The development of paratonsillar abscess is most often the result of the consequences of tonsillitis or wrong treatment.
The disease is fraught with serious consequences and complications.
Contents
- Explain the terms
- Classification of the disease
- Causes of the disease
- How the inflammation manifests itself
- Therapy methods
- Very dangerous and fraught!
- Prophylaxis of phlegmous sore throat
Explain the terms
The diagnosis of parathonsillar abscess implies the spread of acute inflammation in the circumfluorocellular tissue.
Paratonzillitis( phlegmous angina) is caused by infection in the area around the palatine tonsil. As a result of infection of tissues in loose fiber there is abscess, which is accompanied by an expressive mucous edema and an increase in the temperature of the patient.
Classification of disease
Types of paratonsillar abscess:
- Anteroposterior inflammatory process is the most common and occurs in 70% of cases. The upper zone of the amygdala is located in the depression, where the outflow of the contents of the lacuna is difficult. Localization of pathology occurs between the palatine-lingual arch and the upper pole of the amygdala. The defeat of the soft palate protrudes from the front and the abscess can be drained independently.
- The lower abscess of is rare and is often the result of odontogenic( out-of-teeth) causes. The location of the paratonsillar abscess is fixed on the lower third of the amygdala.
- The back version of is detected in 10% of cases and is very dangerous. It is accompanied by another symptomatology and can cause a laryngeal edema and respiratory failure. The focus of inflammation is localized between the palatine-pharyngeal arch( sometimes in it) and the amygdala. The patient does not experience difficulties in opening the mouth and this is an important indicator in the diagnosis of the disease.
- External( external) view of pathology is very rare and is located outside the tonsil.

Causes of the disease
The etiology of the development of the disease is reduced to the virulent properties of the infection. Disease bacteria penetrate from purulent tonsil follicles into the surrounding cellulose, where increased looseness is observed.
Through the depressions( lacunae) microbes pass thin walls of capsules and form suppuration in the upper pole of the tonsils.
Pathogens penetrating the tonsillogenic pathway:
- streptococci;
- of staphylococci;
- yeast fungi of the genus Candida;
- haemophiles Influenzae;
- klebsiella;
- escherchia colli.
Not only complications of angina or streptococcal pharyngitis may be the cause of paratonsillar abscess.
Injuries to the mucosa, foreign body, dental inflammations - can cause an abscess.
How the inflammation of the
manifests itself Clinical picture begins to manifest with pain in the throat and difficulty swallowing even before the appearance of the abscess. Unlike tonsillitis, the disease can affect both children and adults.
After the first pain symptoms within a week, the paratonsillar abscess develops - the capillaries are filled with blood and there is edema.
Compared with quinsy, the condition becomes worse, the pain is expressed by colic and cut even in a calm state. Trism may be observed and chewing and eating is difficult. The patient often tilts his head in one direction because of the painful sensations in his ear.
With the appearance of an out-of-period abscess, the following symptoms develop:
- is an ever-increasing pain in the throat, swelling closes the tonsil and displaces the tongue in the opposite direction from the inflammation;
- chills, febrile condition and fever to 39-40˚C.
Intoxication of the body, accompanied by headache and weakness, sleep disturbance. There is an increase in lymph nodes and painful sensations, irradiating in the teeth or ears. Extraneous odor from the mouth and sometimes a tonic spasm of the chewing muscles.
In some cases, laryngeal edema requires immediate medical attention.
Therapy methods
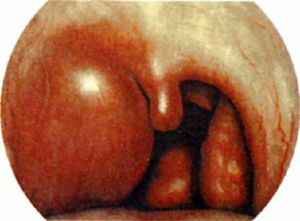
In the photo, the paratonsillar abscess of the larynx
In the initial stages of the disease before the abscess, conservative treatment methods are used. Can be appointed UHF and thermal procedures, mineralotherapy.
In parallel, rinsing of the throat with chamomile infusions, disinfectants or saline solution is shown.
Topical use of Fusafungin( Bioparox) has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect, suppresses the reproduction of microbes on the mucosa.
Antibiotics of wide action for gram-positive and gram-negative strains of microorganisms are prescribed:
- Amoxicillin with clavulanic acid;
- Ampicillin with sulbactan;
- Cephalosporins of the second and third generations( Cefazolin, Cefuroxime);
- Clindamycin;
- Metronidazole.
Tetracyclines and the aminoglycoside series of antibiotics give low effectiveness of treatment.
Simultaneously with the aminopenicillin series and macrolides, analgesics, anesthetics, restorative drugs, vitamins should be used.
Intravenous injections of glucocorticosteroids can accelerate recovery and alleviate the course of the disease. 
The appearance of the abscess is treated surgically, warming in this case is contraindicated. There is an opening of the abscess abscess, which provides relief of the inflammation of the inflamed tissue and the reduction of acute pain and the risk of complications.
After the opening of the abscess, conservative medication is used.
Types of surgical treatment for paratonsillar abscess:
- The palliative method of is performed punctually with suction of pus. With this technique, there is not always a full recovery, the hole can stick together. Then the wound is dilated and drained for several days.
- The radical method allows you to drain the wound and remove the focus of infection. The doctor performs tonsillectomy - a bilateral incision is made.
There are contraindications to the use of surgical techniques - blood diseases, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus.
Very dangerous and fraught!
Angina Ludwig
Weakened immunity of the patient can lead to infection from infected fiber to the near-pharyngeal space.
The possibility of the appearance of phlegmon from the near-pharyngeal part is accompanied by diffuse purulent inflammation. An acute course of pathology can seize the areas surrounding the phlegmon. The patient's condition deteriorates sharply and purulent mediastinitis develops.
Phlegmon can cause other problems:
- development of sepsis;
- tissue necrosis;
- angina of Ludwig;
- internal vein thrombosis;
- opening of bleeding of cervical vessels.
Prevention of phlegmous sore throat
Timely and correct treatment of pathological conditions is the main measure of disease prevention. Strengthening immunity and compliance with sanitary standards increases the body's resistance to the spread of pathogenic microflora.
Everyday exercise, water treatment, hardening - all this increases the protective function. It is necessary to treat teeth in time,  not to admit adenoids, observe the rules of personal hygiene and sanitize the oral cavity.
not to admit adenoids, observe the rules of personal hygiene and sanitize the oral cavity.
Exacerbations of chronic diseases of the pharynx occur most often in the autumn-spring period. But in the summer, the use of cold drinks provokes a peak of paratonlesillar abscesses. The annual statistics of diseases of phlegmous angina is 11.5%.
Address to a specialist and timely treatment can prevent complications and chronic forms of the disease.
