Rudiments of the eye are laid in the earliest stages of embryo development: by the third week on the head end of the neural tube you can see two eye blisters.
The process of forming the organs of vision, long and complex, continues throughout pregnancy, and does not always end at the time of the birth of the child, often capturing the first weeks of his life.
Not always everything goes according to plan: unfavorable external factors, genetic defects, accidental breakdowns lead to congenital developmental defects. Among them is the coloboma of the eye.
- 1. What is coloboma?
- 2. Causes of
- 3. Symptoms and Diagnostic Techniques
- 4. Treatment of
- 5. Prevention of
- 6. Forecast of
- 7. Conclusion
What is coloboma?
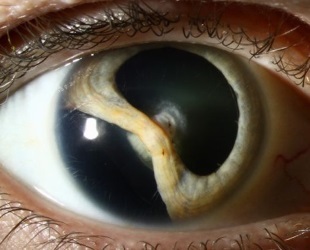
Coliboma of the eye - the absence of tissue sections of various parts of the eye and its appendages, most often occurring during intrauterine development.

It leads to improper closure of the slit of the eye glass, which occurs on the 4-5 week of intrauterine development.
All parts of the eye can be damaged, starting with the optic nerve and ending with eyelids. Very often it is accompanied by microphthalmus - a sharp decrease in the size of the eyeball, as well as increased intraocular pressure.
Traumatic coloboma is much less common congenital .It is usually caused by mechanical damage to the eyeball.
In some cases, it is the result of an operation in which the excision of the eyes affected by the tumor or necrotic process was performed.
Types and types of
colobanks It is divided into the following types:
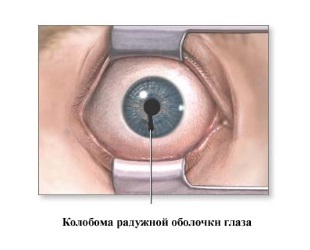
- Iris coloboma is the most common type of this defect. With its congenital form, the pupil usually has the form of a drop or keyhole. The functions of the pupil muscles are preserved, it reacts to light, so for a small defect size, vision can not be disturbed. With the acquired coloboma, the pupil's sphincter often does not work.
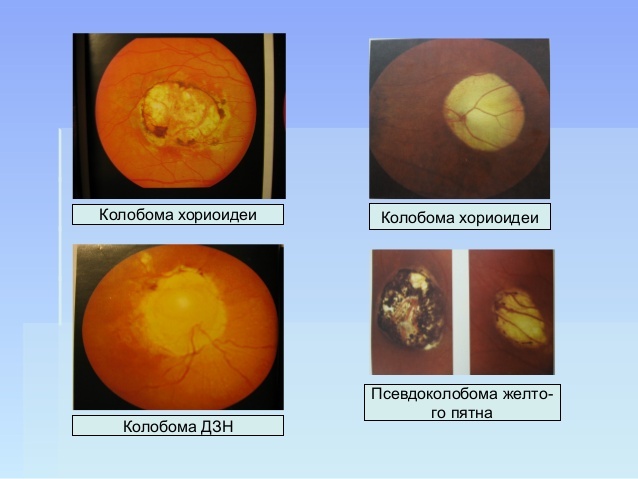
- Coliboma of the choroid - absence of a part of the choroid of the eye.
- Coliboma of the ciliary body worsens the work of the accommodative apparatus and leads to visual impairment.
- Coliboma of the lens and optic nerve is much less common than other forms. It affects the eyesight negatively, accompanied by strabismus.
- Coliboma of the eyelid usually affects the lower eyelid, with a significant defect size, the eyeball may dry up, which is fraught with a corneal ulcer and other secondary diseases.
Different types of congenital colobanks are often found simultaneously. It can be either an one-way or an two-way .
If the sagging defect of the iris and other eye tissues is located in its lower part, from the side of the nose, then the coloboma is called the of the typical if its localization is other than atypical .
Distribution of
It is one of rare, or orphan defects, and occurs in one newborn for ten thousand. The disease is not related to the race and age of the mother.
Causes of
The cause of traumatic colobodies, as its name implies, is damage to the tissues of the eye. Congenital coloboma can develop due to the reasons described below.
Systemic malformations of
With syndromes of Down, Patau and Edwards, partial trisomy, basal encephalocele, focal hypoplasia of the skin, and syndromes under the abbreviations CHARGE and COACH and some others, coloboma of the optic nerve is most common.
