which appears with excess skin folds on the upper eyelid, as well as hypotension of the eyeball.
To determine the cause of ptosis is an important task for the doctor, since the surgical treatment of acquired and congenital ptosis is significantly different.
Interesting fragment from the transfer "Live healthy" about the ptosis of the upper eyelid
Symptoms of the disease
One of the main manifestations of ptosis is the directly lowered upper eyelid.
The following symptoms of ptosis stand out:
- inability to blink and completely cover the eye,
- eye irritation due to the fact that it is not possible to close them,
- increased eye fatigue for the same reason,
- possible doubling in eyes due to vision loss,
- habitualthere is an action when a person sharply throws his head back or strains his forehead and eyebrows muscles to maximally open his eyes and lift the lowered upper eyelid,
- may cause strabismus and amblyopia if treatment is not started on time.
Diagnosis of the disease
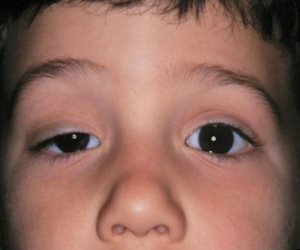
If a depressed eyelid is detected, which is visible even with the naked eye, doctors need to determine the cause of the disease in order to prescribe a treatment.
The ophthalmologist measures the height of the eyelid, studies the symmetry of the position of the eyes, the movement of the eyes, and also the strength of the muscle that the eyelid should lift. When diagnosing necessarily pay attention to the possible presence of amblyopia and strabismus.
In those patients who have acquired ptosis during their lifetime, the muscles that raise the eyelid are quite elastic and elastic, so they can completely close the eye when their eyes are lowered down.
In congenital ptosis, the eye can not completely close even at the maximum lowering of the glance, and the upper eyelid makes movements of very small amplitude. This often helps to diagnose the cause of the disease.
The importance of determining the cause of ptosis is that with congenital and acquired ptosis, different parts of the visual analyzer suffer( in the case of congenital ptosis, the muscle that lifts the eyelid directly, and if acquired - its aponeurosis).Accordingly, the operation will be carried out on different parts of the century.

Records of an ophthalmologist, on the treatment of retinal angiopathy. You will learn about the effective, comprehensive treatment of this disease.
The article( link) describes the methods of solving the problem of the twitching eye.
What to do if my eyes are itchy? The answer is not so simple - http: //moezrenie.com/simptomy/ zud-v-glazakh.html
Treatment of the disease
Neither congenital nor acquired ptosis passes independently and always requires a surgical operation. It is better to start treatment as early as possible in order to increase the chances of preserving vision, since ptosis is not only an aesthetic and cosmetic defect.
The operation is performed by an ophthalmic surgeon under local anesthesia, with the exception of children, sometimes under general anesthesia. The operation takes from half an hour to 2 hours.
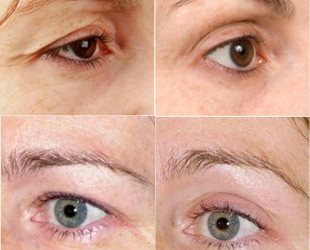
While the operation is not scheduled, you can keep the eyelid open during the day with a plaster band so that children do not get strabismus or amblyopia.
If the acquired ptosis appeared due to some disease, then in addition to the ptosis itself, it is necessary to treat simultaneously and provoking the disease.
For example, with neurogenic ptosis the main disease is treated, UHF procedures are prescribed, galvanization, and only in the absence of the result - surgical treatment.
The operation to eliminate the acquired ptosis is carried out as follows:
- removes a small strip of skin from the upper eyelid,
- then cuts the orbital septum,
- cuts the aponeurosis of the muscle, which should be responsible for raising the upper eyelid,
- aponeurosis shortened by removing its part and sutured to the cartilage of the eyelid(or tarsal plate) slightly lower,
- sutures the wound with a cosmetic continuous suture.
In the operation for the elimination of congenital ptosis, the surgeon's actions are as follows:
- also removes a thin strip of skin from the eyelid,
- cuts the orbital septum,
- isolates the muscle itself, which should be responsible for lifting the eyelid,
- perform muscle plication, i.e.impose several seams on it to shorten,
- suture the wound with a cosmetic continuous seam.
When the congenital ptosis of the upper eyelid is strongly pronounced, the muscle lifting the eyelid is attached to the frontal muscle, thereby the eyelid will be controlled with the tension of the frontal muscles.
When the operation is completed, a bandage is applied to the operated eyelid, which can be removed after 2-4 hours.
Pain during and after surgery usually does not. Sutures are removed 4-6 days after the operation.
Bruising, swelling and other effects of surgery usually disappear after a week. The cosmetic effect of treatment remains unchanged for life.
Operation for the treatment of ptosis can trigger such side effects:
- pain in the eyelid and decrease in their sensitivity;
- incomplete closure of eyelids;
- drying of eyes;
These symptoms in most cases disappear by themselves a few weeks after the operation and do not require any treatment. Some patients may experience subtle asymmetry of the upper eyelids, inflammation and bleeding of the postoperative wound. The cost of surgery for the treatment of ptosis in Russian clinics varies from 15 to 30 thousand rubles.
Conclusion
We highlight the main theses of the article:
- Ptosis is a disease of the upper eyelid, in which it is not naturally omitted.
- The disease can be congenital or acquired.
- Ptosis can adversely affect vision.
- Treatment is possible only surgically.
