
In a healthy eye, the cornea and lens have a regular hemispherical shape.
The light passing through them is refracted equally in the horizontal and vertical planes.
With astigmatism, the wrong shape of the lens or cornea results in a disruption in focus.
Refracted in the eye, a ray of light gathers not at one point on the surface of the retina, as in the eye of a healthy person, but dissipates over several, behind or in front of the retina.
Because of this, the eye can not focus on objects in the field of view, and the image is blurred.
In most cases, astigmatism is asymmetric, which makes it difficult to select the means to correct it. In addition, very often it is accompanied by other eye diseases: from microphthalmia to nearsightedness.
- 1. What is it?
- 2. Types of
- 3. Reasons for the emergence and development of
- 4. Symptoms and diagnostic methods for
- 5. Treatment of
- 6. Prevention of
- 7. Forecast of
- 8. Conclusion of
- 9. Video to
point What is it?
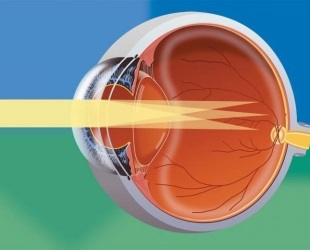
Astigmatism may not be the only violation of refraction in the eye.
In many cases, it is accompanied by hyperopia( hyperopic), nearsightedness( myopic), and also shortsighted in one of the optical axes and far-sighted - on the other( mixed astigmatism).
Types of
Myopic astigmatism is the most common of the listed species of varieties.
Like any other type of astigmatism, it can be classified according to several signs into different species. Next, consider them.
Corneal( corneal) and lens
Deformation of the cornea is usually acquired, it occurs due to injuries, eye diseases, often accompanied by opacities and scars on its surface and much more affects the eyesight.
Lenticular astigmatism is usually the result of birth defects in the development of eye tissues arising from the effects of adverse factors on the fetus during pregnancy or hereditary predisposition.
Simple and complex
With simple astigmatism, refraction of light is disturbed only by one of the main visual meridians, with complex - on both.
Complex astigmatism, in turn, is direct when distortions predominate along the vertical meridian, and vice versa, when they are more pronounced along the horizontal meridian.
Correct and Wrong
Correct astigmatism is predominantly innate, with its deformation of the lens or cornea relatively soft giving an incorrect point of light focusing behind the retina or in front of it.
If the astigmatism is incorrect, the disturbances in their shape are coarser, resulting in light being focused at several points.
Wrong astigmatism gives more severe visual impairment, its correction is much more complicated and requires an individual approach in each case.
In terms of severity, three degrees of astigmatism are distinguished. A mild degree of the disease often occurs imperceptibly and gives a vision impairment of up to 3 D, with an average degree of 3 to 6 D, and at a high of 6 D and above.
Brief history of the disease
Astigmatism as an independent pathology was described in 1670 by Newton, but it got its name much later: the term "astigmatism" was introduced only in 1869.
During the XIX century, the disease was actively studied, the first methods of its correction appeared. First of all, these were lenses, which ensure the correct focusing of light on the surface of the retina.
However, attempts have also been made to promptly treat with scleral circular incisions. These operations were ineffective.
In the XX century, more effective ways to combat astigmatism, both conservative and surgical, were developed, and the reasons leading to its development were identified.
Prevalence and Significance of
According to different data, astigmatism suffers to varying degrees from 48% to 58% of people, and about 15% of them need glasses, contact lenses or surgical treatment.
Light forms in most cases remain undetected throughout life, leaking almost asymptomatically.
Heavier, in turn, significantly impair vision and lead to a variety of complications, such as amblyopia and strabismus.
Risk Factors
Hereditary predisposition is one of the main risk factors for the onset of astigmatism. It can also be a consequence of trauma or inflammatory disease of the cornea of the eye.
Reasons for the emergence and development of
The overwhelming majority of cases of astigmatism originate from hereditary transmission of the disease: astigmatism is not only inherited from parents, but also part of many syndromes.
Often in such cases, other violations of the development of the eyeball.
Some drugs with a teratogenic effect, transferred by the mother during pregnancy, radiation exposure also have a negative effect on the formation of the eye.
Congenital astigmatism is usually associated with deformation of the lens.
Corneal astigmatism is caused by various mechanical damages due to ingress of foreign bodies into the eye, as well as diseases such as keratoconus - cone-shaped cornea proliferation of unclear genesis, corneal ulcer.
The following image clearly shows the differences between different visual impairments:

Symptoms and diagnostic methods of
Symptoms of myopic astigmatism are very similar to the symptoms of myopia proper, but if only the lens or cornea deforms with it, then the entire eyeball is stretched out for myopia. The methods of treating these diseases differ, so it is important to differentiate them from each other.
Myopic astigmatism manifests itself:
- impaired vision, in severe forms - double vision, distortion of the shape of objects;
- violation of focusing on distant objects;
- with dizziness and headaches, especially after work requiring eye strain;
- with lacrimation and a burning sensation in the eyes;
- loss of appetite, general deterioration of well-being.
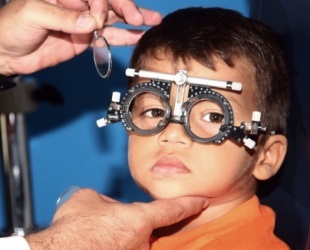
In young children, it is difficult to identify the disease: they rarely complain of vision problems.
But if the child is constantly screwed up, closes one eye, focusing on the subject, becomes whiny and refuses to read and watch television, it makes sense to check his eyes for the disease.