Adverse effects on the embryo
The risk of having children with coloboma and other facial deformities, such as the cleft palate, cleft lip, hypertelorism, is much higher in mothers who:
- used alcohol, narcotic substances( especially cocaine, which has a pronounced teratogenic effect) in early pregnancy;
- were infected with cytomegalovirus infection due to which intrauterine infection of the fetus occurred.

Genetic mutation
Calaboma can develop due to a genetic mutation inherited from the parent or de novo.
Hereditary coloboma is transmitted by an autosomal dominant type, that is, one copy of the damaged gene is sufficient for the development of the disease.
But, since the size of the defect in different people can vary, the sick parent sometimes does not know what the coloboma has: a small notch in the tissues of the eye is not visible without examination and has no symptoms.
Very rarely there is a coloboma with an X-linked type of inheritance. Its gene is transmitted in the same way as the gene for hemophilia and other related diseases of the female chromosome: the sick father transmits a defect to a healthy daughter bearer, whose sons, in turn, are 50% likely to be sick.
Symptoms and Diagnostic Techniques
Iris coloboma is a disease that is usually seen with the naked eye, as well as eyelid defects. But its other varieties can not be so obvious, masquerading as other eye diseases. What are the symptoms of coloboma?
- In the case of damage to the iris, the cosmetic defect in the form of a deformed pupil is in many cases the only symptom, with a small area of its function, the organ of vision does not suffer. But with a large defect affecting the sphincter of the pupil, the patient is significantly impaired vision in bright light and in the dark.
- With coloboma of the choroid, the nutrition of the retina is disturbed, which leads to scotoma - a "blind spot" that captures part of the field of vision. Its dimensions are related to the size of the missing tissue site.
- Coliboma of the ciliary body is manifested by accommodation disorders, farsightedness - it is easier for the patient to focus the view on distant objects, rather than on those that are near.
- In the coloboma of the optic nerve scotoma is observed, as well as accommodation disorders and strabismus.
- The columboma of the lens gives symptoms similar to astigmatism due to loss of the lens by a natural spherical shape.
To detect defects in the deep tissues of the eye, a comprehensive examination is necessary, including ophthalmoscopy, refractometry and biomicroscopy.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with atrophic foci, resulting from toxoplasmosis infection, degenerative myopia.
Treatment of
The only way to treat eye colitis is operative. It is impossible to eliminate a tissue defect with drugs or physiotherapy.
However, the operation is not required in all cases: with a small coloboma of the iris, which does not affect the patient's vision, there is no need to expose the eye to traumatic and complex interference from the outside.
To ensure that the deformed pupil does not attract attention, color contact lenses are often used, with light photophobia - dark glasses in clear weather.
In cases where the size of the iris cleft is large enough, its edges are excised, and then tightened and sewn to form a pupil of normal size.
Similarly, the coloboma of the century is treated. After a fairly simple operation, the protective function of the century is fully restored.
With coloboma of the lens, as with other defects, it is replaced by an artificial lens. Modern implants in their refractive qualities are in no way inferior to the lens of a healthy eye, and some of them are capable of accommodation.
Coliboma of the visual eye and the choroid are not treated: it is impossible to restore the nervous and vascular tissues of the eye affected by these forms.
In those cases where coloboma is combined with other eye diseases or affects their immediate function, treatment should be comprehensive.
In the case of the dry eye syndrome that has arisen against the background of the coloids of the century, the patient needs drops and tears, glaucoma requires taking medications that reduce intraocular pressure, with reduced vision, a specialist prescribes glasses or lenses with the appropriate number of diopters, and in the case of retinal detachment, a photocoagulation procedure around the colobacillus is required.
As supportive therapy, it is permissible to use multivitamin complexes, lutein, beneficial for the eyes of herbs, such as leaves of blueberries, eyes, chamomile, linden.
Vegetable products are practically safe, but in the case of colobodies they can not radically change a patient's condition.
Prevention
Preventative measures against congenital colobomas are mainly related to the behavior of the expectant mother during pregnancy. Abandonment of teratogenic substances significantly reduces the likelihood of its development in the fetus, either as an independent disease or as part of a complex developmental malformation. However, this does not insure against hereditary colobanks or random mutations.
Forecast
The prognosis for coloboma is favorable, in itself it does not threaten the health and life of the patient. Dangerous can be other vices, which are observed in a significant part of people suffering from coloboma.
Conclusion
Summing up, we can say the following:
- Coloboma is the absence of a part of the tissues that arises from mechanical damage to the eye or congenital malformation.
- Congenital coloboma is very often accompanied by other defects in the eyes and face.
- The only way to treat it is surgery, but not necessarily treatment.
- The disease can adversely affect eyesight, but not life-threatening.