Without timely treatment, strabismus and amblyopia are often associated with astigmatism, especially at an early age.
In order to diagnose and detect the degree of visual impairment, a comprehensive examination of the organs of vision is necessary. It usually includes:
- Measurement of the length of the eyeball. This is necessary in order to distinguish myopic astigmatism from actually myopia;
- Visometry. In this procedure, an ophthalmologist determines visual acuity;
- Skiascopy. With its help, the degree of refraction of light by the cornea and the lens is revealed;
- Determination of the difference in the curvature of the cornea ;
- of the eye with which you can get an idea of the degree of deformation;
- Measurement of intraocular pressure .
In addition, additional tests may be needed: ophthalmoscopy, keratotopography, aberrometry.
Treatment of
Depending on the severity of myopic astigmatism, the treatment methods vary considerably. With its light forms, there is no need for correction of vision, but heavier ones need correction.
Drug therapy and the use of folk remedies in this disease are ineffective.
Phytotherapy, massage, gymnastics for the eyes can slightly improve the overall condition of the eyes, but do not directly treat the disease itself, therefore can only be considered as ancillary measures.
Conservative treatment of
Conservative treatment consists in the appointment of contact lenses and glasses. They do not eliminate the problem, but return the patient's vision to the limits of the norm.
Contact lenses with astigmatism are toric and thicker than normal, so they may not be used by all patients: they often cause discomfort, a feeling of dryness in the eyes.
In addition, they do not correct severe forms of astigmatism. Lenses from the outer toric surface are effective for visual impairments up to 4 D, from the internal - up to 6 D.
Points with myopic astigmatism are most often made individually. Over time, they often have to be replaced, since the disease can progress.
The only way to permanently get rid of astigmatism is surgical intervention.
Surgical treatment
Correction of astigmatism by surgery takes its roots back in the century before last, but this method became really effective only in the middle of the 20th century.
Currently the most widely used methods of operative correction of astigmatism:
| Astigmatic keratotomy | Minor incisions are made on the surface of the cornea. After healing, its curvature changes. It is quite traumatic and fraught with complications in the form of ulcers, erosions, purulent inflammation of the cornea method |
| Photorefractive keratectomy | Using the laser, the upper layers of the cornea evaporate, its surface is smoothed. The procedure is not performed simultaneously in both eyes due to her traumatic condition. For several days while the laser-treated surface is healing, the patient may experience pain, burning and dry eyes |
| Laser keratomileus( LASIC) | The upper layer of the cornea is separated and the underlying tissue evaporates with the help of the laser, after which the cut flap returnsin place. This protects the wound surface and promotes rapid healing, therefore the recovery period after this operation is short enough and it is often performed on both eyes simultaneously |
In some cases, these operations are ineffective. Specialists can prescribe other methods of operative treatment of astigmatism: the implantation of a focal lens, full or partial corneal transplantation, the replacement of the lens.
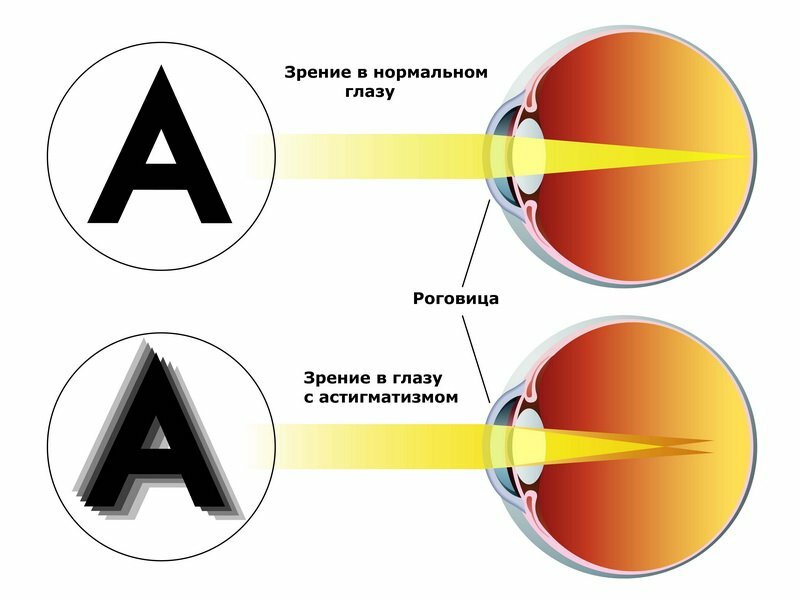
All this will help restore good eyesight. Here is an example of the difference between normal vision and the vision of the world with astigmatism:
Prevention
Since the disease is most often hereditary or occurs due to other eye problems, there are no specific prevention methods.
To avoid damage to the cornea, follow the safety precautions for potentially traumatic activities.
Forecast
Myopic astigmatism is not dangerous for the patient's life, but eye problems can be a serious obstacle in professional activity and daily life.
Developed at an early age, it often leads to complications such as convergent and diverging strabismus, as well as a difficult correction amblyopia. In addition, in some cases it progresses with age.
Conclusion
In summary, the following can be said about this disease:
- Myopic astigmatism often occurs due to a hereditary predisposition, but it can also be a consequence of congenital malformations, injuries and illnesses.
- Symptoms are similar to myopia, but not accompanied by a change in the shape of the eyeball;
- By severity, it is divided into three degrees, and in mild forms it often remains undiagnosed;
- The disease does not threaten the life of the patient, but can significantly worsen its quality and entail serious complications.
Video to point
Additionally we suggest you to watch the following video:
